
New research reveals that women who test positive for COVID-19 at the time they give birth pass along antibodies in breast milk, protecting their newborns from infection
Laurie Saloman is a seasoned medical journalist who has written extensively about HIV, influenza, Zika, Covid-19, cancer, endocrine disorders, mental illness, and other infectious and non-infectious diseases. Her work has appeared in Contagion, The American Journal of Managed Care, Pfizer’s Breakthroughs.com, Health After 50, and the journal of the Emergency Nurses Association, among others. A member of the Association of Health Care Journalists and the American Society of Journalists and Authors, Laurie lives in New Jersey with her family. You can reach her on Twitter: @LaurieSaloman

New research reveals that women who test positive for COVID-19 at the time they give birth pass along antibodies in breast milk, protecting their newborns from infection
COVID-19 testing has been an integral part of our country’s strategy to limit disease transmission. Here’s the latest information on types of tests, when they’re appropriate to use, and what they realistically can and cannot do to curb infection.

The federal agency and infectious disease organization have teamed up to offer a wealth of resources for health care professionals on the frontlines of treating the virus.
The National Foundation for Infectious Diseases (NFID) recently sponsored a media briefing addressing the risks of contracting influenza and pneumococcal disease in the midst of a still-flourishing COVID-19 pandemic.

Parentless youth living on the streets had the highest rates of HIV and death, but extended-family living situations were not necessarily better than institutional care.

As school districts nationwide begin the fall semester in person, questions about keeping children and staff safe as the delta variant romps across the country consume parents, pediatricians, and administrators.
Infection with hepatitis B (HBV) can be challenging. What will patients accept in exchange for the chance of a functional care?

Recent breakthrough infections have experts looking closely at the true risks of the COVID-19 delta variant and how we can protect ourselves.

A recent press briefing by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) addressed the need to have new antibiotics in the pipeline to answer the rising challenge of drug resistance.
Brain tissue in people who died of SARS-CoV-2 look suspiciously like that of people with various forms of dementia and other neurocognitive conditions.
Because the number of children hospitalized with COVID-19 is so low, facilities should ensure clinical data is easily available and shared across healthcare platforms.

EUAs can enable people to get immediate access to preventive therapy or treatment, but is it always worth aiming for full approval?

The guidelines were welcomed by some, but infectious disease providers say caution is needed moving forward.

The success of the US effort to tamp down the virus with testing and vaccination cannot blind us to the situation in the rest of the world.

With its mRNA COVID-19 vaccine authorized, the company is employing the technology to take aim at a variety of pathogens.
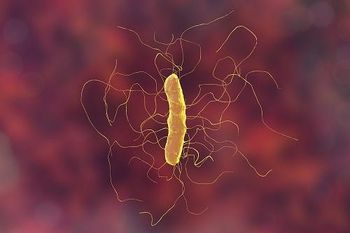
The discovery of C diff’s ability to harness heme to shield itself from the body’s immune responses hopefully brings a new dimension to the fight against the damaging pathogen.

The Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) discusses some of the new treatments show measurable impact on severe disease and death.

Getting kids back in classrooms is crucial, and it can be done with planning and forethought.

As more people contract and recover from COVID-19, a small percentage suffer from lingering or even new symptoms for months. Post COVID clinics aim to address the causes and provide relief.

Quality face masks remain an important part of our fight against the virus, as most people are still unvaccinated. New virus variants may mean extended mask wearing.
Roughly half the US population is now eligible to get a COVID-19 vaccine, according to health guidelines, but supply cannot keep up with demand.
Authorization for a COVID-19 vaccine in the US appears imminent, bringing with it a host of concerns including the speed of development, inclusivity of clinical trials, safety of mRNA technology, and how to raise levels of trust in vulnerable populations.

Initial high hopes for third vaccine available to the public, in addition to Pfizer and Moderna’s versions, are tempered as further data is sought.

HIV care has made leaps and bounds over the past few years. New guidance for primary care physicians addresses these changes and acknowledges the diversity and complexity of individuals with HIV.

The country moves into a difficult phase of the pandemic as fall slides into winter with no national mandates and no vaccine.
Aggressive sanitation measures in operating rooms means more time between surgeries. If anesthetizing patients is not an aerosol risk, could these extra cleaning measures be skipped to save time and ease patient backlog?
Many unknowns remain as the scientific community focuses on its goal of issuing a vaccine for COVID-19.

When drug resistance means ART options are exhausted, HIV patients need newer choices. A new study shows that novel prodrug fostemsavir is an effective alternative.
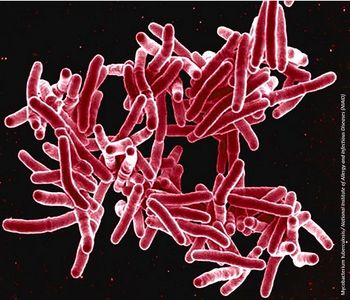
Relying solely on blood tests means clinicians may miss cases of potentially deadly M tuberculosis—and waiting days to treat suspected cases could prove fatal.

The US government has ambitious goals to expand the number of people tested and treated for HIV in the coming years. A new study details the best interventions to make the biggest difference for the most people.