
Does pharmacist presence in an urgent care center have an effect on antibiotic prescribing practices?

Does pharmacist presence in an urgent care center have an effect on antibiotic prescribing practices?

Contagion® editor-in-chief Jason Gallagher, PharmD, FCCP, FIDSA, BCPS, recaps his presentations from MAD-ID 2019.

As clinician are growing interested in the use of extended infusion beta-lactams for gram-negative bacteremia, a team of investigators noticed that available data are unclear and solely focus on clinical cure and/or mortality outcomes.

At MAD-ID 2019, Monica V. Mahoney, PharmD, BCPS (AQID), BCIDP, presented a workshop on formulary management strategies in antimicrobial stewardship.

A study found that patients with complicated C diff infections were more likely to have been previously hospitalized with numerically less time between hospitalization and recent C diff episode.

Brandon J. Smith, MD, PharmD, describes a case of a patient who was treated for mycobacterial infection after ground-glass opacity was detected in her lung.

Ryan K. Shields, PharmD, MS, discusses his research presented at MAD-ID 2019 on T2Candida's place in rational antifungal management.
The total number of bed days saved with outpatient oritavancin administration was 683 days throughout the study period.
A team of investigators from the University of North Carolina Medical Center found that oseltamivir prophylaxis did not reduce the rate of influenza within the first year following a lung transplant.
The primary outcome of the study, which seeks to fully assess infection-related clinical outcomes and microbiological cure rates of PZT for ESBL infections, was clearance of the causative organism from index infection site on first follow-up culture.

A study at SUNY Upstate University Hospital found that AUC-based vancomycin monitoring does not result in higher total drug and monitoring cost compared to trough-based monitoring for patients with MRSA bacteremia.

In order for stewardship programs to be successful they must be supported by all of the health system’s stakeholders – but are we forgetting valuable stakeholders?
In patients with MRSA bacteremia, implementing AUC/MIC-guided vancomycin dosing resulted in decreased average troughs and a decrease in daily vancomycin dose administered.
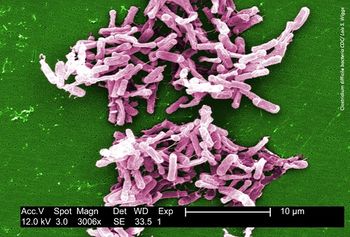
A study found that there was no statistically significant difference in CDI recurrence within 12 weeks between patients receiving oral vancomycin prophylaxis compared those who did not.

Use of Verigene Blood Culture Gram-Negative without stewardship involvement was shown to improve time to optimal therapy, which was primarily driven by decreased time to antibiotic escalation.

In both the lefamulin and moxifloxacin treatment groups, the median time from treatment initiation to clinical response was 4 (3-5) days.

Patients with only a gram-negative infection and/or mixed gram-negative/gram-positive pathogens were more likely to receive IET (22.8%, 270 out of 1184; and 22.8%, 633 out of 2778, respectively) compared with patients with infections caused by only gram-positive organisms (6.5%, 381 out of 5891).

Compared with no pharmacist involvement, a greater number of appropriate antiretroviral regimens were initiated with partial pharmacist involvement (62% vs. 32%, p = 0.0096).

Contagion® will be heading to Orlando, Florida, on Wednesday, May 8, 2019, to report on the annual Making a Difference in Infectious Diseases (MAD-ID) 2019 conference.