For people living with chronic hepatitis D, the latest study results confirm the benefit of injections of this first-in-class entry inhibitor.
Laurie Saloman is a seasoned medical journalist who has written extensively about HIV, influenza, Zika, Covid-19, cancer, endocrine disorders, mental illness, and other infectious and non-infectious diseases. Her work has appeared in Contagion, The American Journal of Managed Care, Pfizer’s Breakthroughs.com, Health After 50, and the journal of the Emergency Nurses Association, among others. A member of the Association of Health Care Journalists and the American Society of Journalists and Authors, Laurie lives in New Jersey with her family. You can reach her on Twitter: @LaurieSaloman

For people living with chronic hepatitis D, the latest study results confirm the benefit of injections of this first-in-class entry inhibitor.
A new study looks at vitamin D’s role in acting as a deterrent to the proliferation of C diff bacteria.
Although vaccine effectiveness against the Omicron variant drops rapidly over time, a booster dose bolsters protection levels.

A retrospective study indicated higher rates of neurodevelopmental abnormalities in areas such as motor function and speech and language during the first year among babies born to women who had experienced a COVID-19 infection during pregnancy.

A study demonstrated patients were frequently prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics when more narrowly tailored antibiotics were considered the optimal choice.

A single dose of pegylated lambda-interferon delivered within a week of the start of COVID-19 symptoms appears to significantly reduce the likelihood that a patient will end up hospitalized from the disease.
Sky-high costs with little wiggle room to negotiate mean fidaxomicin remains underprescribed for recurrent C diff, despite favorable outcomes.

Although medical masks were noninferior to N95 in a multinational study of frontline health care workers, variability in circumstances between countries prevented researchers from drawing firm conclusions.

A deep dive into the number of deaths from COVID-19 and other causes reveals a significant disparity between the US and its peer nations.
An easy-to-administer oral biologic kept repeat C difficile infections at bay in a new study.
With proper treatment, even the youngest sufferers can recover. Know the signs when treating potentially infected children, especially if they have environmental risk factors.

As greenhouse gas emissions result in floods, heat waves, and more extreme weather events, people and pathogens are thrown closer together.
A new study found that patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are at significantly higher risk for venous thromboembolism in the ensuing 3 months than are patients hospitalized with influenza.

Durable immune responses are seen in all age groups, even with significant discrepancies in antibody levels between children and adults.

With antimicrobial resistance a rising threat, the World Health Organization is working to heighten awareness of the urgent need for new therapies.
What are the impacts of COVID-19 and other respiratory-based diseases on neurological processes? A new observational study assesses the likelihood of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and stroke in people who contract COVID-19 as well as influenza and pneumonia.

The stress of enduring an infectious disease pandemic expresses itself in a variety of mental health conditions, but the likelihood of experiencing particular symptoms depends on who you are.

Immunization against COVID-19 benefits pregnant women as well as their offspring.
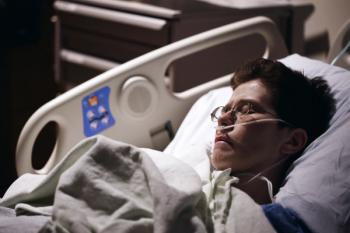
Available literature on thrombosis occurrence in COVID-19 patients focuses on hospitalized cases. A new study sheds light on the incidence of thromboembolism in less severe cases of disease,

Data on hospitalizations of children during the pandemic highlighted the seriousness of MIS-C, particularly in children of color.
Antibiotic overuse is a longstanding problem in the medical community. A new study highlights the benefits of accurate point-of-care testing to differentiate between bacteria and viruses.
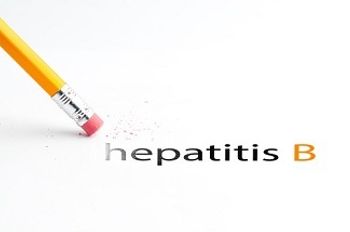
A shorter dosing period and no extra risk of suffering acute myocardial infarction means the newer 2-dose hepatitis B vaccine is an attractive option for protection.
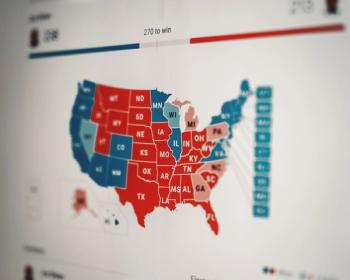
The public health policies enacted in republican and democratic states have never been more different, and the gulf shows no signs of narrowing.

Popular pain and fever-reducing drugs can have unintended consequences when it comes to infectious diseases.

The waning of protection after full vaccination matters more than the advent of the more transmissible Delta variant in subjects who tested positive for COVID-19.
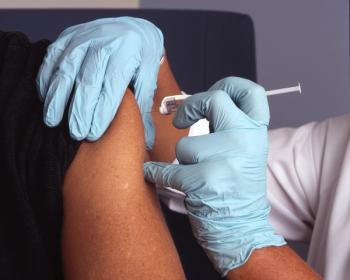
Not all people unvaccinated against COVID-19 people are actively avoiding the vaccine. A new study shows that Black people were vaccinated at lower rates than White people in the US early on, even after they indicated they were willing to get the shot. The study’s authors explain the reasons behind this.

Backed by solid data, clinicians can work to overcome vaccine hesitancy due to fears about negative pregnancy outcomes.

For already-vulnerable cancer patients, a COVID-19 diagnosis is especially concerning. A new study reveals that when it comes to disease outcomes, geographical location is not a factor—but individual cancer centers can make a difference.

Immigrant communities may be more hesitant to disclose personal health information due to fears of bullying or deportation, a new study finds.
Planning travel and social gatherings as Omicron gathers steam requires extra preparation and a degree of flexibility.

Published: December 19th 2021 | Updated:
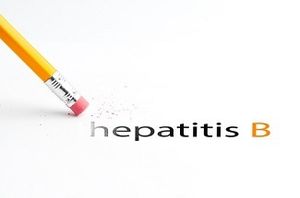
Published: April 26th 2022 | Updated:

Published: November 24th 2016 | Updated:

Published: December 1st 2016 | Updated:
Published: December 5th 2016 | Updated:
Published: December 7th 2016 | Updated: