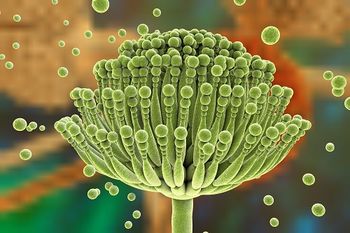
The most common presentation for pediatric invasive aspergillosis patients was a pulmonary infection.

The most common presentation for pediatric invasive aspergillosis patients was a pulmonary infection.
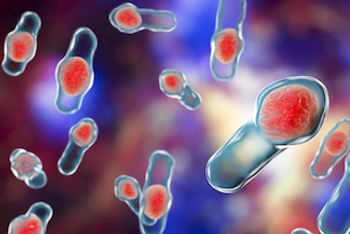
RBX2660, a microbiota-based drug, was safe and efficacious for preventing recurrent C diff infection with clinical durability to 24-months after treatment, independent of age or sex.

The FDA has approved a pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) indication for Descovy (emtricitabine 200 mg and tenofovir alafenamide 25 mg tablets; F/TAF).

The phase 1/2 trial of a prime-boost vaccine to prevent chronic HCV infection was completed in an at-risk population of in people who inject drugs.
A team of investigators set out to evaluate whether TORC1 inhibitor RTB101 could increase antiviral gene expression and decrease the incidence of RTIs in older adults.

The analysis of the survey responses found a statistically significant association in denial of the biomedical discourse and dissatisfaction or mistrust of the Ebola response as indicators of social resistance.
In the Opening Plenary of IDWeek 2019, 2 bright lights in infectious disease research spoke on the sea-change brought by genomics to biomedicine and the response to infectious disease outbreaks.

Adverse events led to premature discontinuation in 14% (21) of ISA patients and 53% (85) of patients receiving VOR prophylaxis.

A presentation at IDWeek 2019 gives hope for the rapid identification and isolation of extensively drug-resistant organisms.

In a new study, a team of investigators set out to determine if oritavancin use can reduce the sequelae from ABSSSI treatment failures, while also preventing infection recurrences and improving patient outcomes.

An oral abstract session on public health covers the full gamut of new outbreaks, challenges from around the world.
When it came to infection prevention measures, 5 of the 9 Orange County facilities with C auris displayed hand hygiene adherence < 50%, 3 had limited access to alcohol-based hand rubs, and < 60% of assessed high-touch surfaces were clean.

Awareness for HIV PrEP was high for all racial and ethnic groups, but black and Hispanic MSM discussed its use with physicians less often than white counterparts.
Investigators assessed 90-day all-cause mortality between patients with Candida bloodstream infections who did and did not receive an infectious disease consultation.

A total of 543 human cases of West Nile virus disease have been reported to the CDC in 46 states and the District of Columbia as of September 24, 2019.
In part 2 of our Q&A with Fair, we talk about the challenges ahead in the fight against Ebola in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

As September draws to a close, the Contagion® editorial team is recapping the trends and top infectious disease news of the month.
The NFID released data revealing that only 52% of adults in the United States plan to get vaccinated against the flu this season.

Pharmacists could help improve antibiotic treatment of pediatric patients, particularly in facilities that don’t regularly treat children, according to a recent review article.
STI rates have been growing significantly in the United States and around the world. To fix the problem, we need a renewed focus on this therapeutic area, according to top public health officials.

Here is a look at infectious disease-related US Food and Drug Administration news from the week of September 22, 2019.

We’ve rounded up a list of important US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and US Department of Agriculture (USDA) recalls from this past week.

Stay up-to-date on the latest infectious disease news by checking out our top 5 articles of the week.

Use of high-risk antibiotics is linked to C diff infections, but the class of antibiotics with the strongest link has changed over time underscoring the need for ongoing assessment.

The Contagion® editorial staff will be providing exclusive written and video coverage from IDWeek 2019.

According to results from the Rwanda Population-based HIV Impact Assessment (RPHIA), 76% of all adults living with HIV in Rwanda have achieved viral load suppression.

The FDA has approved treatment for adults and children with all genotypes of hepatitis C and compensated cirrhosis that shortens duration of treatment to 8 weeks.

A hospital sheds light on how dogs can help identify C diff contamination.
Investigators of a new study assessed data from a 14-year-period and found that the prevalence ratio for heart infections related to drug abused jumped from 8% to 16%.

Investigators used national electronic health record data to determine the proportion of American adults who have been tested for HIV.