NIAID researchers have discovered that a rare genetic mutation can increase susceptibility to catching human rhinoviruses.

NIAID researchers have discovered that a rare genetic mutation can increase susceptibility to catching human rhinoviruses.

Conan MacDougall, PharmD, MAS, BCPS-AQ ID, sheds light on behavior change interventions that could positively affect antibiotic prescribing practices.

New research suggests that making drug use a crime may negatively impact the prevention and treatment of HIV.

Through the use of citizen science, researchers were able to identify the distribution of ticks and tick-borne diseases in a particularly hyperendemic region of the United States.
Jerod Nagel, PharmD, highlights how rapid diagnostic tools can be utilized in antibiotic stewardship programs to improve outcomes for patients with S. aureus.
Johns Hopkins Armstrong Institute of Patient Safety and Quality researchers have shown that by adhering to evidence-based practices, frontline healthcare staff members can reduce ventilator-associated events.

The quality improvement group at the UNC Infectious Disease Clinic has come up with a process to increase rates of STD screening that includes providing patients with the option to self-swab.
An outbreak associated with a rare, paralytic illness has hospitalized several individuals and claimed one life thus far.
Yemen has been hit by a resurgent cholera outbreak and health officials are focusing all of their efforts into infection control.

On Hepatitis Testing Day, healthcare providers and the public work together to promote awareness and encourage those at risk to get tested.

On HIV Vaccine Awareness Day, we reflect on the advancements made in the fight against HIV and the ongoing efforts to reach the collective goal of developing a safe, effective vaccine.
Several individuals in one US state and in Europe have fallen ill due to infection with hepatitis A.
NICHD researchers find that tiny cell particles released by HIV-infected cells might help the virus spread to new cells.
The CDC released new preliminary surveillance data showing that over five years, the number of new hepatitis C infections has nearly tripled in number.
UNC School of Medicine researchers have identified a new HIV reservoir, a finding that can be used to inform cure research.

There has been an increase in STDs seen in US emergency departments, a setting that proves to be less than optimal for providing STD care.

Today, May 5th, is Hand Hygiene Day, a day that reminds healthcare workers, visitors, and policy makers alike, that frequent handwashing can be used to fight the growing threat of antibiotic resistance, and ultimately, save millions of lives.
The rates of primary and secondary syphilis in the United States have increased by 19% from 2014 to 2015, and the CDC notes that preliminary data suggests that there was a “similar rate of increase in the first 6 months of 2016.”
In a collaborative effort, scientists from Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and George Washington University have found that defective HIV proviruses can complicate monitoring the true viral load within patients and distract the immune system from attacking the functional virus.

The NIH has developed a platform called SHERLOCK, capable of quickly detecting small amounts of nucleic acid sequences—and it’s cheap.
In a recent study, scientists from the NIH identify a set of protein complexes that are recruited viral genes and stimulate not only initial HSV infection, but also reactivation of dormant HSV.
Manufacturing issues have led to a shortage of the only yellow fever vaccine licensed in the United States; now, that shortage is expected to lead to a complete depletion of available vaccine by mid-2017.
The CDC offers insight into why a rare exception to the general recommendation of either brand of MenB vaccine had been made for the Rutgers outbreak in 2016.

On World Malaria Day, the world focuses on how to eliminate malaria once and for all.

Using statistical mapping strategies, UCLA researchers have found that the WHO and UNAIDS strategy to eliminate HIV in sub-Saharan Africa is not feasible because it doesn’t consider several important factors.
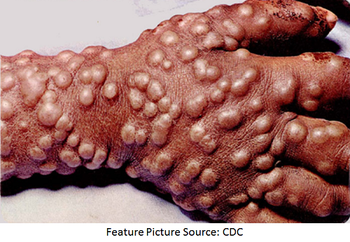
Although the eradication of smallpox was declared by the World Health Assembly in 1980, the deadly disease might make a comeback. The question is, will we be prepared for it?
The FoodNet report in the CDC’s most recent MMWR provides insight on food-borne illnesses in 2016.
A new treatment for antibiotic-resistant bacteria may reduce effects of chronic infections, lessen the days spent in hospitals, and reduce the use of antibiotics.
A new mathematical model developed by Yale School of Public Health estimates that vaccines used in tandem with interventions can potentially avert millions of HIV cases in the upcoming years.

Each year, on April 18th, we recognize the importance of HIV testing and status awareness as well as prevention and treatment efforts among transgender individuals, a population particularly at risk for the virus.