
Leptospirosis is an important zoonotic bacterial disease of worldwide public health importance. It affects humans, domestic animals, and wildlife and is caused by different Leptospira serovars.

Leptospirosis is an important zoonotic bacterial disease of worldwide public health importance. It affects humans, domestic animals, and wildlife and is caused by different Leptospira serovars.

A recent report describes a case of infectious aortitis and resultant mycotic abdominal aneurysm that arose as rare complications of exposure to Pasteurella multocida from a cat bite in a male patient.

A molecule in green tea, known as epigallocatechin (EGCG), blocks the entry of a Brazilian strain of Zika virus into host cells, and may hold potential benefit for prevention of Zika virus infections, a new study has found.
In a recent clinical alert, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) warned US healthcare facilities about Candida auris, an emerging multidrug-resistant (MDR) yeast that is causing severe, and sometimes fatal, healthcare-associated infections.

A new case report about the death of a woman from rabies emphasizes the importance of rabies awareness and education among the public.
Administration of cholesterol-lowering statins to mice reduced the number of Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria in the rodents and helped to prevent the spread of Lyme disease, a new study has suggested.
A new study has suggested that Yersinia pestis—the causative agent of plague—likely entered Europe only once, and later spread to China where it has become the source of modern plague outbreaks.
A recent study has estimated the seroprevalence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection to be 0.5% in the antenatal population.

In a webinar presented on June 9 by The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Working Group on Lyme and Other Tick-borne Diseases, a panel of speakers discussed trends in tick-borne diseases (TBDs) in the United States.
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) cure when using direct-acting antiviral (DAA) agents in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-coinfected patients is lower in real-world settings than when patients are enrolled in clinical trials, a new study has found.

Wet steam processing of fruits has the potential to significantly reduce the incidence of food-borne illness associated with contaminated fresh-cut fruits, a new study has suggested.

Each year, norovirus infection is responsible for an estimated 684 million episodes of diarrhea and 212,000 deaths worldwide, and results in approximately $4.2 billion in healthcare costs and $60.3 billion in societal costs, a new report has highlighted.

For the first time, a recent study has captured African monkeys eating bats—a finding that raises concern about the spread of zoonotic diseases such as Ebola.

A recent study in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection has shown that ledipasvir/sofosbuvir (LDV/SOF) combination therapy produces similar sustained virologic response (SVR) rates in clinical trial-based studies and real-world studies.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has released updated guidelines for the use of nonoccupational post-exposure prophylaxis (nPEP) in persons in the United States, after exposure to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) outside the health care setting.

Researchers have identified US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drugs that could help in the fight against post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome (PTLDS).

In a recent publication, Catherine F. Decker, MD, from Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, discussed some infections that have recently emerged as important sexually transmitted diseases.

This new approach could hold promise as a novel method of vaccinating against herpes simplex-2 virus (HSV-2).

A recent study has demonstrated that, although annual HIV infection and transmission rates declined in the United States over the last 5 years, they fell short of the goals outlined in the US National HIV/AIDS Strategy.
A recent study has shown that human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) enters cells throughout the entire female reproductive tract from the labia to the ovary—not just in the cervix, as previously thought.

A recent study has shown that stress and depression in adolescent females are linked to human papillomavirus (HPV)-related health problems—in particular, whether the viral infection persists long enough to increase the risk of cervical cancer.

In a recent study, researchers explore and discuss the development and implementation of a new insecticide resistance management plan in Zambia between 2009 and 2014.
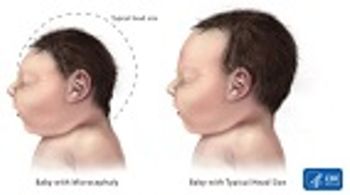
Recent data from Bahia State, Brazil, show that Zika virus infection during the first trimester of pregnancy, or early in the second trimester, is associated with the observed increase in infants born with microcephaly.
Two new inhibitory compounds—named KKL-10 and KKL-40—could hold the key to preventing the proliferation of the highly virulent bacterium Francisella tularensis, according to a recent study.

A recent study has shown that although the CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology can stop human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) replication, it also results in unexpected viral resistance and thereby limits use of the technology in HIV therapy.

In a recent study of 1,812 human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected individuals in sub-Saharan Africa, researchers found that none of these individuals had confirmed hepatitis C virus replication.

According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in 2014, nearly 17% of new HIV diagnoses were in the over-50s.
Scientists have developed a new ultra-sensitive screening technique for diseases such as HIV and cancers that may be 10,000 times more sensitive than those currently used clinical tests.
A new study has identified compounds that can reduce the virulence of the pathogenic bacterium Listeria monocytogenes.

This article is the third in a 3-part series on parasitic diseases of the central nervous system (CNS) and it highlights some of the treatment advances that are available for patients with these diseases, as well as disease control strategies that have been implemented by the World Health Organization (WHO) and other partners.