
Updated guidelines on the treatment and management of HIV in children and adolescents reflect new data on antiretroviral drugs as well as a call for mental health screenings.

Updated guidelines on the treatment and management of HIV in children and adolescents reflect new data on antiretroviral drugs as well as a call for mental health screenings.

A 21-week-long flu season begins to wind down while investigators find that flu infections in consecutive seasons are more likely in young children.
A 2017 pediatric tetanus infection case in a child who was not vaccinated led to nearly 2 months of hospitalization and more than $800,000 in medical costs.
A new study may help to explain how bacteria present at low levels in healthy human mouths can persist for months and cause hospital outbreaks of drug-resistant infections.

Following a 2018 outbreak in the US of acute flaccid myelitis, a new paper calls for research into the causes of this surge of a usually rare disease.
In a new trial, an experimental antibody suppressed HIV in patients on short-term pause from their daily antiretroviral therapy regimens.

Ebola virus survivors experience ongoing symptoms following infection, and a new study tracks how those patients compare in health with close contacts who weren’t infected.

Although the rate of outpatient antibiotic prescriptions is down overall, a new study highlights how the United States may be falling short of meeting antibiotic stewardship goals.
Following years of research and development, NIAID scientists have begun enrolling participants in the first human trial of a universal flu vaccine candidate.

An antiviral drug that could offer months of protection against the flu may be on the horizon and ready to fill in some of the gaps of the seasonal flu vaccine.
A recent study has found that a new method of testing circulating H3N2 flu viruses may help flu experts in selecting seasonal vaccine components.

Following a 1-month delay, WHO experts have issued a recommendation for a new influenza A(H3N2) component for next flu season.
A new report indicates that resistant isolates of gonorrhea were detected in more European countries in 2017, and may soon threaten the current recommended treatment protocol.

On the anniversary of the discovery of the bacterium that causes tuberculosis, world health leaders are highlighting an epidemic that kills nearly 4500 people each day across the world.
Although the cause of childhood-onset type 1 diabetes remains unknown, a new study links a precursor of the condition to an abundance of certain viruses in the gut.
Although 30% of adults with XDR TB are successfully cured or complete treatment, a new study has found that children have far more favorable outcomes and lower mortality rates.
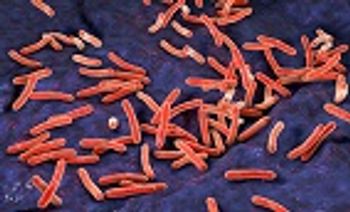
A new study examining tuberculosis and HIV coinfection in patients in Latin America has found that those with TB had higher mortality rates over the course of a decade, despite successful TB treatment.
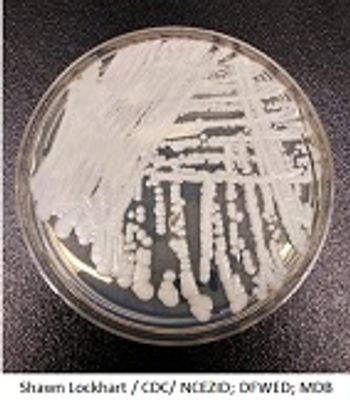
It’s become a serious global health threat, and now a new study investigating 9 cases of Candida auris infections in Brooklyn highlights the importance of quickly identifying these fungal infections.

Prior studies have indicated that patients with influenza A infections fare worse than those with influenza B, and now a new study backs it up.

Although influenza A H1N1 continues to dominate the current flu season in the US, H3N2 viruses are on the rise in some parts of the country.

Powassan virus counts in the United States have been on the rise over the last decade, and now a new study sheds light on how ticks rapidly transmit the rare disease.
A new study finds that regular use of tenofovir gel helped reduce the risk of genital herpes acquisition in women in sub-Saharan Africa.
Although IV antibiotics have been the standard of care for bone and joint infections, a new study finds that oral antibiotics were non-inferior.
As flu activity remains elevated in all regions of the United States for the fifth week in a row, a new study quantifies the impact of flu vaccination last season.
A new study reports that Zika antibodies persist for longer than initially believed, with antibodies detected in symptomatic patients 18 months after illness onset.
In a report detailing the hospitalization of a college student with complications from a herpes zoster infection, investigators say a corticosteroid prescription likely impaired the patient’s antiviral immune response.

In an ongoing study spanning more than 15 years, investigators have made key discoveries about how HIV and TB drugs affect pregnant and postpartum women, leading to new safety and dosing recommendations for several medications.
Investigators compared an antibiotic monotherapy and a combination therapy for MSSA bacteremia and found that both had similar results, raising the call for new treatment options.

A new study identifies several easy-to-adopt strategies that can help individuals to remember to take PrEP at roughly the same time every day.

Investigators in the United Kingdom are closer to understanding how a 5% genetic difference between global Salmonella and a virulent strain of African Salmonella which leads to nearly 400,000 deaths each year in sub-Saharan Africa.