
Liver fibrosis and subsequent cirrhosis result from chronic damage to the liver that is caused by most types of chronic liver disease, including chronic hepatitis C virus infection and alcohol abuse.

Liver fibrosis and subsequent cirrhosis result from chronic damage to the liver that is caused by most types of chronic liver disease, including chronic hepatitis C virus infection and alcohol abuse.

Although several ambitious initiatives intended to put an end to the AIDS epidemic have been developed and implemented, this laudable goal will be difficult to achieve without substantial and wide-scale changes in HIV prevention strategies.

WRAIR announced that their Zika purified inactivated virus vaccine succesfully prevented infection in nonhuman primates.
Researchers from the Oxford University Clinical Research Unit have found that a 5-minute CRP test can assist in the ongoing fight against antibiotic resistance by reducing antibiotic misuse for respiratory infections.
Chlamydia has posed a healthcare challenge for clinicians due to the serious complications associated with it.

Researchers at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital discovered that adjuvanted flu vaccines do not protect obese mice as they do their lean counterparts from flu infection.
According to IDSA, early diagnosis reduces the need for otherwise unnecessary testing and treatment.
Additional study findings indicated that patients with AD had a significantly higher risk for S. aureus colonization of lesional skin as compared with those without AD.
The approach used in the development of this vaccine was previously implemented by NIAID in a West Nile virus vaccine, which was found to be safe and effective in Phase I trials.
The CDC is providing $67 million to the nationwide effort to fight antibiotic resistance.
The researchers analyzed stool samples from travelers, both before and after their trips, and found that the intestinal tracts of 76% were colonized with superbugs.
Engineers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have developed a new type of customizable vaccines using messenger RNA that has proven to effectively combat a wide range of lethal pathogens when administered to mice, and might be able to reduce disease outbreak response time in the future.

Researchers at the University of Virginia School of Medicine have made a discovery that may offer a way to boost patients’ immune systems using M-CSF.

The rapid spread of Zika throughout Puerto Rico coupled with the introduction of active transmission in Florida has prompted the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to award millions in Zika funding to US states and territories.
A new study has confirmed that significantly more women than men diagnosed with Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia will die within 30 days of acquiring the infection.
An ongoing outbreak of cholera in Rayagada, India has reportedly claimed the lives of 5 people in the region some 950 miles southeast of New Delhi.
A new treatment has been discovered by researchers at The University of Sheffield that can be used to fight antibiotic-resistant bacteria, such as MRSA, by using proteins called tetraspanins.

The US Food and Drug Administration approved the VERSANT Zika RNA 1.0 Assay (kPCR) Kit for Emergency Use Authorization, as the number of locally transmitted Zika cases rose to 14.
In a recent study, researchers identified three key factors that increase the risk for patient-to-patient transmission of carbapenemase-producing carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriacecae (CP-CRE).

The IDSA and ATS have updated the Clinical Practice Guidelines for HAP & VAP for the first time since 2005 to recommend that each hospital generate antibiograms and reduce the use of antibiotics in treatment regiments.

The world’s largest public-private partnership has been formed in a collective effort to battle antimicrobial resistance through a global project, CARB-X, which will be comprised of expert product developers who will research and develop new antimicrobial products.

In HIV controllers, both T follicular helper (TFH) and non-TFH lymph node CD4 T cells contain HIV.

Researchers have made an important breakthrough in efforts to develop a test to help clinicians determine whether a patient has a microbial infection or sterile trauma, a new study shows.

The four previously reported non–travel-related cases of Zika infection have now been confirmed to be locally acquired in Miami-Dade county, Florida.
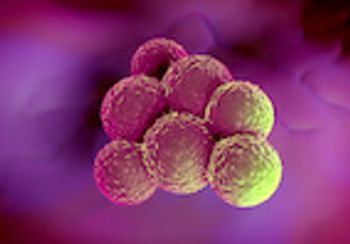
A new study conducted by Andreas Peschel, PhD, and colleagues at the University of Tuebingen in Germany, has shown that lugdunin, a bacteria naturally produced by the human body, can be used as an antibiotic that can eliminate Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).

An international team of researchers has identified a potential role for certain monoclonal antibodies in developing a treatment for Zika virus.

In response to the growing outbreak, and the escalating need for a vaccine that can be used in infants, those who are immunocompromised, and other populations in whom currently available vaccines are not to be administered, the NIAID has entered a vaccine manufactured by Bavarian Nordic into Phase I trials.

World Hepatitis Day aims to increase awareness and understanding of viral hepatitis. The ECDC discusses Europe’s plan to eliminate hepatitis by 2030.

After failed requests for funding and warnings of the inevitable, the Florida Department of Health is investigating what could be the first cases of active Zika Transmission in the United States.

Through the use of targeted screening programs, the ECDC has found that foreign-born migrants are at a higher risk of hepatitis B and C. Identifying risk groups can help practitioners reduce the burden of chronic hepatitis.