
Shionogi’s therapy, ensitrelvir, was found to reduce and prevent these issues.

This week we covered antibiotic de-escalation, the approved fecal microbiota options for prevention of recurrent Clostridioides difficile, the CDC's recommendations for HCV testing in the pediatric populations, and examining pragmatic approaches to skin and soft tissue Infections.
At the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) meeting held last week, Barinthus Biotherapeutics announced the presentation of data from its hepatitis B clinical trials.

The proposed clinical benefits of de-escalation has contributed to its lukewarm adoption in some settings. This article looks at the challenges in measuring the impact of de-escalation, and the ongoing search for more meaningful metrics to evaluate the success of antimicrobial stewardship (AMS) programs.

Seres Therapeutics reported its financials recently including the performance of it therapy, Vowst, as well as updates on its business and one of its investigational therapies.

The investigational agent, afabicin, was developed by private company, Debiopharm, and a clinician offers some insights on the therapy in these 2 therapeutic areas.

Empirical antibiotic therapy in diabetic foot ulcer infections increases hospitalization and prolonged symptoms in patients being treated for lower limb cellulitis are common. Two recent papers examine the need for effective communication, the importance of objective findings in cellulitis management, and the benefits of culture-based antibiotic therapy in diabetic foot ulcer cases.

We’ve compiled a list of key food safety tips that you need to know in order to have a safe, bacteria-free holiday.
With the FDA approval of 2 of these products, which are indicated for recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI), a study reviewed which types of clinicians are prescribing them and the protocols in using them.

CDC recommends HCV testing in these populations as a critical step to achieving national priority of eliminating HCV.

Although the current reimbursement model makes it difficult for pharmaceutical companies to recoup their investments, a subscription model like the prospective congressional bill, the Pasteur Act, may help change that paradigm. In addition, there are international measures being carried out that may bring about changes.
The companies announced a licensing agreement on cefepime-taniborbactam.

ACON Laboratories’ Flowflex COVID-19 Antigen Home Test completed the premarket review pathway and is the first test indicated for use in children under 18.

This week read about virus testing, the dosing of one of the COVID-19 vaccines in the pediatric population, HAI grades in hospitals, and live biotherapeutic products in preventing recurrent CDI in older adults with comorbidities.

Valneva’s VLA1553 (Ixchiq) vaccine was shown to met its preliminary endpoint, with 98.9% of participants reaching protective levels of chikungunya virus neutralizing antibodies 1 month after vaccination.
Use of antiviral therapy was linked to a decreased risk of multiple cardiovascular outcomes and mortality compared to patients not using antiviral therapy.
With the addition of 2 new live biotherapeutic products, a clinician reviews the application, storage and administration techniques for them.
New data showed an approximate 60% success rate of recurrent C difficile prevention in adults with comorbid conditions including CKD and cardiac disease.
S salivarius probiotic reduces relative abundance of nasopharyngeal otopathogens but not incidence of acute otitis media in children.

The Leapfrog Group finds there were improved health care-associated infection (HAIs) rates following an earlier spike during the acute phase of the COVID-19 pandemic.

The federal agency was made aware some health care providers had administered the full single dose vial of the vaccine, which contains “notably more” volume than the 0.25 mL volume indicated for children aged 6 months to 11 years.

New phase 1b data supports further investigation into Adiso Therapeutic's prospective treatment, ADS024.
With these infections being problematic, a newer antiviral offers an alternative option for these patients.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) looked at outbreak-related deaths and found a majority of decedents had existing preexisting conditions.

This week's stories include study data on 2 RSV vaccines for seniors; an update on C diff therapies; looking at Ending the HIV Epidemic initiative; and a study on Paxlovid and Long COVID.
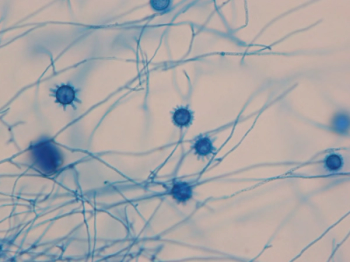
A patient with a history of lupus nephritis initially presented with right hand and arm symptoms that were attributed to a lupus flare. However, eight months later, the patient experienced increasing pain and edema in his right hand, leading to a diagnosis of Histoplasma tenosynovitis.

Drawing parallels between liver health and everyday choices, such as diet, alcohol consumption, and drug use, can help individuals take responsibility for their actions and their overall well-being.
This discussion revolves around diagnostics for viruses and best practices and challenges.

Two RSV vaccines for seniors were FDA approved this year and here is an overview of the vaccines and the study data.

Learning about these barriers is the first step to overcoming them.