
Study links inappropriate, off-guideline antibiotics to increased, avoidable allergic and adverse events in children.
Ken reports on medical innovations and advances in practice and edits presentations for news and professional education publications. He previously taught and mentored pharmacy and medical students, and provided and managed pharmacy care and drug information services. He regularly contributes to Contagion Live, Patient Care Online and Pain Medicine News.

Study links inappropriate, off-guideline antibiotics to increased, avoidable allergic and adverse events in children.

Active immunization of pregnant women with investigational vaccine protected infants from RSV from birth through at least 6 months.

Historically low incidence of dengue in southeast Asia and Latin America linked to COVID-19 restrictions suggests potential future interventions.

Correlating immune response to COVID-19 vaccination in persons with HIV to their CD4 T-cell count could inform optimal vaccine strategy.

Investigators consider the low rate of vaccination in the rapidly increasing migrant populations in Europe, and call for improved strategies.
Selecting initial antibiotic for ventilator-associated pneumonia from Gram staining and resistance records could reduce broad spectrum agents.

Adding v-safe active monitoring to VAERS passive reporting produced "most comprehensive" program, and affirmed COVID-19 vaccine safety.
Bedaquiline-resistant tuberculosis is characterized in South Africa, where it has not been reserved as last resource for drug-resistant TB.

Both noncarbapenem β-lactams and carbapenems produced good outcomes in UTI from β-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales.

First-in-class triaminopyrimidine demonstrates antimalarial efficacy in first-in-human test of dosing, kinetics, and clearing parasite in infected volunteers.
Study with Medicare beneficiaries found those at highest risk of severe COVID-19 among least likely to receive monoclonal antibody treatment.
Investigators finding high risk for cardiovascular complications post-acute COVID-19 urge increased monitoring and preparedness.
Final analysis of phase 3, placebo-controlled trial confirms efficacy and safety of single-dose adenoviral vector vaccine against COVID-19.
Infection-acquired immunity to SARS-CoV-2 remains higher for longer when followed by vaccination.
A booster vaccination increases protection against COVID-19 whether homologous or heterologous with the primary vaccine.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) compared 2-dose mRNA vaccination to third dose booster and to unvaccinated, against both Omicron and Delta variants of SARS-CoV-2.

With fewer monoclonal antibody treatments effective against the Omicron variant, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) now recommends direct-acting antivirals.

Casirivimab/imdevimab protected uninfected contacts from COVID-19 and reduced symptomatic infections in trials before Omicron emerged.
Study finds high false positive results with one batch of a rapid antigen test for SARS-CoV-2 but "very low" overall false positive rate.
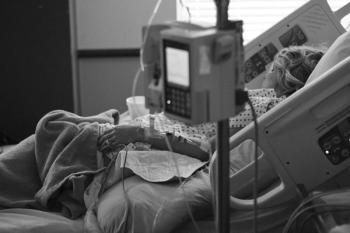
Implementation of CMS Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Management Bundle did not reduce mortality rates in study of 114 hospitals.

No influenza-related hospitalizations of children were found in a nationwide study of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the 20/21 flu season.
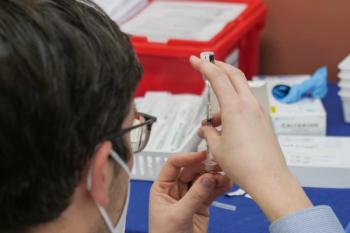
Clinical trial compares immunogenicity of mixing mRNA, adenoviral and spike-adjuvant vaccines in 2-dose series against COVID-19.

A booster dose of the m-RNA vaccine reduced COVID-19 and the rates of severe illness across adult age groups.

Neonatal vancomycin trial found loading with more frequent dosing over shorter time comparable to standard regimen but adversely affected hearing.

Inhaled ciclesonide did not shorten duration of mild to moderate symptoms of COVID-19 in outpatients, but lessened hospitalizations.

The report on antimicrobial resistance finds new therapeutics are "essential to future of clinical medicine" but may not be viable in present market.

The report assesses progress of a US national action plan to combat antimicrobial resistance, called for by 2015 World Health Assembly.

In the second installment discussing this report, the authors point out that the approval of new diagnostics can help facilitate better stewardship.

The National Academies report reviews several challenges, and ways to overcome them for optimal antimicrobial stewardship.
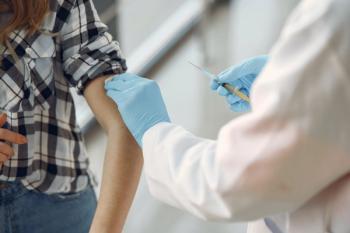
The latest National Immunization Survey-Child, for children born in 2017- 2018, reveals different rates of vaccination by demographic and disease.