A study evaluates the efficacy of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in COVID-19 treatment across variants.

A study evaluates the efficacy of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in COVID-19 treatment across variants.

The company is going to submit their data to the FDA to seek approval for people within this age group.
A study on Italian vaccination rates and factors influencing Rotavirus vaccine acceptance.
Study shows GBP1 assists HCV in the replication and spread against antiviral expectations.

The federal agency has given the nod for dolutegravir/lamivudine (Dovato) for teens living with the virus and offers a novel option for patients.
Trial examines high-dose vs. standard-dose influenza vaccines.

As a potential alternative to antibiotic treatments, this investigational immunization offered protection for several years.
Evaluating the importance of RSV vaccination implications for adults.

Emergency use authorization for CorDx TyFast Flu A/B & COVID-19.

FDA approves Zevtera a new treatment option for bacterial infections, a comprehensive look at coccidioidomycosis, the impact of guidelines on reducing hospital-onset CDI incidence, and more this week from Contagion.

Dr. Thomas Holland discusses the breakthrough in antibiotic development.

During the 2014-2016 African epidemic, investigational Ebola vaccines demonstrated safety and immunogenicity.

Alcohol Awareness Month highlights the need for action amidst the alcohol crisis in the US.

An FDA decision on the company’s mRNA-1345 is slated for May 12.
Examining the implications and challenges of coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and blastomycosis diagnosis during the COVID-19 pandemic.

The RSV prefusion F protein–based maternal vaccine phase 3 trial was halted due to the risk of this adverse event.

Zevtera approval shows efficacy and marks a new treatment option for bacterial infections including MRSA.

Here is a case study involving a patient with the virus and the clinical approach in thinking about appropriate treatment while keeping stewardship in mind.
A comprehensive look at coccidioidomycosis (valley fever) through diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and climate change impact.
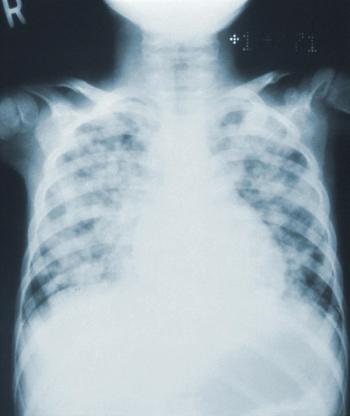
Community acquired pneumonia is often inappropriately diagnosed in hospital admissions, particularly among older adults with dementia, and can lead to in-hospital antibiotic-associated adverse events, such as Clostridioides difficile.
Bavarian Nordic's JYNNEOS available to healthcare providers nationwide.

The case was confirmed in Texas and the person was in contact with cows. CDC says the risk for infection remains low.

April marks STI Awareness Month; guidelines decreasing the incidence of chlamydia and syphilis, future work needing to be done with regards to doxy-PEP, an increase in STIs during the pandemic, and more from this year by Contagion.
This very large study reviewed data, which showed people vaccinated for the virus had a substantial reduction of risk for these types of events.

Rising dengue incidence in Puerto Rico signals broadening health concerns.
Clinicians review a patient case including diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up.
A study on the impact of guidelines on reducing hospital-onset CDI incidence.

Clinicians discuss screening and treatment approaches for the disease.

FDA authorizes Ito Invivyd’s pemivibart (Pemgarda), insights on Sofosbuvir levels in pregnant women, the effectiveness of fidaxomicin vs vancomycin for CDI treatment, and more this week from Contagion.