
At a recent event called "The Next Pandemic," researchers agreed that the world is not ready for the next big flu pandemic and discussed what it will take to strengthen preparedness.

At a recent event called "The Next Pandemic," researchers agreed that the world is not ready for the next big flu pandemic and discussed what it will take to strengthen preparedness.
A new study suggests that village clinics are not properly dealing with the ongoing problem of tuberculosis in rural China.

In a new study, a pair of Australian virologists argue that we cannot predict virus outbreaks, looking at the “fault lines” of interaction between humans and animals may help us be better prepared.
Two new studies highlight just why the flu vaccine isn’t working and one new approach that may give way to a universal vaccine.

While a new FDA report shows antibiotic resistance remains low among many food-borne bacteria, some pathogens are increasingly showing multidrug resistance.

Researchers from The Scripps Research Institute have discovered why egg-based influenza vaccines offer a lower level of protection against H3N2 viruses.
As health officials continue to recommend the injectable influenza vaccine to prevent illness this season, a new study examines whether vaccination rates changed after the CDC stopped recommending the nasal spray vaccine

A new CDC report finds that although vaccination coverage is high for kindergarteners in the United States, pockets of undervaccination are a cause for concern among health officials.

A pair of papers published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases highlight the effort to fight and monitor drug-resistant HIV, which poses a threat to achieving the global targets designed to end the AIDS epidemic.

A new article details how researchers are working to develop a universal flu shot.

A new literature review of 60 papers and studies finds that voluntary medical male circumcision programs in Africa also have benefits for women’s health.

Researchers in a pediatric hospital in Tokyo see positive results following the implementation of an antibiotic stewardship program limiting carbapenem use.

Researchers from the University of Colorado Boulder have developed nanoparticles capable of boosting the effectiveness of antibiotics against drug-resistant superbugs.
Flu season has officially begun in the United States, as the first cases and deaths of the season are reported, prompting health officials to press for vaccination.
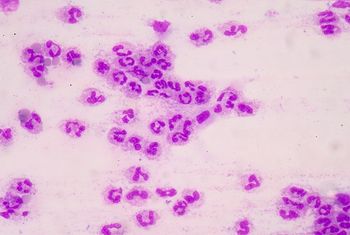
A recent study found that a sepsis care bundle program implemented in The Mount Sinai Hospital in New York coincided with an increase in antibiotic prescriptions and higher rates of Clostridium difficile infections.
A new antibiotic susceptibility testing device developed by scientists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology could offer doctors a faster way to prescribe the right antibiotic.

With Lyme disease incidence in the United Kingdom on the rise in recent decades, a new report from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence aims to help doctors spot cases of the tick-borne disease.
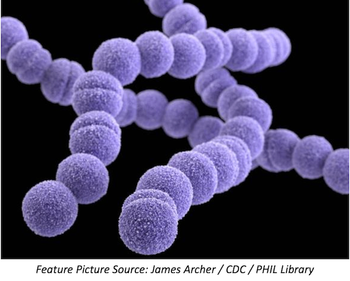
A new discovery about Group A Streptococcus may lead to the development of a new vaccine or antibiotic to prevent flesh-eating infections.
With new West Nile virus cases reported in California and Washington state, health officials are reminding the public that it’s not too late in the season to catch the mosquito-transmitted disease.
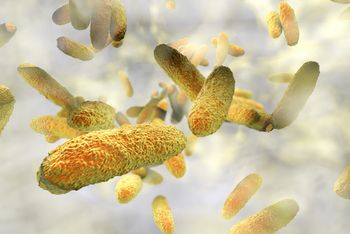
Following a deadly pneumonia outbreak in a Chinese hospital last year, researchers have identified a dangerous new superbug that is drug-resistant and highly virulent.
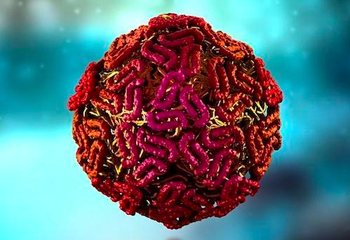
New cases of West Nile virus springing up around the country are a reminder that the virus can continue to cause new infections well into fall, as mosquitoes continue to stay active where it’s still warm.
In a new study reviewing existing literature, researchers have found that more than 2 dozen viruses have been detected in human semen.
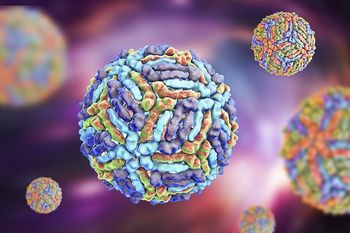
Although West Nile virus activity is set to taper off in the coming weeks, state health agencies are continue to report new cases, reminding the public that mosquito activity and new infections may continue well into fall.
Researchers have developed a map of the networks of B-cells in the human body, shedding light on the intricate workings of the immune system.

In a new study on factors that make individuals susceptible to infectious diseases, researchers have found that cholesterol-lowering drugs may reduce susceptibility to certain diseases.
As the United States enters the final weeks of West Nile virus season, state health officials from around the country report several new deaths caused by the virus.

A new study suggests that sexual transmission of Zika virus may create a higher risk for fetal disease than transmission via mosquito.
A new study suggested that neonatal sepsis, which kills 1 million infants around the world each year, may be prevented with synbiotic treatment.

With federal and state officials rescuing Texas and Louisiana residents from the floodwaters of Hurricane Harvey, health experts are looking into the storm’s impact on mosquitoes carrying West Nile and Zika viruses.
As cases of murine typhus in Texas are on the rise and occurring in more counties in the state, researchers are investigating the spread of the flea-borne disease.