
Novavax updates its COVID-19 vaccine, locally acquired malaria is reported in Maryland, deadly listeria outbreak is linked to milkshakes, and vibriosis in the northeast.
John Parkinson is the assistant managing editor for Contagion. Prior to joining MJH Life Sciences in 2020, he has covered a variety of fields and markets including diabetes, oncology, ophthalmology, IT, travel, and local news. You can email him at jparkinson@mjhlifesciences.com.

Novavax updates its COVID-19 vaccine, locally acquired malaria is reported in Maryland, deadly listeria outbreak is linked to milkshakes, and vibriosis in the northeast.

Poll conducted by University of Michigan had a majority of people wanting to know more about it.

This week: the FDA accepts NDA for investigational antibiotic; mRNA COVID-19 vaccines update protections; counseling families on nirsevimab; and how antibiotic actions on gut microbes of patients might affect the microbiome of housemates.

The strain, Eris (EG5), is from the Omicron lineage, and the expectations are the newest vaccines will protect against it, and other variants from the same family.
With the FDA approval of nirsevimab-alip (Beyfortus), which is indicated for prevention of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in infants, clinicians will need to have important conversations with families around this monoclonal antibody, beginning this fall.

The Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) action date is scheduled for the first quarter of 2024.

The agency says additional time is needed to decide upon a phase 4 program.

This week's news included managing infants with RSV, how COVID-19 surveillance has evolved, and looking at changing criteria for initial and sustained response to antibiotic treatment for C diff.

A clinician offers a glimpse of what it is like to treat infants with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). And with the recent FDA approval of nirsevimab, how that will likely benefit families and the youngest population.

From news about RSV to vaccines to an investigational hepatitis therapy, this week's Infectious Disease Update has something for everyone.

A new study confirms this form of surveillance to collect metrics for SARS-CoV-2 to understand infection prevalence on a bigger scale.

The federal agency’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) also added the recently approved therapeutic to the Vaccines for Children program.

A new study demonstrated Moderna having a greater efficacy and slightly less adverse event profile in this patient population vs the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine.
The twice-yearly injectable shown to be beneficial in conjunction with an optimized background regimen.
A new study being presented at the ongoing IAS conference showed that people with HIV found the injectable therapy, Cabotegravir plus long-acting Rilpivirine (Cabenuva) is more conducive to today’s lifestyles, reduced stigma, and improved adherence.

New study demonstrates benefit of adhering to treatment regimen and also calls for simplifying viral testing in other parts of the world where updated panels technology may not be available.

Coverage this week included how COVID-19 vaccines in patients with cancer fared; analysis of non-COVID-19 adult vaccines; a company is developing a platform to enable engineering of the first recombinant human polyclonal antibody therapies with the goal of creating a functional cure for hepatitis b; and how a hospital modified testing for C difficile.
New report published this week shows the decrease over the last 2 reportable years.
This conference is addressing antimicrobial resistance (AMR) from different perspectives and look at strategies to reduce this global health problem.

The Gates Medical Research Institute (MRI) is conducting a study looking at the effect of bifidobacterium longum subspecies infantis (B infantis) as a supplement.
A company is developing a platform to enable engineering of the first recombinant human polyclonal antibody therapies with the goal of creating a functional cure for hepatitis b (HBV).

The monoclonal antibody is indicated for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in newborns, infants, and young children.
Lumen Bioscience's C diff therapy, LMN-201, combines four therapeutic proteins that act synergistically to neutralize both the C difficile bacterium and the toxin that causes its virulence directly in the patient’s gastrointestinal tract.

Although there are certain specialties in medicine that seemed to benefit from this newer former of clinical visits, infectious disease and others did not.

The Peggy Lillis Foundation (PLF) for C diff Education & Advocacy has been busy this year in Washington DC with an FDA event and their Summit and Advocacy Day with lawmakers.
The vaccine candidate, M72/AS01E (M72), could potentially become the first new vaccine to help prevent pulmonary TB, a form of active TB, in more than 100 years.
Although the literature and science may change, hanging onto beliefs about therapeutics is a tradition passed down from instructors to learners. A change in this paradigm may be warranted.
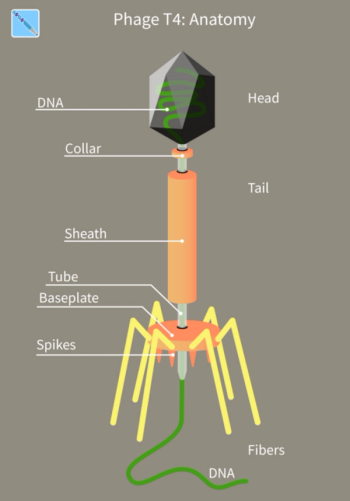
This long-time, understudied virus, can fight bacterial infections and may be poised to become an important treatment option in western medicine.
This rare side effect was witnessed in a small number of people post-vaccine administration.
This variant, which is an ancestor of Omicron, is an emerging variant that is being seen most frequently in Utah, California, and New York State.