
CDC has released mid-season estimates indicating approximately 84,000 Americans have been hospitalized for the influenza so far this season.

CDC has released mid-season estimates indicating approximately 84,000 Americans have been hospitalized for the influenza so far this season.
New evidence suggests that use of certain opioids may increase the risk of developing pneumonia, particularly in patients with HIV.
Investigators in Canada link larger HIV reservoir sizes to a virus gene that is more functional in one subtype of the virus, with findings which may one day contribute to the development of an HIV cure.
When combination antiretroviral therapy does not lead to sufficient HIV suppression, a new study finds that PrEP can become cost-effective for couples with differing HIV status who are trying to conceive.
While the United States has seen significant increases in pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) use among those at risk for HIV infection, PrEP uptake rates are still low overall in men who have sex with men, as well as in transgender individuals. A new study examines how a behavior model may help increase PrEP use in these at-risk groups.

After 6 NIH hospital patients developed infections from waterborne bacteria, investigators found contamination in facility pipes and faucets.
With early season flu vaccination rates up from 2017-2018 early season rates, new pediatric influenza deaths around the country are prompting health officials to call for even higher vaccination rates.

In a new study, researchers with the US Department of Veterans Affairs found that metronidazole is as effective as vancomycin for treating mild cases of Clostridium difficile infection, despite new guidelines no longer recommending metronidazole.

New findings on the ways Ebola proteins connect with human proteins may lead to a novel treatment for Ebola virus infections.
A recently launched clinical trials is investigating the use of an intravenous combination therapy including vitamin C for use in sepsis patients.
While most infants exposed to Zika in utero show no severe developmental defects, a new study offers an estimate of the impact of Zika-associated impairment within the first 2 years of life.
Concerns over the influenza vaccine’s effectiveness and its side effects are causing many Americans to forego an influenza vaccine this season, despite the severity of the 2017-2018 Season.

As the World Health Organization has reported an increase in malaria cases in 10 African countries, a new study offers open source findings on more than 600 new potential antimalarial drug candidates.

A new report from the ECDC and WHO shows the disparity of new HIV diagnoses across Europe, with more than 80% of new cases occurring in Eastern Europe in 2017.
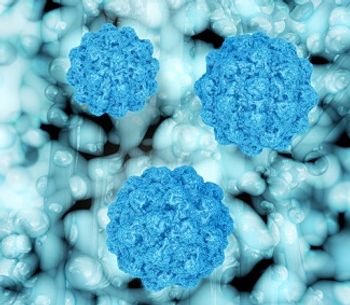
Investigators have determined that norovirus outbreaks occur most frequently in health care settings and are often caused by strains of a virulent genotype.
Results from 2 new studies completed in the United States and Canada indicate that probiotic supplements do not produce any benefits for children with gastroenteritis.

A new survey has found that 34% of US parents are not planning to have their child vaccinated against influenza.
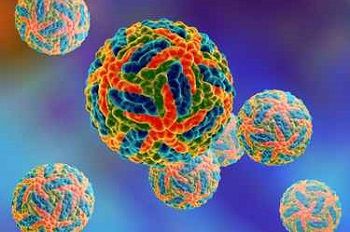
Two new studies highlight how antibodies from prior infection with Zika or Dengue may increase the severity of illness in the other, impacting the infants of pregnant women who are infected.
A new approach to hepatitis C virus infection treatment could shave time and costs off the current standard regimen.

A new study explores the concept of an epidemic calendar, with new findings suggesting that all infectious disease outbreaks have a seasonal element.

A new study on a novel experimental nanotechnology-based organ transplant acceptance therapy offers hope for reduced organ rejection without immune suppression.
A new study examining cytokines in the blood of pregnant women infected with Zika may help investigators create a screening test for early detection of fetal abnormalities from the virus.

Investigators have found that children who received a flu shot in consecutive years did not see a decline in vaccine effectiveness.
The results of a new study suggest that a high-dose trivalent influenza vaccine recommended for older adults may also benefit patients with kidney disease who are on dialysis.
Building on decades-old research, scientists in France say they’ve developed an effective rectal delivery formulation of an antibiotic used to save infants with life-threatening neonatal sepsis.

A new study by investigators in Japan finds that earlier antibiotic stewardship intervention decreased antibiotic usage and costs and were associated with reduced rates of antibiotic resistance.
Rezafungin, a drug in development for the treatment and prevention of invasive fungal infections, is set to move to phase 3 trials following new data.

A study of more than 500 outpatient clinics reveals a new view of antibiotic overprescribing practices in the United States.
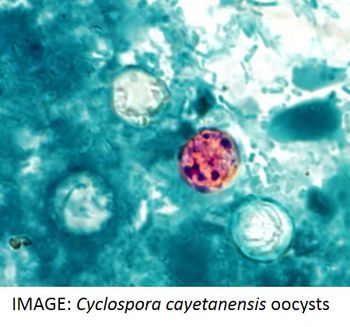
Following a significant spike in cases of cyclosporiasis, the CDC is investigating whether changes in diagnostic testing may be partially responsible for the rise in recent case counts.

Investigators from the University of Colorado Boulder have developed a strategy to fight antibiotic-resistant E coli using genetic disruption.