
This cephalosporin antibiotic was examined against colistin-susceptible gram-negative infections.

This cephalosporin antibiotic was examined against colistin-susceptible gram-negative infections.
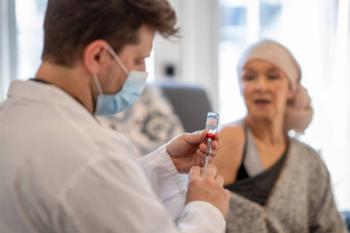
C-SMART trial results presented at ESCMID show a reduction of COVID-19 incidence in cancer patients.
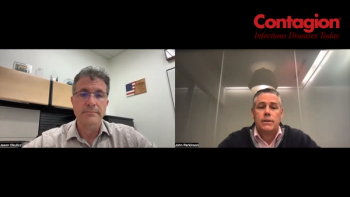
A large study being presented at ESCMID shows the therapy was associated with a significantly lower mortality at 14-days and 28-days.

A novel approach using this emerging technology looks to interfere with antibiotic resistance expression and reduce this global health issue.
Insights into host-directed therapies (HDT) for tuberculosis (TB) gaining traction among experts aiming to combat the disease's various forms, including drug-resistant strains.
A study finds that despite the development of some new agents for highly-resistant pathogens, prescribers are reluctant to utilize these therapies.

Public health alert over ground beef, FDA approves antibiotics for female adults with uncomplicated UTI, The NYC Department of Health and Mental Hygiene reports a record amount of Leptospirosis cases, and more this week from Contagion.

New data reinforced the safety and tolerability profile of this antiretroviral therapy for this patient population who are virologically suppressed.
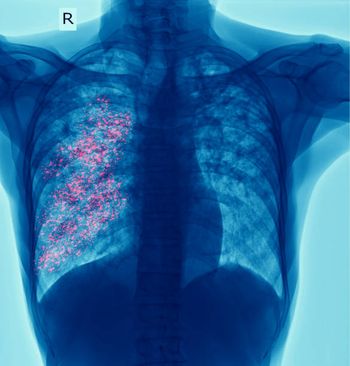
Insights from Pranay Sinna MD on a multicenter prospective cohort study on household contacts.

Despite the disproportionate effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe outcomes on nursing home residents, less than 50% have received the updated 2023/2024 vaccine.
In a collaboration between the University of Oxford, the Ministry of Health in Rwanda, and the Rwanda Biomedical Centre, groundbreaking data on the R21/Matrix-M malaria vaccine, marks a significant shift in the malaria paradigm.

PEN-FAST is a validated risk stratification tool that promotes efficient, safe, and effective de-labeling of penicillin allergies.

Photini Sinnis MD, professor at the Johns Hopkins School of Public Health and Deputy Director of the Johns Hopkins Malaria Research Institute, offers her expert insights into this zoonotic disease.

Study from the Journal of Hepatology aims to characterize immune responses associated with rapid natural clearance of HCV reinfection.

Pivmecillinam (Pivya) was given the nod from the federal agency, and is indicated for female adults with uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs) caused by susceptible isolates of Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis and Staphylococcus saprophyticus.

RedHill Biopharma said it has enrolled its first participant for the study examining the investigational therapy, RHB-107 (upamostat).

FDA recalls, allergy alerts, e coli & salmonella outbreaks, and more.
The study findings imply newly available prevention strategies for which older children—ages 2 to 5 years—are not currently eligible should be prioritized.

Already FDA-approved in the US, TG-1000 confirms safety and prepares for global expansion.

With this approval, aztreonam-avibactam becomes the first β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor antibiotic combination approved in the European Union for treating multidrug-resistant infections, including metallo-β-lactamase-producing bacteria.
Evaluating inpatient mortality for patients without supplemental oxygen at admission across different variants of concern periods with insights from Dr. Andre Kalil.

US Department of Agriculture’s Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) issued a public health alert over the meat.

Monika Pogorzelska-Maziarz, epidemiologist, health services researcher, and associate professor at Thomas Jefferson University, shares insights on COVID-19's influence in acute care hospitals at this year’s Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) conference.
The vaccine’s developer, YS Biopharma, will begin its phase 1 clinical trial in the Philippines this summer.
Study by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) explores future directions for pediatric COVID-19 vaccination amid emerging variants.

Both the United Nations and World Health Organization (WHO) discussed the threat of H5N1, and its potential transmission to other mammals and humans.

The New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene reports a record amount of Leptospirosis cases, the zoonotic disease, from rat urine.

Study highlighting the first documented case of C auris moving from adult to pediatric unit in Maryland, COVID-19 physical health problems lingering 1 year after their hospital stay, 5-in-1 meningococcal vaccine given FDA PDUFA, and more this week from Contagion.
Here is an update on the latest research and clinical management.

Trader Joe’s pulls contaminated organic basil after multi-state illnesses were reported.