
The results of an election poll question on conducting an effectiveness trial using genetically modified mosquitoes to combat the Zika virus revealed mixed feelings among Florida natives.

The results of an election poll question on conducting an effectiveness trial using genetically modified mosquitoes to combat the Zika virus revealed mixed feelings among Florida natives.

A team of researchers from Tufts University and the University of Maryland have discovered a way to predict cholera outbreaks using satellite data from coastal waterways.

Human trials are currently underway for a potential candidate vaccine for the Zika virus and a novel treatment approach has shown promise in mice.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has issued Zika guidance designed to bolster infection control and limit exposure to clinicians and other caregivers.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has identified 18 cases of new swine flu viruses in Ohio and Michigan state fair attendees, highlighting the need for precaution when handling pigs.
Despite the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's recommendation that the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine be routinely given to adolescents and young adults, administration rates for the vaccine are still low.

As travel-related Zika virus numbers continue to grow, New York City bolsters its Zika Preparedness and Response Action Plan.

Students from the University of Sheffield in the United Kingdom have developed a new diagnostic tool which promises a novel way to detect bacterial infections and prevent the inappropriate use of antibiotics for viral infections.

Studies find that a mutated gene that encodes the Ebola virus glycoprotein increased its ability to infect human and primate cells in the 2013-2106 West African epidemic.

A new study by Public Health England researchers finds that disinfectants used against Klebsiella pneumoniae may be helping the pathogen develop new antibiotic resistance.

Weight gain during tuberculosis treatment is an important marker of the restoration of health.
A new study from United Kingdom researchers finds that nearly one-quarter of the global population is infected with latent tuberculosis (TB), a finding that exposes the challenges ahead for the World Health Organization’s End TB Strategy.

The US Food and Drug Administration has approved Selzentry for use in pediatric patients two years of age or older, who weigh at least 10 kg.
Researchers have noted four other features unusual for babies born with congenital infections due to Zika virus infection.
Researchers in the United States and South Korea recently studied the use of an experimental nanoparticle treatment that acts as a decoy to stop and kill the influenza virus.

Researchers at University of Chicago Medicine have created an antibiotic stewardship training program for internal medicine residents that incorporates social media platforms, offering a technological tool for a growing health problem.

There is a stigma that incoming refugees pose a health risk to European communities. In order to assess the risk of possible outbreaks and jump-start prevention, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) recommends implementing a multi-step Syndromic Surveillance system.
Drug maker Melinta has submitted their new antibiotic Baxdela for review by the US Food and Drug Administration, with the hopes that it will bring a new treatment option for people suffering from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).

The World Health Organization (WHO) has released their Global Tuberculosis Report for 2016, emphasizing that today’s global actions and investments are falling far short of what is needed to stop the worldwide tuberculosis (TB) epidemic.

A new study found that Lyme disease cases in the Western United States could rise as a result of weather changes caused by El Niño.

Rotary International teamed up with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to hold a briefing on the eradication of polo despite past setbacks.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention teamed up with Rotary International to host a live media briefing to highlight progress in the global fight against polio.

Speakers at the annual meeting of the Infectious Diseases Society of America discussed infectious disease epidemics across the globe.
A study using different criteria for urine testing than those outlined by the current Infectious Disease Society of America (IDSA) guidelines, has proven to cut down on the testing of urine samples and inappropriate use of antimicrobials.
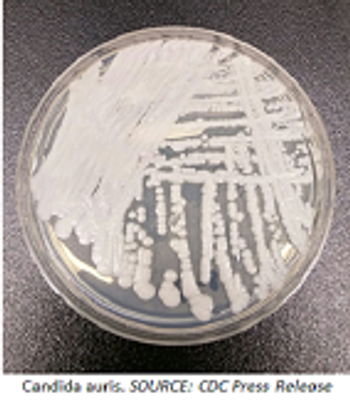
Seven cases of Candida auris have been identified within the United States, according to a report in the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.

At the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2016 STD Prevention Conference, lead authors of several studies discussed how researchers are taking novel approaches to sexually-transmitted infection screening.

The first case of Mayaro virus has been reported in Haiti.
Rapid syphilis screening tests can be useful in community-based facilities, according to the results of five studies presented in a mini-plenary on September 22 at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2016 STD Prevention Conference in Atlanta, Georgia.
At the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's 2016 STD Prevention Conference, researchers discussed three novel prevention strategies for HIV, other STIs, and unintended pregnancies.

With new US Food and Drug Administration rules on antibiotics in agriculture taking effect at the start of 2017, challenges remain when it comes to the reduction of antimicrobial use in livestock.