
After plaguing much of Brazil and the Caribbean since late 2014, the Zika virus “crisis”—such as it is—seems to have migrated eastward—far eastward.

After plaguing much of Brazil and the Caribbean since late 2014, the Zika virus “crisis”—such as it is—seems to have migrated eastward—far eastward.
Researchers at Central Michigan University have found that proteins in the saliva of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes bind to Dengue virus and inhibit disease transmission to human cells and mice.

When researchers recently discovered a strain of Escherichia coli resistant to the final resort antibiotics colistin and carbapenem in the United States, it marked an increasing pattern of pan–drug-resistant bacteria appearing worldwide. A new report from France, though, may indicate that identifying and isolating these deadly superbug strains may help us control their spread.

On September 21, 2016, delegates at the 71st meeting of the United Nations (UN) General Assembly gathered to discuss the shared danger of antimicrobial resistance, signaling the global scale of this urgent public health crisis while pledging to collectively tackle the problem of superbugs.

Researchers are gathering more evidence of the exact effects of Zika virus infection on eye health.

Bartonella henselae, the bacterium that causes Cat-Scratch Disease, is carried in the claws and mouth of infected cats and spreads through bites, scratches, or licks to an open wound.

With so much of the world focusing on Zika virus in the Americas and Southeast Asia, it’s easy to forget that there are other mosquito-borne viruses causing serious public health problems globally—namely, Dengue fever and Chikungunya.

The World Health Organization credits contraception with preventing pregnancy-related health risks in women, reducing adolescent pregnancies, and lowering infant mortality rates. What researchers are now discovering is that hormonal contraceptives containing progesterone may also protect women against influenza infections and repair lung damage caused by inflammation.

With more than 90 locally transmitted cases of Zika virus infection confirmed in Florida, and states from the southeast to the Midwest fearing similar outbreaks, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has made bolstering its network of approved testing laboratories for the virus a priority.

Health officials around the world agree that our one of the best steps to reducing the problem of antimicrobial resistance is scaling back on unnecessary overprescribing of these medications. As doctors in many countries work to implement these efforts, a new report out of the United Kingdom shows some progress in the fight against drug-resistant “superbugs,” along with plenty of work to still be done.
As so-called “superbug” bacteria continue to develop new ways of resisting antibiotics, scientists are on the search for new and alternative treatments. Promising news from a recent study is now showing that we may be able to battle the most virulent strains of the Clostridium difficile bacteria with a class of drugs already on the market.

Mumps outbreaks have recently been reported within the school systems of three states: Arkansas, Oklahoma, and New York.

The number of illnesses, hospitalizations, and deaths caused by Salmonella have been steadily rising each year, and now findings from new report on nontyphoidal Salmonella enterica show that some 20% of blood isolates of the bacteria have antibiotic resistance.

Health officials in Singapore have reported a significant increase in the incidence of Zika virus infection in the country in recent weeks.

As health experts around the world take on the problem of antimicrobial resistance and overuse of antibiotics in humans as a prime cause, world leaders are reminding us of another contributor to this global health issue: our farming system.
Researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill have found out how hepatitis A causes acute liver injury.

On the same day officials in Florida declared the Wynwood section of Miami, “ground zero” for the Zika virus in the state, no longer “active” for local transmission, officials from a state halfway across the country expressed concerns over a “pending disaster” involving the mosquito-borne infection.

The United Kingdom Food Standards Agency has published a guidance for health care and social service organizations who care for vulnerable populations at greater risk for contracting listeriosis and other food-borne diseases.

A team of scientists from Rutgers University and Columbia University recently discovered a new strain of Escherichia coli (E. coli) believed to be the first in the United States with resistance to two kinds of antibiotics considered to be last resort weapons to prevent dangerous infections.
We hear a lot about influenza types A and B every year when flu season approaches, and occasionally about the less severe type C. Now researchers have identified a newly recognized form of the virus—influenza D.

In Quebec, Atlantic Shellfish Products Inc. is recalling oysters from the marketplace after possible Salmonella contamination.

In a collaborative effort, researchers have discovered what they refer to as a “Trojan Horse” strategy that uses two developed bispecific antibodies that have proved active against all five strains of the ebolavirus.
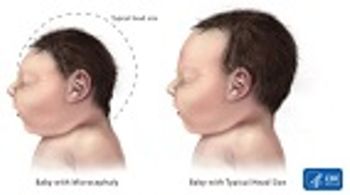
A study comparing babies born with microcephaly and closely matched, but otherwise healthy, controls has confirmed a link between the birth defect and Zika virus.

When the colistin-resistant gene, mcr-1, was first found in China in 2015, health officials around the world knew that the gene would inevitably appear in their countries. It has since been detected in other parts of Asia, Europe, and North America, including Canada, which just released a 2016 report from their Canadian Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System.
To find the next great innovation to fight the spread of drug-resistant bacteria, the National Institutes of Health has announced the launch of a new federal prize competition dubbed the Antimicrobial Resistance Diagnostic Challenge.
Hepatitis A cases have been reported throughout at least nine different US states and the number of cases continue to rise.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention may revisit its travel guidance on south Florida as soon as early next week, if there are no new cases involving local transmission of the Zika virus in the region; however, local businesses continue to be impacted.

By targeting CabA, an extracellular matrix protein essential for biofilm formation, it may be possible to reduce the incidence of food-borne illnesses caused by the potentially lethal Vibrio vulnificus marine bacterium found in biofilms on oyster shells and meat.

Using the mainstream media as the medium for their message, some of the nation’s leading physicians urged Congress to pass a “clean, bipartisan funding measure” to fight the spread of Zika, both in the United States and abroad, and to “protect pregnant women” from the complications associated with the virus.