
Alftan Dyson, PharmD, AAHIVP, FNPhA, discusses the significance of Black HIV/AIDS Awareness day as well as the importance of taking the discussion around HIV prevention and sexual health out into the communities to have those conversations.

Alftan Dyson, PharmD, AAHIVP, FNPhA, discusses the significance of Black HIV/AIDS Awareness day as well as the importance of taking the discussion around HIV prevention and sexual health out into the communities to have those conversations.

The latest CDC numbers show a significant increase week-to-week.

In a phase 3 trial, the novel oral antiviral pritelivir demonstrated superior lesion healing and better tolerability than existing therapies in immunocompromised patients with refractory or resistant herpes simplex virus infections.

The FDA recently approved intravenous fosfomycin (Contepo), which is a new option for adults with complicated urinary tract infections, including those caused by resistant Gram-negative pathogens. Here is an overview of the therapeutic including its mechanism of action, data, availability, and prospective costs.

This is the fourth time the antimicrobial bill looking at a subscription-payment model has been introduced in the Congress and has some updates in how these therapeutics are developed and paid for with help from the federal government.
In the latest From Pathogen to Infectious Disease Diagnosis podcast, Andrea Prinzi, PhD, MPH, SM(ASCP), talks about diagnostic stewardship and that when it is grounded in collaboration, education, and thoughtful test use, it can improve patient care while helping clinicians navigate increasingly complex diagnostic tools.

Findings from a growing body of randomized trials and real-world analyses show that starting metformin during acute SARS-CoV-2 infection is safe and significantly reduces the risk of developing long COVID.

Paul Offit, MD, voices concerns over the CDC’s surveillance capabilities, the federal agency’s lack of movement to address vaccine needs during outbreaks, and diminishing herd immunity, making the vulnerable at risk for contracting disease.

A global review finds growing antimicrobial resistance among the main bacteria causing meningitis—especially in low- and middle-income countries—raising concerns about the continued effectiveness of standard treatments and the urgent need for stronger surveillance.

As the spending bill makes its way through Congress, the HIV+Hepatitis Policy Institute's Carl Schmid provides some insights on the latest wranglings on the HIV bill and the domestic programs.

MicuRx Pharmaceuticals has received FDA clearance to begin a phase 2a clinical trial of MRX-5, a novel oral antibacterial therapy for patients with Mycobacterium abscessus pulmonary disease.

In the second installment of our 2-part interview, infectious disease pediatrician Sharon Nachman, MD, discusses this very rare adverse effect that can occur after immunization administration.

This week, read about the latest number of confirmed cases of measles in the US, novel findings around UTI treatment failure, an overview of zoliflodacin and gepotidacin, and more.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provided its latest figures today on the confirmed number of cases in the US.

The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) has published its 2026 immunization schedule, reaffirming routine vaccination to protect children and adolescents against 18 preventable diseases.

Infectious disease pediatrician Sharon Nachman, MD, discusses the vaccine data the federal agency disclosed in the recent letter they sent to the manufacturers.

Fedora Pharmaceuticals is presenting new preclinical data at the IMARI conference demonstrating that its lead candidate, FPI-2119, shows strong activity against some of the most dangerous drug-resistant Gram-negative infections, supporting its advancement toward clinical trials.

This past December, the FDA approved both zoliflodacin and gepotidacin for this sexually transmitted infection marking a significant advance amid rising antibiotic resistance. Here is an overview of the antibiotics.

In the final FY2026 spending bill, Congress rejected proposed House Republican cuts of more than $1.7 billion and instead maintained bipartisan funding for HIV prevention and treatment programs, while urging the Trump administration to focus on effective implementation.

In the second installment of a 2-part interview, Jacinda Abdul-Mutakabbir, PharmD, MPH, offers some novel findings around UTI treatment failure associated with levels of education and insurance payers.

The workgroup is examining the vaccine’s schedule including the age it is administered, dosage, and the safety and efficacy of the vaccines.

Jacinda Abdul-Mutakabbir, PharmD, MPH, discusses her research in this area and how to potentially mitigate these treatment disparities.

The federal agency gave the nod for Acon Laboratories’ Flowflex Plus RSV + Flu A/B + COVID 4-in-1 test that can detect all those respiratory viruses in a single test, which is indicated for use in both adults and children as young as 6 months.

Scynexis has secured FDA Qualified Infectious Disease Product (QIDP) and Fast Track designations for its next-generation antifungal SCY-247, underscoring the drug’s potential to address the escalating global threat of multidrug-resistant fungal infections such as Candida auris.

This week, read about the CDC's analysis on the continuing burden of COVID-19 on a certain population, watch an Emory nurse provide an overview of donning and doffing personal protective equipment when caring for patients with high-consequence infectious disease, a review of diagnostics and treatments for invasive candidiasis, and more.

Kirk Milhoan, MD, PhD, said vaccine choice is the most important element to the public even with the possibility of people contracting this disease or others when given the right to opt out of vaccination.

In a joint statement by Secretary of State Marco Rubio and Secretary of Health and Human Services Robert F Kennedy, they announced the termination of the country’s membership in the global health organization.

Although the declared COVID-19 pandemic public health emergency has passed, the CDC reports continued high numbers of illnesses, medical visits, hospitalizations and deaths.

Emory’s Jill Morgan, RN, BSN, discusses what they do after removal of personal protective equipment (PPE) and if a provider has experienced a potential exposure to a high-consequence infectious disease.
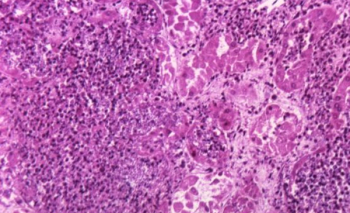
Disease management now centers on more precise, context-driven diagnostics, restrained empiric antifungal use, echinocandin-focused therapy, and risk-based ophthalmologic evaluation aligned across global and US guidelines.