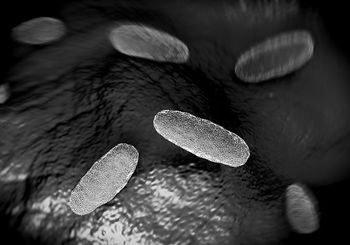
Researchers in China have discovered a troubling case of the presence of a variant of the multidrug-resistant gene MCR-1 in a common strain of Salmonella in a healthy patient.

Researchers in China have discovered a troubling case of the presence of a variant of the multidrug-resistant gene MCR-1 in a common strain of Salmonella in a healthy patient.
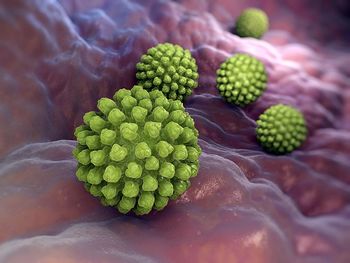
Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health researchers report that a new rotavirus vaccine was found to be 66.7% effective.
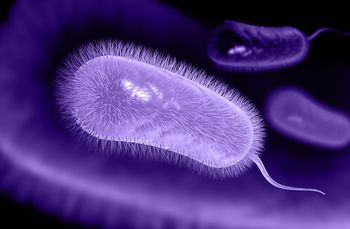
According to the team’s research, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, H. pylori uses a unique biosynthetic pathway to synthesize vitamin K2, which is essential to many vital chemical reactions that keep the organism alive.

This traditional St. Patrick’s Day food could cause severe illness if not prepared correctly.
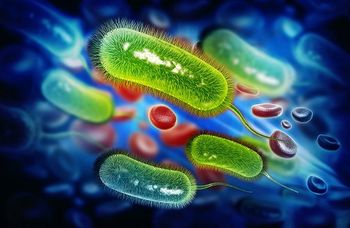
In a new study, researchers have discovered that Helicobacter pylori, the presence of which is a risk factor for stomach cancer, uses multiple acid sensors to control colonization of the stomach.

The results of a new study show that taking antibiotics for traveler’s diarrhea could increase the risk of acquiring an extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (ESBL) infection.
A new study from the United Kingdom highlights the importance of antibiotic restriction in the reduction of hospital-acquired C. difficile infections.

Through environmental cleaning and student-oriented education, Humber College in Toronto, Canada, has managed to quell a nasty outbreak of norovirus.
The study is the first “head-to-head” comparison of fecal transplants and antibiotic treatments, which are presently the “standard” of care.

A new study has provided more evidence to show that certain heartburn medications may make individuals more susceptible to gastrointestinal infections.

UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon offers a public apology for a role in Haiti’s devastating cholera outbreak.

A recent study lead by researchers from the University of Freiburg analyzed the occurrence of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli in European hospitals.

A study from University of Washington researchers uncovers how hospital laundry facilities may harbor dangerous Clostridium difficile spores, creating a potential community source for the bacterial pathogen.

Doctors at the Children’s Hospital Colorado have published their research on a new approach to antibiotic stewardship, with promising reductions in antibiotic use and rates of Clostridium difficile.
Consumer Reports recently evaluated more than 3,100 hospitals in the United States and found that about a third of them received a low rating for controlling infections from Clostridium difficile.

According to newly published research, high levels of zinc changes microbiota in the gut decreasing resistance to infections from Clostridium difficile.
As so-called “superbug” bacteria continue to develop new ways of resisting antibiotics, scientists are on the search for new and alternative treatments. Promising news from a recent study is now showing that we may be able to battle the most virulent strains of the Clostridium difficile bacteria with a class of drugs already on the market.

A team of scientists from Rutgers University and Columbia University recently discovered a new strain of Escherichia coli (E. coli) believed to be the first in the United States with resistance to two kinds of antibiotics considered to be last resort weapons to prevent dangerous infections.

Based on 2D and 3D in vitro models, treatment with mycophenolic acid confers very high levels of drug resistant rotavirus viral replication suppression and may therefore be a useful immunosuppressive agent for preventing rotavirus infection in transplantation patients.
With schools and colleges back in session, so too are contagious illnesses such as hand, foot, and mouth disease, which has recently broken out in two New Jersey high schools and a Florida university.

The CDC recently announced that their investigators have identified a strain of Escherichia coli with the colistin-resistance gene mcr-1 in a Connecticut child, in what is now the fourth patient in the United States to test positive for an isolate with mcr-1.

The FDA has granted biopharmaceutical company, MGB Biopharma’s lead candidate, MGB-BP-3, Qualified Infectious Disease Product (QIDP) designation for the treatment of Clostridium difficile-associated Diarrhea.

Dubbed 'the perfect pathogen' by researchers, norovirus possesses all the markers of an ideal infectious agent.

Utah Department of Health officials are investigating a cluster of illnesses associated with raw milk from Heber Valley Milk in Wasatch County.
In the United States, Shigellosis causes approximately 500,000 illnesses annually and resistance to drugs to treat the infection, such as ciprofloxacin, ceftriaxone, and azithromycin, is emerging.