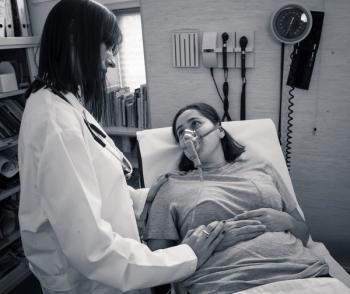
While COVID-19 patients had a higher risk of venous thromboembolic disease compared to influenza and sepsis patients, the risk of other adverse outcomes was comparable.

While COVID-19 patients had a higher risk of venous thromboembolic disease compared to influenza and sepsis patients, the risk of other adverse outcomes was comparable.
Competition among species has therapeutic implications, the authors found.

ABNCoV2, a non-adjuvanted COVID-19 booster vaccine by Bavarian Nordic, demonstrates promising results in phase 2 trials. The vaccine generates strong immune responses, neutralizing multiple variants of concern, including Beta, Delta, and Omicron.
In a large observational study, significant information was obtained about protection against acute infection and disease severity in this age group.

This past weekend, vaccine scientist and physician Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, was stalked outside his home after facing online scrutiny from Twitter CEO Elon Musk and controversial podcaster Joe Rogan. His story is severe, but Hotez is far from the first health advocate to be harassed online since the COVID-19 pandemic.

Infants age 2 to 6 months who were perinatally exposed to hepatitis C infection should be tested with a single HCV RNA test for optimal results, a recent study suggests.

Gathering data in the field, especially when it relates to infectious disease may have potentially profound implications for research because it enables scientists to generate valuable data quickly and efficiently without having to be in a laboratory setting.

While African American/Black participants were less likely to meet treatment criteria, treatment receipt did not significantly differ by race, indicating equitable access to treatment.

The agency said that in recent days a few more suppliers initiated a voluntary recall of additional select packages sold at national stores.
The post-hoc gastrointestinal microbiome analyses of recurrent C diff patients from 2 phase 3 studies was shown at the conference.

The differences in unfavorable social determinants of health among Black and White adults explains the differences in premature mortality rates, the study authors wrote.

This week, the FDA’s vaccine advisory committee unanimously voted the next generation of COVID-19 vaccines should be updated to a monovalent XBB strain. Read all about this and other top infectious disease headlines.

The federal agency explains this increase in 2022 was substantial compared to previous years, and recommends this population be up-to-date on vaccines for it.
The vaccine induced seroprotective chikungunya virus neutralizing antibodies in 98.9% of participants, regardless of age, and levels were maintained for up to 180 days.

The first patient was dosed for this open-label trial.
The FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) unanimously voted 2023-2024 COVID-19 vaccines should be updated to a monovalent XBB strain.
The American College of Physicians (ACP) CEO says it is important for physicians to move away from this traditional approach to transition to an empathetic style of discussion with patients so they can better relate and help those in need get back on track with their health post-COVID and schedule routine tests and immunizations.

With an estimated 30% of Americans living with a tattoo, the federal agency has developed guidance designed to give manufacturers information and resources to prevent potential health issues.

This model proposes a risk threshold for recommending rabies postexposure prophylaxis (PEP), potentially reducing unnecessary treatments and associated costs.

In phase 3 studies, the company’s investigational therapy, aztreonam-avibactam (ATM-AVI), had favorable results over other treatments used for complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI), hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP), and ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP).
"It does take the immune system a while to build up antibodies and recover," said Madeline King-Patel, PharmD, BCIDP, "So you don't want to give the vaccines too close to each other, or you're not going to get the full benefits."

The new guidelines for the first time offer guidance for patients who are not fully adherent to direct-acting antivirals.

As the first line of acute care, emergency departments are key stewards of antibiotics.
So far, the Virginia Mason Medical Center in Seattle has confirmed 33 patients have been infected with Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria, 9 of whom have died.
A study of hospitalized patients with diarrhea found that collecting stool samples and testing all of them identified almost 30% more cases of C. diff than the standard of care.

In a guest commentary, Thelma Thiel, RN, Cofounder of The Liver Health Initiative provides a personal perspective on her son’s liver issues and the importance of why everyone should get tested for HCV.
Rates of hospital-onset multidrug-resistant P aeruginosa infections have increased significantly in recent years.

Metformin was shown to decrease the condition by 41%; whereas, ivermectin and fluvoxamine treatment did not see a clinical benefit.

The management of hospital-acquired pneumonia requires use of preventive bundles, mitigative of risk factors, and prompt diagnosis with initiation of treatment when highly suspected.
Due to worsening headaches and unrevealing cross-sectional imaging and ascites fluid analyses, this patient's differential evolved toward a central nervous system source.