There are several diseases that pose a high risk in the dental healthcare setting; a review article highlights ones that are preventable by immunization.

There are several diseases that pose a high risk in the dental healthcare setting; a review article highlights ones that are preventable by immunization.

This week’s Public Health News Watch focuses on news that the new American Healthcare Act (AHCA), recently approved by the House, reportedly will not cover those with preexisting conditions.

A former Food and Drug Administration (FDA) deputy commissioner, Scott Gottlieb, MD, was confirmed by the Senate by a vote of 57-42 to be the next commissioner of the FDA.

In a recent webinar, the CDC and the HHS’s National Vaccine Program Office discussed global efforts being made to eradicate polio, measles, and rubella in the United States.
Health officials in Minnesota have linked the state’s biggest measles outbreak in decades to anti-vaccination efforts centered on one immigrant community.

There has been an increase in STDs seen in US emergency departments, a setting that proves to be less than optimal for providing STD care.

In case you missed them, here are last month's Top 5 news articles from Contagion®.

In case you missed them, here are our top 5 articles for the week of April 30, 2017.

The CDC just released updated testing recommendations for asymptomatic pregnant women with possible exposure to the Zika virus.

Today, May 5th, is Hand Hygiene Day, a day that reminds healthcare workers, visitors, and policy makers alike, that frequent handwashing can be used to fight the growing threat of antibiotic resistance, and ultimately, save millions of lives.
Epidemic Intelligence Service officers from the Centers for Diseases Control and Prevention recently released research revealing that cases of Q Fever may be underreported in the United States.

The results of a recent study reveal a high prevalence of colonization of multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria in nursing home residents, emphasizing the need to enhance infection control and prevention in these institutions.

Despite the best intentions, hospital accreditation surveys have become a breeding ground for low expectations.
The rates of primary and secondary syphilis in the United States have increased by 19% from 2014 to 2015, and the CDC notes that preliminary data suggests that there was a “similar rate of increase in the first 6 months of 2016.”

In certain locations in China, it’s now as easy to purchase an HIV test kit as it is a snack. But are rapid HIV self-tests the next big thing, or a big bust?

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) just released new guidelines on community-based pandemic prevention.

A shift in materials used in developing shaving brushes in the United States and England during WWI may have resulted in an increase in anthrax cases.

This week’s Public Health News Watch captures the all-too-common story of TJ, an American who brings his ailing mother across the border into Mexico for healthcare that he is otherwise unable to afford at home.
In a collaborative effort, scientists from Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and George Washington University have found that defective HIV proviruses can complicate monitoring the true viral load within patients and distract the immune system from attacking the functional virus.
Researchers may have discovered a way to prevent Zika, Dengue and Chikungunya viruses from replicating in human cells.

Here’s how we are missing the bigger picture in the Sage chlorhexidine wipes debacle.

A study using the Taiwan National Health Insurance research database investigated the efficacy of statin use on preventing the development of liver decompensation in patients with different cirrhosis etiologies.
Many women who are infected with hepatitis B (HBV) during pregnancy go untreated, leaving their offspring at risk for a chronic HBV infection.

The NIH has developed a platform called SHERLOCK, capable of quickly detecting small amounts of nucleic acid sequences—and it’s cheap.
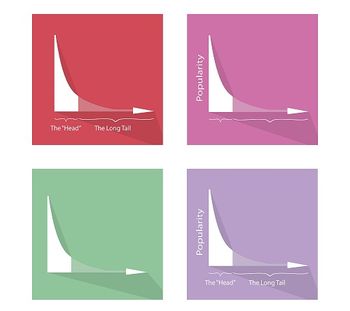
Could a power law be used to predict food-borne outbreaks and thus help public health agencies better prepare?
Researchers from Rutgers University have identified a group of compounds that may stop tuberculosis from becoming drug-resistant.

Researchers from Zhejiang University in China take a closer look at how the incidence of different infectious diseases have changed in the first decade after the SARS outbreak.

In case you missed them, here are our top 5 articles for the week of April 23, 2017.

Not much is known about how the genetic makeup of the virus impacts infected individuals, at least, until now.

We are adding 2 more reasons to the 7 reasons we are more at risk than ever for a global pandemic.