
A retrospective study indicated higher rates of neurodevelopmental abnormalities in areas such as motor function and speech and language during the first year among babies born to women who had experienced a COVID-19 infection during pregnancy.

A retrospective study indicated higher rates of neurodevelopmental abnormalities in areas such as motor function and speech and language during the first year among babies born to women who had experienced a COVID-19 infection during pregnancy.

Vilobelimab (Gohibic) was granted Emergency Use Authorization to treat adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19 infection.
Investigators reviewed the current literature on the utility of oral vancomycin prophylaxis (OVP), and offered guidance for when this approach may be beneficial.

Nursing home residents 85 years and older or with comorbidities were the most susceptible to COVID-19 breakthrough infections.

First global meta-analysis of direct surveys of HIV, HCV incidence in people who inject drugs (PWID) finds youth and women most affected.

According to the CDC, the outbreak strain of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa with Verona integron-mediated metallo-β-lactamase and Guiana extended-spectrum-β-lactamase (VIM-GES-CRPA), has never been reported in the US prior to this outbreak.

COVID-19 prevention practices such as masking, social distancing, and school closures lowered children’s exposures to circulating respiratory viruses and other environmental triggers of asthma.

A novel "antibody-mimetic" molecule administered intranasally in animal model prevented coronavirus infection from older, current and emerging variants.

A recent study of patients evaluated for chronic hepatitis B in Austria found that 9.2% had severe fibrosis or cirrhosis, 5.7% were coinfected with hepatitis D, and up to 30% met treatment criteria.

COVID-19 stories continue to be the most-read, but last month's top stories described how contracting COVID-19 increases the risk of gastrointestinal infection, C difficile infection, and cardiovascular disease.

These findings suggest the World Health Organization's definition of post-COVID-19 condition (long COVID) may be too broad.

After assessing the landscape, the company is leaving the adult RSV vaccine market.

Ensitrelvir is an investigational 3CL protease inhibitor that reduced COVID-19 illness duration by 1 day.
Aaron Ferguson’s diagnosis completely changed his life’s path. Since then, he has helped others overcome their addictions and get hepatitis C (HCV) treatment. In his home state of Texas, a new health initiative is looking to get more people into the continuum of care for this curable virus.

Increased sales of these antibiotics during the COVID-19 pandemic raise concerns about the growing threat of antimicrobial resistance.

ViiV Healthcare is working with 3 companies to manufacture generic versions of cabotegravir long-acting (LA).
This study examined the impact of COVID-19 vaccination and infection on the risk of cardiac and all-cause mortality in young people aged 12-29 years.
The CDC’s recent warning of the rising incidence rates of the fungal infection is cause for concern, but understanding which patients and settings are at a higher risk is equally as important. The lead author in the CDC’s recent C auris study offers some insights for both medical institutions and the general public.

Because trust in science predicts willingness to get a COVID-19 vaccine, the results of this study have significant public health consequences.

The oral RNA destabilizer, AB-161, developed by Arbutus Biopharma, started dosing its first participant for the small trial.
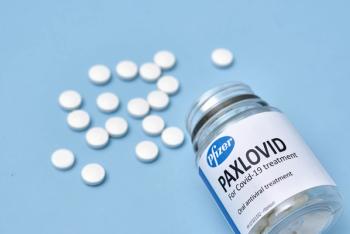
Early treatment with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (Paxlovid) was associated with the greatest clinical benefit in reducing COVID-19 hospitalization and death.

The virus can maintain a reservoir in these white blood cells even in those who have been virally suppressed for years.

The findings of this study are consistent with other findings that maternal viral infection during pregnancy increases the risk for neurodevelopmental morbidity in offspring.

When given within 5 days of COVID-19 symptoms, Paxlovid appeared to reduce risk for developing Post-COVID-19 Conditions (PCC).

A new study found negative expectations prior to COVID-19 vaccination were associated with more systemic adverse events in individuals receiving their second dose of a COVID-19 vaccine.

A midsized study demonstrated no therapeutic benefit to patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 taking this class of anthelmintics.

"Antibiotics can safely be withheld in most patients with viral respiratory infections,” these study authors wrote.
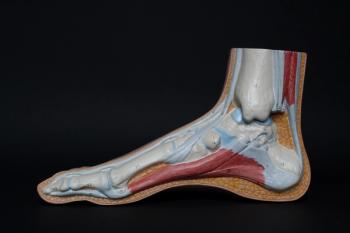
An intensive care physician offers some insights looking at fluoroquinolone-associated tendinopathy and using this social media platform to provide education and an open discussion around it.

Risk factors for VTE among COVID-19 patients included age greater than 55 years, male gender, a history of thrombophilia, and obesity.
Data from the US Veterans Affairs found a wide range of gastrointestinal disorders were more likely among patients who had been infected with SARS-CoV-2 within a year after the acute phase of the disease.