
A recent study suggests that patient-to-patient transmission of norovirus is potentially overestimated within clinical settings.

A recent study suggests that patient-to-patient transmission of norovirus is potentially overestimated within clinical settings.

In a recent study, researchers investigated the treatment and prevention of HIV within trauma-informed care.

A new Zika virus case cluster has emerged in Miami, according to the Florida Department of Health.

In a recent study in mice, researchers used a synthetic peptide to disrupt the bacterial stress response that causes abscess formation in skin infections with drug-resistant bacteria.
Researchers have predicted that less than 10% of Escherichia coli 0157:H7 strains are likely to have the potential to cause human disease.

A team of researchers at the University of California has found that veterans infected with both hepatitis C and human immunodeficiency virus sought treatment more often than those infected with just one of the viruses.

The US Food and Drug Administration has approved its quadrivalent formulation of the Flublok influenza vaccine.
As hospitals continue to search for new ways to limit their number of patients acquiring Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) infections, a new study shows promise in the use of ultraviolet light technology for ridding patient rooms of highly resistant C. difficile spores.
Although they’re often life-saving, all hospital operations come with the risk of surgical site infections. C-section are no different, researchers, in a recent medical trial, have found a way to slash post-operative infection rates with the use of an extra antibiotic.

With the use of antibiotics remaining high and steady in American hospitals and healthcare facilities, new rules on infection prevention and antibiotic use are set to bring changes to thousands of nursing homes, nationwide.
In the 10 years since the human papilloma virus (HPV) vaccine first became available, a series of new studies have come out showing just how effective the virus really is and how HPV vaccination rates can be improved in adolescents.

Researchers in a recent study investigated how mixed messages delivered by vaccine manufacturers may prevent women from receiving the safe and effective influenza vaccine during pregnancy.
The recent spate of hand, foot, and mouth disease outbreaks continue to vex East Coast schools and universities, as health officials are reporting new and continuing clusters of the virus.

The National Institutes of Health have granted $3 million to researchers at the University of Missouri Bond Life Sciences Center to study hepatitis B and develop new, effective treatment options.
In addition to licensed pharmacists, student pharmacists can play an important role in helping more Americans get vaccinated by participating in immunization campaigns throughout their communities.

A recent study details a case of a man with a confirmed Zika virus infection accompanied by papular descending eruption, petechiae on his palate, and hyperemic sclerae.

Researchers recently studied the way people expressed their pro-vaccination and anti-vaccination opinions on Facebook to understand how people discuss and spread these views.

In response to the serious global concern of growing drug-resistant “superbugs,” thirteen leading pharmaceutical companies have pledged to clean up pollution from company factories and prevent overuse of antibiotics.

A case of hepatitis A in a bakery employee at a Shop ‘N Kart located in Washington state has been confirmed by the Lewis County Public Health & Social Services Department.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has awarded scientists combating antibiotic resistance with more than $14 million in funding for new research and innovations by universities, nonprofits, and the business community.

The Joint Commission considers hand hygiene the most important intervention for preventing healthcare-associated infections, which are responsible for 75,000 deaths annually.
Consumer Reports recently evaluated more than 3,100 hospitals in the United States and found that about a third of them received a low rating for controlling infections from Clostridium difficile.

Following the recent United Nations General Assembly meeting to discuss the growing global threat of antimicrobial resistance, health experts are highlighting the role vaccines can play in preventing dangerous infections.

To assess factors associated with the likelihood that healthcare providers will accept seasonal influenza vaccine policy changes, Nova Scotia researchers examined the roles that their knowledge and attitude play in the matter.

Pharmacists are critical to expanding access to pandemic vaccination. However, little is known about the relationships and planning activities between public health programs and pharmacies.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recently met to establish new guidelines for the Southern Hemisphere’s 2017 influenza virus vaccine.

Researchers have now identified virologic evidence of Zika virus in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome, showing that the onset of the neurologic disorder can parallel the onset of systemic manifestations of the mosquito-borne infection.

Recently, WHO published a paper outlining their decade-long initiative to increase access and regulate production of the influenza vaccine.

As antibiotic-resistant bacteria continue to endanger public health, greater attention from health officials and new US federal funding aimed at fighting superbugs, signal a new urgency in this battle.
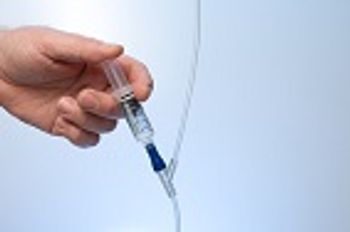
A voluntary recall has been initiated by Nurse Assist. All unexpired lots of IV Flush Syringes have been potentially linked to bloodstream infections from Burholderia cepacia.