People who inject drugs who are infected with hepatitis C virus can achieve sustained viral response, despite imperfect adherence, according to the results of a new trial.

People who inject drugs who are infected with hepatitis C virus can achieve sustained viral response, despite imperfect adherence, according to the results of a new trial.
A fixed-dose combination therapy (Vosevi, Gilead) was highly effective after 12 weeks in retreating direct-acting antiviral-experienced patients with hepatitis C virus infection, with and without HIV co-infection, including those with prior noncompletion of treatment or poor adherence.

Efforts such as improved indication documentation and antimicrobial stewardship involvement may improve patient outcomes in some patients who are on outpatient parenteral antimicrobial therapy (OPAT) for ease of administration (EOA) that are readmitted to the hospital.

New software to facilitate prior authorization helped streamline the approval process and increase antimicrobial use tracking at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania.
The combination of direct-acting antiviral agents glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (G/P), sofosbuvir, and ribavirin is now approved for new patient populations.

Study results suggest that HPV testing is able to detect cervical intraepithelial neoplasia earlier and more accurately than cytology.
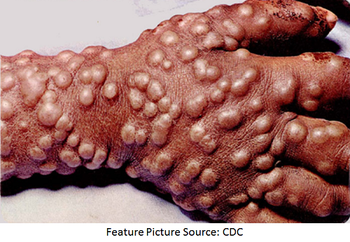
Development of the drug has been deemed necessary because of the potential for the use of the virus in a bioterrorism attack and waning herd immunity against the virus among the general population.

Molecular diagnostics provide faster, more complete results than traditional culture-based tests, and their use may improve outcomes for patients with chronic wounds and skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs).
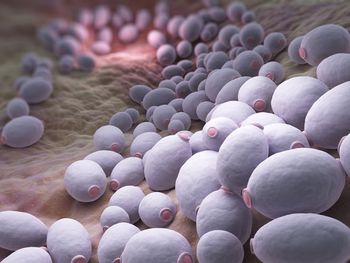
Emerging Candida species prove capable of virulent spread in health care facilities, leading to outbreaks.

Sixty-nine out of the 70 colistin-resistant isolates had either mcr-1 and/or mcr-3 genes.
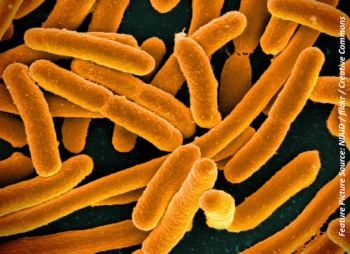
Empiric use of fluoroquinolones looks to be an alternate option for the treatment of gram-negative bloodstream infections when risk factors for antimicrobial resistance are not present.

Although most health care providers are adhering to the recommended regimen, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that about 20% of patients with uncomplicated gonorrhea are not receiving the recommended dual regimen designed to ward off resistance.
A study shows that pharmacist-driven education and encouragement of antibiotic self-stewardship can decrease the duration of therapy for broad-spectrum antibiotics.

This emotional drive carried throughout the continuum of the prescribing pathway, from initial prescription to stopping or de-escalating antibiotics.

According to recent research from Johns Hopkins Medicine, when it comes to making choices on appropriate antibiotic prescribing, outpatient providers are making the decision based on patient demand, not necessarily on what's actually appropriate for the condition.
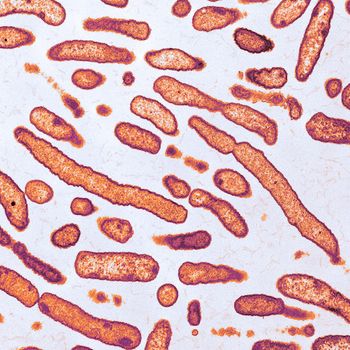
Previously seen in Wisconsin in 2015-2016, Elizabethkingia seems to have made its way to the Empire state.

In the wake of news of 10 travelers being infected with yellow fever, 4 of whom have died, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) are urging anyone considering travel to yellow fever endemic regions of Brazil to be vaccinated prior to travel.

Posthoc analysis of the EMERALD trial reveal the combination regimen of D/C/F/TAF performs well in HIV-positive patients across different race, gender, and age subgroups, who may have failed previous antiviral regimens.

Interim results of the HOPE study reveal that the vaginal ring reduced women’s risk of acquiring HIV by more than 50%. Women in this study are also using the ring more than in previous studies.

Study results revealed that dolutegravir appears to be effective and well-tolerated in HIV/tuberculosis (TB) co-infected adults also receiving rifampin-based TB therapy.
University of Western Ontario investigators have found that the genetic diversity of HIV-1 during early infection is greater in the vaginal tract than in the bloodstream.
Investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have made some interesting findings about methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureu (MRSA) that may hold the key to curbing lymphatic repercussions.

The World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended visitors to Sao Paulo, Brazil, should consider getting the yellow fever vaccine before visiting.

Seeing upwards of 85% of children in the United States each year, dentists are key to promoting HPV prevention methods, but more training and education is needed first.

The vaccine is the only 2-dose regimen for the prevention of infection by all known subtypes of hepatitis b in adults 18 and older.
A new review article shows that if a child has a serious reaction to a vaccine, the chances of it happening again are very small.

The results of a new study from Vanderbilt University provide more support for breastfeeding, revealing that sugars in human breast milk can help protect babies from bacterial infections.

Reports of increasing cases of antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea are on the rise and in fact, the World Health Organization has designated the infection as high priority as it poses a great public health threat.

The World Health Organization (WHO) recently sent out a global alert warning of the growing threat of resistance to HIV drugs.

Outbreaks of measles have resulted in over 14,000 infections and the loss of 35 lives across Europe since January 2016.
Published: January 5th 2017 | Updated:

Published: January 10th 2017 | Updated:
Published: January 18th 2017 | Updated:

Published: February 7th 2017 | Updated:

Published: March 18th 2016 | Updated:

Published: March 21st 2016 | Updated: