Review and meta-analysis identifies clinical manifestations, risk factors, and maternal and perinatal outcomes associated with COVID-19 in pregnancy.
Ken reports on medical innovations and advances in practice and edits presentations for news and professional education publications. He previously taught and mentored pharmacy and medical students, and provided and managed pharmacy care and drug information services. He regularly contributes to Contagion Live, Patient Care Online and Pain Medicine News.

Review and meta-analysis identifies clinical manifestations, risk factors, and maternal and perinatal outcomes associated with COVID-19 in pregnancy.
Outbreaks in countries with high vaccine uptake prompted reassessment of the immunogenicity and persistence of trivalent measles, mumps and rubella vaccine
The CMS Sepsis Bundle Core Performance Measure of sepsis treatment could contribute to the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics
The 2-step algorithm for diagnosing Clostridioides difficile infection is difficult to interpret in patients who have cancer or are immunocompromised.

Mathematical modeling for tracing COVID-19 contacts can account for likely scenarios of inconsistent physical distancing and quarantine adherence
The short-lived designation of remdesivir as an Orphan Drug to treat COVID-19 exposed loophole in the Orphan Drug Act.
A systematic review and meta-analysis was undertaken to ascertain optimal route and duration of antibiotic treatment of acute cellulitis

Postmarketing vaccine experience with vaccines suggests the candidates approved by the FDA for COVID-19 will be safe and effective
A recent increase in stress cardiomyopathy (Takotsubo Syndrome) could reflect the severe psychosocial pressures of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Although plasma levels of lopinavir increase as its metabolism is inhibited by inflammation in COVID-19, levels in the lungs remain subtherapeutic.

Contracting influenza increased the risk for invasive pneumococcal disease in a study conducted across 3 countries.
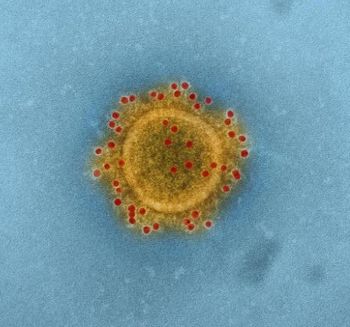
Over 200 scientists issued alert to medical community that COVID-19 is transmissible over longer distances via smaller aerosolized droplets.

Hollow-fiber infection model (HFIM) facilitates comparison of intermittent vs continuous infusion of ß-lactam antibiotic for K. pneumoniae

A high proportion of N95 masks failed to fit properly with the extended use and reuse recommended by the CDC for conserving PPE during the shortage.
Regional disparity in prior authorization requirement for insurance coverage of Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for HIV could be discriminatory.

Less ACE2 in nasal epithelium in children could present barrier to SARS-CoV-2 and explain the lower observed rate of pediatric infections.

Adding thromboelastogram to D-dimer measure could enable early ID of patients who require aggressive anticoagulation for severe COVID-19.

Two patient case series suggest pronation could improve oxygenation with non-invasive ventilation in some patients with coronavirus.

A risk score that predicts critical illness in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 could help inform allocation of clinical resources.

A series of essays consider the privileges and ethics of an immunity-based "passport" to proceed with fewer restrictions in the age of COVID-19.

Medical journal editors call for managed expectations for the numerous clinical trials that will soon release results on potential COVID-19 treatments.

Reduced T cell count in patients with coronavirus could be as important an indicator for urgent intervention as reduced respiratory function.

Even after putting public health policies in place, the state reached 2600 nursing home cases before the end of April.

Half of surveyed hospitals have no ventilator triage policies, and existing policies differ substantially and often lack guidance on implementation.

New expert recommendations follow from evidence showing the virus is a thrombo-inflammatory process that can affect multiple organs in addition to the lungs.

A hospital case series of patients with both COVID-19 and HIV describes recovery, but highlights the need to refine treatment.
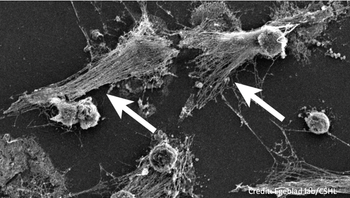
An immune system defense that ensnares pathogens in neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) could underlie severe respiratory distress, thrombosis in COVID-19.
Investigators assure that effective treatment of COVID-19 can be found without losing scientific integrity and public confidence.

Germany's National Academy of Sciences issued statements in March and April detailing necessary containment measures and a path to normalization.

A modelling study to forecast COVID-19 spread in China and inform decisions on relaxing restrictions, predicts a second wave that could require greater restrictions.