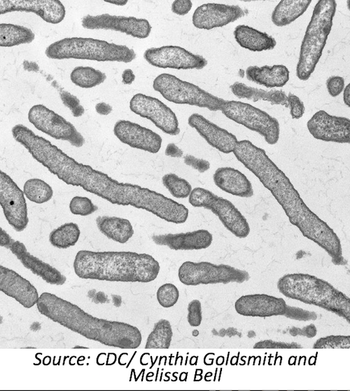
Researchers from Pasteur Institute, Paris, France, and the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention, examine the genomic features of the E. anophelis strain behind the 2015-2016 Wisconsin outbreak.

Researchers from Pasteur Institute, Paris, France, and the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention, examine the genomic features of the E. anophelis strain behind the 2015-2016 Wisconsin outbreak.
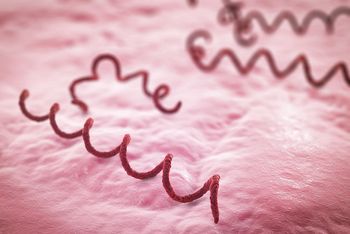
Despite initial attempts by WHO to eradicate yaws from Asia, several island nations in Asia continue to report active cases of the disease in humans.

Researchers use protein misfolding cyclic amplification to screen blood samples for abnormal prions that would indicate Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD).

Researchers from the University of Würzburg in Germany discuss the use of marine natural products to fight drug-resistant pathogens.
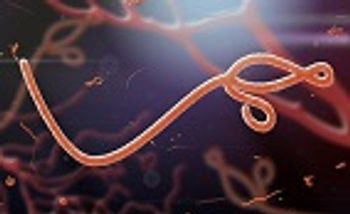
Researchers from Erasmus disease the key factors needed for successful human-to-human contact-transmission of zoonotic pathogens.
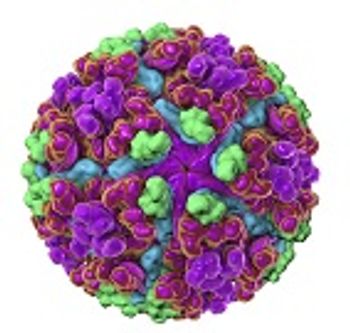
With an increase in attention on arthropod-borne diseases this year, scientists from Erasmus discuss the key factors involved in human-to-human transmission of these pathogens.
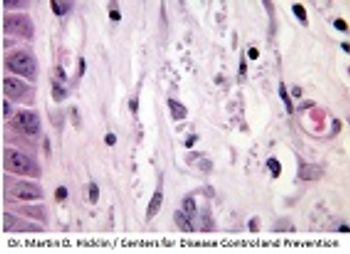
Researchers have found cases of atypical cutaneous leishmaniasis (ACL) in northeast Brazil are caused by distinct strains of Leishmania braziliensis.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention teamed up with Rotary International to host a live media briefing to highlight progress in the global fight against polio.

Health leaders call for manufacturers to consider the customer when developing diagnostic tests and discuss the need to develop direct-from-specimen tests to characterize pathogens.

Experts in clinical diagnostics and tracking food-borne outbreaks discuss using culture-independent diagnostic tests (CIDTs) as well as how the use of CIDTs is currently working in Colorado.

Researchers discuss five strategies to aid in the control of neglected tropical diseases.

Researchers review recent progress made on neglected tropical diseases since 2010.
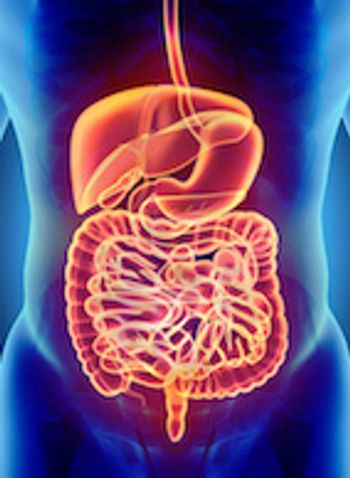
Recent studies have shown how a commensal intestinal bacterium produces an enzyme that can help protect against pathogenic bacteria.

A recent study suggests that patient-to-patient transmission of norovirus is potentially overestimated within clinical settings.

In a recent study in mice, researchers used a synthetic peptide to disrupt the bacterial stress response that causes abscess formation in skin infections with drug-resistant bacteria.
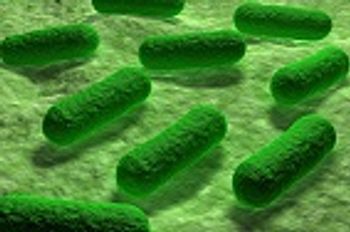
Researchers have predicted that less than 10% of Escherichia coli 0157:H7 strains are likely to have the potential to cause human disease.
A 44-year-old man from Britain could become the first patient ever to be cured of HIV, thanks to a groundbreaking new therapy developed to eradicate the virus.

The transdermal vaccine route offers an opportunity to improve vaccine administration.
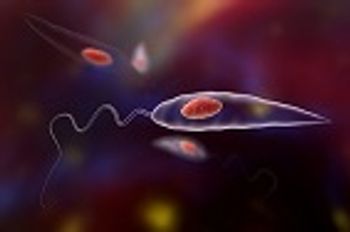
Authors of a recent review article discuss how the Leishmania parasite interacts with the immune system of its mammalian host, and how these interactions affect both the parasite and the host.

According to a recent study, people’s food preferences during times of sickness may be linked to the type of infection they have and to the type of food the immune system needs to combat the infection.
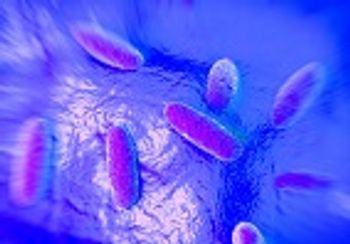
A recent study has shown that disabling bacterial flagella could prove to be an effective new method by which to fight some bacterial infections.

According to new research, applying antimicrobial coatings to whole cantaloupes during storage significantly reduces contamination and has the potential to improve their microbiological safety and extend their shelf life.
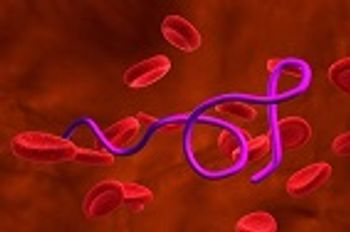
A recent study has shown that Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacterium that causes Lyme disease, spreads throughout the body by crawling along the inside wall—the endothelium—of blood vessels.
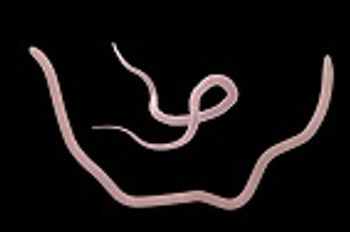
New information about how helminths regulate their hosts’ immune system may provide valuable insight for therapies to fight inflammatory diseases.
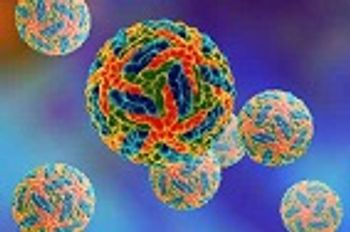
Researchers analyzed soluble forms of the B cell antigens CD27 and CD38 (sCD27 and sCD38, respectively) in the plasma of children with dengue and have suggested a role for these soluble forms as biomarkers of progression of the disease.

Liver fibrosis and subsequent cirrhosis result from chronic damage to the liver that is caused by most types of chronic liver disease, including chronic hepatitis C virus infection and alcohol abuse.
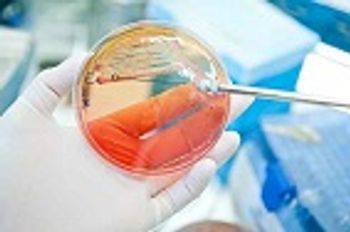
The researchers analyzed stool samples from travelers, both before and after their trips, and found that the intestinal tracts of 76% were colonized with superbugs.
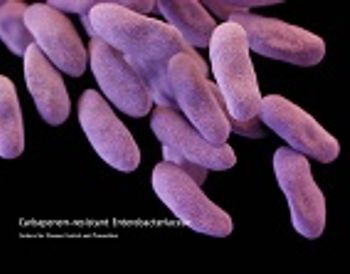
In a recent study, researchers identified three key factors that increase the risk for patient-to-patient transmission of carbapenemase-producing carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriacecae (CP-CRE).

Researchers have made an important breakthrough in efforts to develop a test to help clinicians determine whether a patient has a microbial infection or sterile trauma, a new study shows.

A recent study has described the use of next-generation sequencing to develop novel approaches that could serve as a public health tool to track pathogens such as Escherichia coli during disease outbreaks.

Published: March 5th 2016 | Updated:
Published: December 9th 2016 | Updated:
Published: December 27th 2016 | Updated:
Published: December 29th 2016 | Updated:

Published: December 29th 2016 | Updated:

Published: December 30th 2016 | Updated: