
Although Cuba reported no cases of Zika virus in 2017 and 2018, investigators used travel data and genomic epidemiology to uncover a large, “hidden” Zika outbreak.

Although Cuba reported no cases of Zika virus in 2017 and 2018, investigators used travel data and genomic epidemiology to uncover a large, “hidden” Zika outbreak.
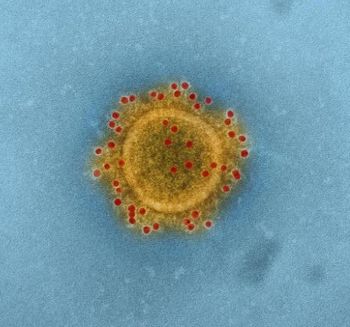
West Nile virus cases have been relatively low overall this summer season but, following a wetter than usual season, Arizona has already seen 6 times the normal number of seasonal cases.
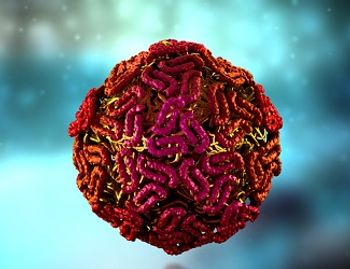
A research team’s latest study offers new insights into a weak point on the Lassa virus surface and the neutralizing antibodies capable of targeting it.
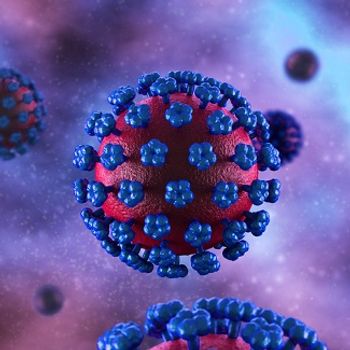
Investigators in the first human trial of a MERS-CoV candidate report strong immune responses and no serious adverse events, advancing the vaccine candidate to phase 1/2a and phase 2 trials.
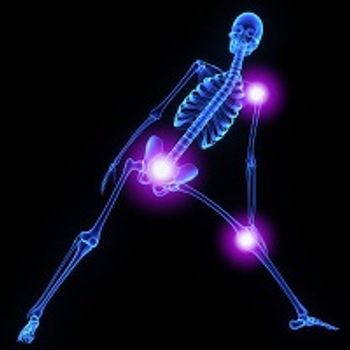
Knee and hip replacement patients who have healthier intestinal microflora may have a lower risk of developing dangerous periprosthetic joint infections than patients with unhealthy guts.
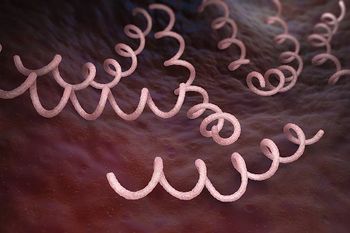
A sharp increase in syphilis cases in Europe is hitting hardest among MSM and has been linked to the use of PrEP drugs and an increase in risky sexual behavior.
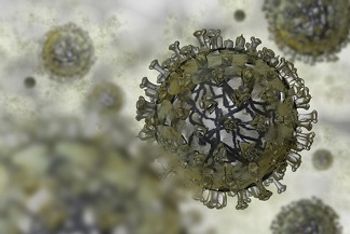
In the wake of prior findings that influenza A viruses exhibited reduced susceptibility to single-dose baloxavir, a new study indicates that the antiviral medication inhibits all 4 types of flu, including viruses with pandemic potential.
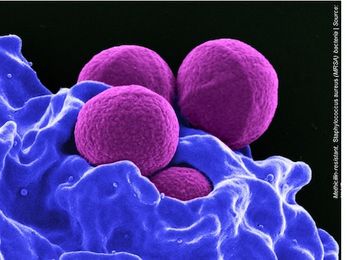
Although conducting whole genomic sequencing creates an upfront cost in screening patients for MRSA, a new study finds that it’s a cost-effective way to prevent new infections and related deaths.

One of the biggest studies to-date on the relationship between cefepime plasma concentrations and neurotoxicity has identified which patients are at greatest risk.

The program combines PrEP administration along with evidence-based behavioral intervention to reduce HIV risk behavior for HIV-negative, opioid-dependent people who use drugs and are receiving treatment.
Although PrEP drugs are key to preventing HIV infection, a new study by French investigators found a high prevalence of high-risk human papillomavirus infection among MSM taking PrEP.

A recent 3-part series details the inevitability of another global influenza pandemic and how better surveillance and new vaccines may protect us in time for the next pandemic.
As injectable influenza vaccine doses from the 2018-19 season are set to expire on June 30, 2019, CDC investigators detail 192 cases of expired vaccine administration over the last year.

With the arrival of summer in the United States, health officials are reminding the public to take precautions to avoid West Nile virus.
A new study finds that age, sex, and site of infection can increase the risk of long-term mortality in the first 5 years following sepsis survival.

Health officials point to substantial progress in flu surveillance, treatment, and prevention; however, the global population remains vulnerable to new emerging viruses.
Although a new study finds that bone toxicities were lower than expected in PrEP users, investigators say that those at higher risk of bone fracture may want to seek PrEP alternatives once available.

A new study combines models on PrEP use in both adult MSM as well as adolescent sexual minority males.

Following a rise in the number of wild poliovirus cases in Afghanistan and Pakistan from 2017 to 2018, a new report details the challenges in interrupting polio transmission.

A research team led by Yale University scientists report that breathing dry air lowers defenses against influenza virus infection.

Few studies have examined the impact of CRE in low-income and middle-income countries, but now new literature provides much-needed data on antibiotic resistance in these settings.

Although antibiotic prophylaxis for new mothers is common following caesarean section births, a new study provides evidence of benefits on infection reduction in women following operative vaginal birth.

Generic PrEP drugs offer a cost-effective way for people to reduce their risk of HIV, though some worry about the authenticity of drugs purchased online.

In a new study, patients receiving CAL02 had faster clinical improvement, including faster resolution of organ dysfunctions, as well as more rapid clearance of pneumonia, when compared with placebo.

In an unexpected discovery, a NIAID-funded study team has found that a human antibody can target a part of the hemagglutinin protein that the influenza virus uses to enter and infect cells.
A revision to the fluoroquinolone antimicrobial susceptibility testing breakpoints for 2 bacteria comes following evidence that previous breakpoints were too high to detect low-level antibiotic resistance.
Following a rise in sexually transmitted infection diagnoses in recent years, NIAID is awarding grants for research into syphilis, gonorrhea, and chlamydia vaccine candidates.
Ahead of the summer travel season, the CDC is reminding Americans traveling abroad to be aware of tickborne rickettsial diseases.
The authors of a new study say the use of antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors are among the list of risk factors for recurring C diff infections.

A new review recommends updated guidelines for diagnosing and managing Candida and C diff coinfection.
Published: November 22nd 2016 | Updated:
Published: November 23rd 2016 | Updated:

Published: November 24th 2016 | Updated:

Published: November 24th 2016 | Updated:

Published: November 25th 2016 | Updated:

Published: November 28th 2016 | Updated: