This study analyzed 81 communities in Los Angeles and found that once vaccines became widely available, there was no significant difference in COVID-19 incidence between communities of varying income levels.

This study analyzed 81 communities in Los Angeles and found that once vaccines became widely available, there was no significant difference in COVID-19 incidence between communities of varying income levels.

Although there are certain specialties in medicine that seemed to benefit from this newer former of clinical visits, infectious disease and others did not.
A new study finds antimicrobial resistance (AMR) evolves rapidly in patients colonized by diverse P aeruginosa populations due to selection for preexisting resistant strains, demonstrating a clear link between within-host diversity and resistance.
Find out why the FDA requested additional data and what this means for dengue prevention.
Though rare, Guillain-Barré syndrome can occur after vaccination. Did Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, or Janssen COVID-19 vaccination increase the risk of Guillain-Barré syndrome?
Here is a brief report of 5 cases of the use of fecal microbiota, live-jslm (Rebyota) in the management of recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection.
This examination of vaccine introductions worldwide reveals significant gaps in access, especially in low-income countries.

The Peggy Lillis Foundation (PLF) for C diff Education & Advocacy has been busy this year in Washington DC with an FDA event and their Summit and Advocacy Day with lawmakers.
Researchers investigated abatacept, cenicriviroc, and infliximab, but found that these medications did not significantly impact the time to recovery from COVID-19 pneumonia compared to placebo.
The vaccine candidate, M72/AS01E (M72), could potentially become the first new vaccine to help prevent pulmonary TB, a form of active TB, in more than 100 years.

These study findings highlight higher in-hospital mortality rates for patients with preventable conditions during COVID-19.
Although the literature and science may change, hanging onto beliefs about therapeutics is a tradition passed down from instructors to learners. A change in this paradigm may be warranted.
6 malaria cases were confirmed in Florida and 1 in Texas, with no connection to international travel.
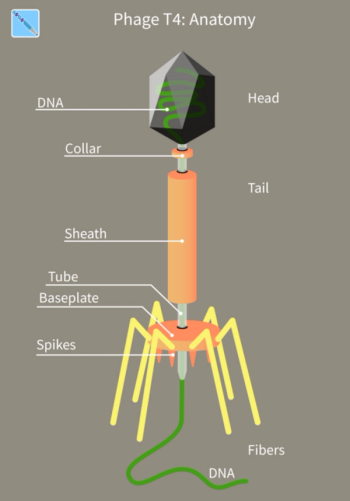
This long-time, understudied virus, can fight bacterial infections and may be poised to become an important treatment option in western medicine.

The nationally-representative sample showed mortality was greater in males even after controlling for levels of misuse.
In a comprehensive economic evaluation, researchers assessed the cost-effectiveness of monoclonal antibodies as a preventive strategy for COVID-19.
This rare side effect was witnessed in a small number of people post-vaccine administration.

Stay informed about the long-term effects of COVID-19, prevention strategies for recurrent C diff, and the emerging threat of drug-resistant Candida auris.

This time of year means new trainees will begin their careers and are excited to take on research projects. However, they may have limited to no experience in this area. Here is an opportunity to give them structure and guidance when committing to longitudinal trainee research.

Infants with non–COVID-19 viruses had a lower risk of UTIs, bacteremia, and bacterial meningitis, while those with COVID-19 had the lowest risk.
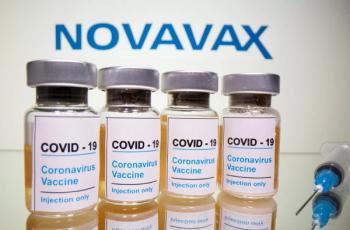
The findings showed that heterologous vaccination, or mixing different vaccines, was safe and effective, with the Novavax vaccine (NVX-CoV2373) providing enhanced protection against the Omicron variant.
This variant, which is an ancestor of Omicron, is an emerging variant that is being seen most frequently in Utah, California, and New York State.

A small study explored the connection between Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) and the COVID-19 condition.

Moderna's RSV vaccine (mRNA-1345) moves closer to regulatory approval with positive data and key submissions to the US FDA, European Medicines Agency, Switzerland's Swissmedic, and Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration.
The CDC recently published an examination of caseloads looking at patient characteristics, mortality rates, and comparing similarities to past studies on this subject.

Among people living with hepatitis C virus (HCV), viral clearance was only 34%. Cure rates were even lower among uninsured persons younger than 40.

Trial of standard vs short course antimicrobial treatment of uncomplicated UTI in children favors standard, but with caveat for early responders.

FMT is a promising intervention for immunocompetent patients with recurrent C difficile infection. However, the safety of FMT remains inconclusive due to limited data on serious adverse events and mortality.

Patients who perceived brain fog within 4 weeks of COVID-19 infection were twice as likely to report symptoms of long COVID than patients without cognitive deficits.
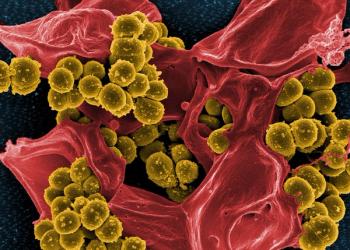
Five organizations have updated the 2014 compendium, "Strategies to Prevent Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Transmission and Infection in Acute Care Hospitals." In doing so, they have elevated antimicrobial stewardship from an “additional practice” to an “essential practice.”