
A voluntarily recall of 2.25 oz and 4 oz packages of Diamond of California Macadamia Nuts has been initiated after a sample tested positive for Salmonella contamination.

A voluntarily recall of 2.25 oz and 4 oz packages of Diamond of California Macadamia Nuts has been initiated after a sample tested positive for Salmonella contamination.
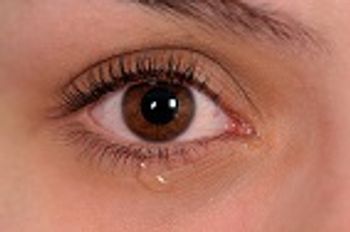
A multidisciplinary team of researchers from Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri and Colorado State University in Fort Collins, Colorado, may have identified another potential pathway for transmission of Zika virus: tears.

In a new ruling, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has declared that companies selling over-the-counter antiseptic washes will no longer be allowed to market their products as such due to doubts over these products’ safety and effectiveness.

Tanner White, a marine who has been diagnosed with HIV is making strides in fighting HIV-associated stigma by providing the public with education on the virus through the creation of his nonprofit organization called, “A Positive Tomorrow.”

A collaborative study at Michigan State University could lead to Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria prevention practices in the cattle farming industry.

On September 5, officials in the Philippines confirmed the first case of Zika in the nation, an indication that the virus is spreading throughout much of Asia.

Utah Department of Health officials are investigating a cluster of illnesses associated with raw milk from Heber Valley Milk in Wasatch County.

A new report from Liberia’s Men’s Health Screening Program provides insight into the persistence of the Ebola virus in the semen of survivors.

American Olympic athletes returned from the 2016 Summer Olympics in Rio de Janeiro with a record medal haul—121 in all, including 46 golds. More importantly, though, none of them came home with the Zika virus, at least according to the most recent reports from the US Olympic Committee.
Add sensory polyneuropathy to the list of potential complications associated with Zika virus, the mosquito-borne infection currently plaguing regions of South America and the Caribbean as well as, in recent weeks, the state of Florida.

A wild mallard duck found near a state wildlife refuge in Fairbanks, Alaska has tested positive for the H5N2 form of avian influenza.

The World Health Organization (WHO) has just released new guidelines for treating chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis; three of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) due to the increased threat of antibiotic resistance.
Researchers have determined that adult as well as fetal neural stem cells are vulnerable to the neuropathology associated with the mosquito-borne virus that has plagued Brazil and the Caribbean and has recently surfaced in Florida.
In the United States, Shigellosis causes approximately 500,000 illnesses annually and resistance to drugs to treat the infection, such as ciprofloxacin, ceftriaxone, and azithromycin, is emerging.

Investigations into a multi-state, multi-year listeriosis outbreak continue, as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) change investigative tools, adding “leafy greens” to their Listeria Initiative questionnaire.
In separate announcements, the government agency revealed its plans to award $2.4 million in funding.
A group of German researchers recently published an investigative study on the source of drug-resistant pathogens in hospitals and treatment centers.
Ohio public health officials are working with pools, schools, and childcare facilities to prevent new infections after Cryptosporidium (Crypto) outbreak grows.

Researchers at the University of Texas Medical Branch Institute for Human Infection and Immunity have confirmed pathway for transmission of the Zika virus that may enable the virus to “survive during adverse conditions,” such as the colder and drier climate conditions of the winter months.

The U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) issued three new Draft Guidances under the FDA Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA).

As cases of Zika infection continue to increase, the Centers for the Disease Control and Prevention and the Department of Health and Human Services have ramped up funding and collaborative efforts in affected regions.
Researchers at the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine have found that HIV-infected adults with depression are at a higher risk for cardiovascular disease and are more likely to experience heart attacks.

Researchers at the NIH’s National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS), working with colleagues at Johns Hopkins and Florida State University have identified compounds that “potentially can be used to inhibit Zika virus replication and reduce its ability to kill brain cells.”
Although Louisiana has yet to see any locally-acquired Zika infections, another mosquito-borne virus, West Nile, remains endemic in the state.

Researchers from Stanford University have developed a new quick and easy test for tuberculosis (TB) which may help doctors in developing nations.
Researchers at the Seattle Children’s Research Institute found a strain of herpes, human herpes 7, in the nervous system of an animal model.

A recent analysis published by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has produced results that strengthen the link between Zika virus infection and Guillain-Barré syndrome.

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the new influenza vaccines AFLURIA and AFLURIA QUADRIVALENT from Seqirus.

As sporadic cases of Ebola continue to arise in West Africa, a controversial approach could be utilized to increase survival rates in those who are infected.
A recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report states that congenital Zika infection may be associated with hearing loss.