
Kirk Hevener, PharmD, PhD, assistant professor of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences at Idaho State University, College of Pharmacy, discusses the advantages of narrow spectrum antibiotics.

Kirk Hevener, PharmD, PhD, assistant professor of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences at Idaho State University, College of Pharmacy, discusses the advantages of narrow spectrum antibiotics.

Kirk Hevener, PharmD, PhD, assistant professor of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences at Idaho State University, College of Pharmacy, explains how clinicians can identify pathogenic organisms to determine which narrow spectrum antibiotic to use for treatment.

For the first time, the National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System includes whole genome sequencing data of bacteria from individuals with antibiotic-resistant Salmonella infections.

Craig Rubens, MD, PhD, co-founder and executive director of GAPPS at Seattle Children’s Hospital, discusses exciting advancements being made in improving the treatment of pregnant women and babies.

Craig Rubens, MD, PhD, co-founder and executive director of GAPPS at Seattle Children’s Hospital, discusses the need for more research on neonatal infections.
A group of German researchers recently published an investigative study on the source of drug-resistant pathogens in hospitals and treatment centers.
Studies demonstrate the effect of antibiotics on patients with hemolytic uremic syndrome and unique therapeutic challenges.
In the battle against drug-resistant pathogens, genetic research holds promising answers to our toughest threats. A new study shows that the best tool for treating Clostridium difficile infections could be within the genome of the bacteria itself.

Emily Heil, PharmD, BCPS-AQ ID, assistant professor at the University of Maryland School of Pharmacy, discusses how a new partnership between pharmacists and veterinarians will impact antimicrobial resistance.

New research from the Imperial College of London now offers a promising novel approach in the fight against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and their findings are decidedly salty.

John Mohr, PharmD, president and founder of Medical Affairs Strategic Solutions, LLC, outlines factors that contribute to antimicrobial resistance and strategies to combat this threat.

As the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria leads to higher rates of life-threatening infections from pathogens such Clostridium difficile and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), researchers are increasingly looking to probiotic treatment as an important part of fighting infections.
A new study conducted by the University of Maryland shows that the majority of the people who think that they are allergic to penicillin are not; increased access to testing within hospitals can improve treatment.

Emily Heil, PharmD, BCPS-AQ ID, assistant professor at the University of Maryland School of Pharmacy, discusses how pharmacists can help decrease antibiotic use in agriculture animals.
Wound care is challenging in today’s era of antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections, but healthcare practitioners treating infectious wounds have some tiny allies.

Emily Heil, PharmD, BCPS-AQ ID, assistant professor at the University of Maryland School of Pharmacy, explains how the FDA Guidance 213 and the Veterinary Feed Directive will change the use of antibiotics for growth promotion purposes in the United States.

While antibiotics serve a meaningful purpose in treating infections, appropriate use of these agents is needed in order to minimize adverse events.
Researchers from the Oxford University Clinical Research Unit have found that a 5-minute CRP test can assist in the ongoing fight against antibiotic resistance by reducing antibiotic misuse for respiratory infections.

Thomas Sandora, MD, MPH, hospital epidemiologist at Boston Children’s Hospital, discusses some up and coming pediatric healthcare associated infection prevention strategies.
A new treatment has been discovered by researchers at The University of Sheffield that can be used to fight antibiotic-resistant bacteria, such as MRSA, by using proteins called tetraspanins.
In a recent study, researchers identified three key factors that increase the risk for patient-to-patient transmission of carbapenemase-producing carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriacecae (CP-CRE).

The IDSA and ATS have updated the Clinical Practice Guidelines for HAP & VAP for the first time since 2005 to recommend that each hospital generate antibiograms and reduce the use of antibiotics in treatment regiments.

Researchers have made an important breakthrough in efforts to develop a test to help clinicians determine whether a patient has a microbial infection or sterile trauma, a new study shows.
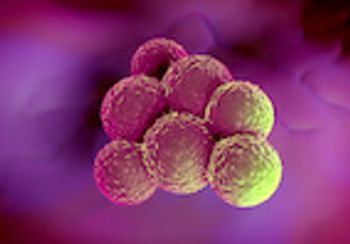
A new study conducted by Andreas Peschel, PhD, and colleagues at the University of Tuebingen in Germany, has shown that lugdunin, a bacteria naturally produced by the human body, can be used as an antibiotic that can eliminate Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).

The belief that patients may face increased risks of complications following reduced antibiotic use after experiencing self-limiting respiratory tract infections (RTIs) may not be well-founded.