
Additionally, its use is associated with colonization of the gastrointestinal tract by lower relative quantities of some potentially protective bacterial organisms.

Additionally, its use is associated with colonization of the gastrointestinal tract by lower relative quantities of some potentially protective bacterial organisms.
In 2015, 60% of foodborne illness outbreaks were associated with restaurants.

The follicular phase of the menstrual cycle may be the most vulnerable time for HIV-1 acquisition in women—not the luteal phase, as previously thought.
Oritavancin is a useful antimicrobial option to help clinicians manage MRSA infections and other serious GPC infections in patients with cancer, including in those at the end-of-life.
A recent study finds that shortening the rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen is both effective and safe.

In the wake of the Ebola epidemic in West Africa, the World Health Organization is working with the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy and the Wellcome Trust to create research & development roadmaps for priority diseases, such as Nipah virus.
A recent study finds that ibrutinib may be associated with serious infections in patients with lymphoid cancer.
The rise in antibiotic resistance has led experts to focus on how to appropriately manage and regulate shared-use antibiotics in humans and animals.
A panel of experts in a recent symposium discuss how dental professionals can play an integral role in increasing HPV vaccination rates and decreasing HPV-related cancer.
In a NIDCR symposium, a panel of speakers discussed autotherapies and how they can enhance the body’s innate healing ability.

A recent study suggests that the new antibiotic combination ceftazidime-avibactam may be a useful alternative for treating hospital-acquired pneumonia.
Investigators describe the current state of identification and management of fungal diseases, and discuss potential approaches for improving their recognition and treatment
A recent study of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains reports a high frequency of STEC antimicrobial resistance to drugs commonly used in human and veterinary medicine.
UCLA researchers have shown that using molecular methods to predict susceptibility testing could serve as a new way to monitor drug-resistant gonorrhea.

NIH scientists have developed a novel organ culture model to study ticks that transmit flaviviruses.
In a recent article, researchers discuss common fungal respiratory diseases in non-immunocompromised patients.
Researchers from the University of Mississippi report a case of an HIV-positive man with pneumonia due to MRSA who was treated with dalbavancin.

A recent study finds that prophylaxis with antifungal agents reduces the risk of invasive fungal infection in patients with hematological disorders.
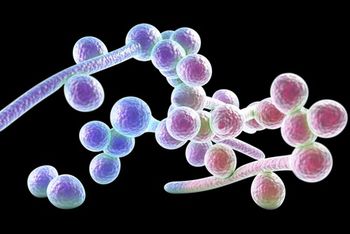
Authors of a recent article takes a look at echinocandins, and how they present some advantages over other classes of antifungal agents.
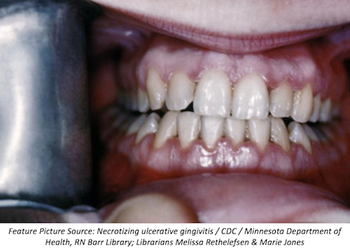
Researchers report a case of undiagnosed HIV infection that first presented as necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis.
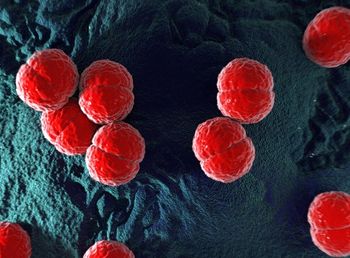
A new study published by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicates that patients receiving eculizumab can still contract meningitis, even if they have been vaccinated.
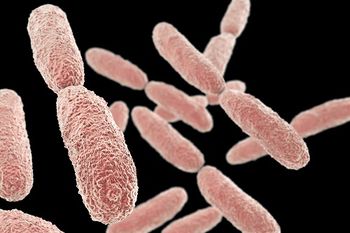
Researchers from the University of Pittsburgh find a way to successfully treat a patient with ceftazidime-avibactam-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae.

Scientists have identified 3 mutations that could allow the avian influenza strain H7N9 to spread among humans.

Researchers discover a new approach for measuring how long it takes an antibiotic to kill bacteria.
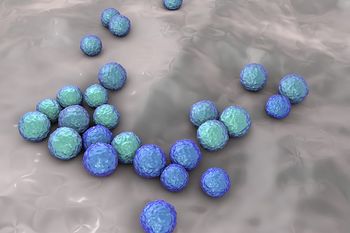
Researchers from Midwestern University Chicago College of Pharmacy highlight correlations between antibiotic use and horizontal transmission of Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) bacterial species.

In a recent webinar, CDC officers discussed challenges in diagnosing Lyme disease, and options to improve diagnostic rates.
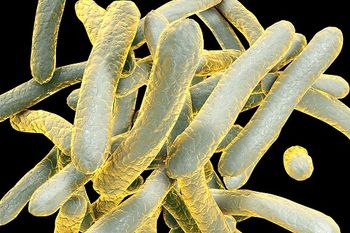
Researchers from Yale University have found a way to make mycobacteria more susceptible to antibiotics.
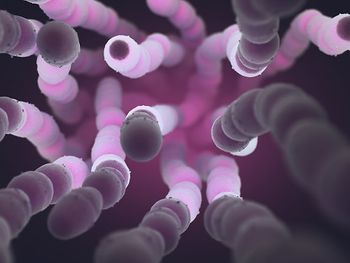
CDC researchers have found that an invasive serotype of Streptococcus pneumoniae belonging to nonvaccine serotype 35B has recently emerged.

A recently published review article analyzed the epidemiology of atopic dermatitis and its increasing prevalence, and found that it may be more common in adults than previously thought.

Experts explore how to develop and deliver effective prevention and treatment methods.
Published: November 19th 2016 | Updated:
Published: November 20th 2016 | Updated:
Published: November 23rd 2016 | Updated:
Published: November 24th 2016 | Updated:

Published: November 30th 2016 | Updated:
Published: December 3rd 2016 | Updated: