
4-way trial assesses non-prescription interventions, including 2 nasal sprays, for reducing seasonal respiratory illness and related antibiotic use.
Ken reports on medical innovations and advances in practice and edits presentations for news and professional education publications. He previously taught and mentored pharmacy and medical students, and provided and managed pharmacy care and drug information services. He regularly contributes to Contagion Live, Patient Care Online and Pain Medicine News.

4-way trial assesses non-prescription interventions, including 2 nasal sprays, for reducing seasonal respiratory illness and related antibiotic use.

Investigators found that 10 days of antibiotics is common for acute otitis media despite that 5 to 7 days is advised by US and international guidelines.
Proposed alternative to "unsustainable" wide use of broad spectrum antibiotic prophylaxis in surgeries confronts antimicrobial resistance.
A new study demonstrates that the continuous infusion of β-lactam antibiotics could offer better clinical outcomes in treating sepsis, despite the nuanced statistical results.
Meta-analysis revealing higher 90-day mortality with intermittent than continuous infusion of ß-lactams for sepsis prompts call for latter to be standard of care.
Purportedly higher sepsis mortality in safety-net hospitals reflects less a difference in acute care than opportunities to discharge to hospice.

Piperacillin-tazobactam was associated with higher mortality than cefepime for empiric treatment of sepsis among patients without indication of anaerobic infection.

Antimicrobial stewardship to reduce multidrug resistance and opportunistic Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) could also guide shorter treatment.

The INSPIRE trials find prompts within computerized provider ordering improves antibiotic utilization for pneumonia and urinary tract infections.

Incidence of hospital-onset Clostridioides difficile infection differed between hospitals that implemented the CDC prevention strategies and those that did not, but not necessarily because of the strategies.

A large trial supports de-escalation from empiric, broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment for Enterobacterales bacteremia to a non-antipseudomonal agent.
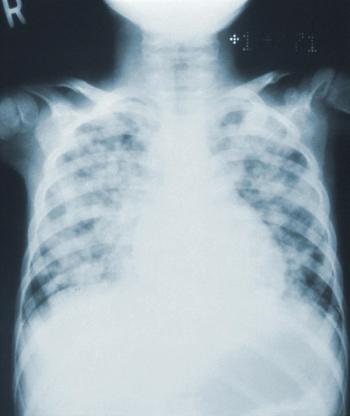
Community acquired pneumonia is often inappropriately diagnosed in hospital admissions, particularly among older adults with dementia, and can lead to in-hospital antibiotic-associated adverse events, such as Clostridioides difficile.

Investigators find that bacteremia rarely develops from asymptomatic bacteriuria, and that empiric antibiotic treatment should be reserved for those at risk.

New analysis indicates that children treated at 3 years of age for perinatally acquired HCV will live longer, with less liver morbidity and lower health care costs than if treated at 6 years of age.

Patients hospitalized for suspected community-acquired pneumonia received targeted treatment more quickly with PCR testing than with culture-based diagnostics.

Inhaled nanoparticles deliver antibiotic and antimicrobial peptides through mucus and biofilm barriers in animal model of infection-exacerbated COPD.

ePOCT+, a digital clinician decision support tool, reduced outpatient antibiotic prescribing without adverse health outcomes, potentially mitigating development of antimicrobial resistance.
New vancomycin dosing regimens are proposed to improve outcome and minimize toxicity in overweight and obese patients with renal insufficiency.

Myopathy, with metabolic disturbances and amyloid deposits, is discovered in persons with Long COVID who experience post-exertional malaise.

Doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) has reduced STIs among men who have sex with men, but poor adherence marred trial results with women.
Investigators studying over 4500 patients with gram-negative bacteremia see opportunities for earlier transition from IV to oral antibiotics.
Investigational 24-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine developed on cell-free protein synthesis platform is first to broaden coverage without reduced immunogenicity.

Infants with HIV could be spared from requiring lifetime ART if treated within hours of birth to disrupt formation of HIV viral reservoirs.

Amikacin inhaled once daily for 3 days reduced risk of developing ventilator-associated pneumonia in placebo-controlled trial in critically ill.

CDC recommends HCV testing in these populations as a critical step to achieving national priority of eliminating HCV.

Veterans Affairs (VA) study finds some reduction in post-COVID thromboembolic events with early use of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir but no protection against 30 other conditions.
Excess death risks from GI diseases, above pre-pandemic patterns, were largest for C difficile colitis, followed by GI hemorrhage, ulcers, and colorectal cancer.

A New Drug Application (NDA) for ceftobiprole was accepted for 3 indications including S aureus bacteremia, days after phase 3 results were published.
Neither alcohol use nor hepatic fibrosis interfered with achieving sustained virologic response with direct-acting antiviral treatment of hepatitis C virus.
Review of hepatitis D virus describes “unique” biologic characteristics and “ominous” medical effect, but constrained as HBV treatments affect HDV life cycle.