Antibiotics
Latest News
Latest Videos

More News

This week, OPAT for gram-negative infections expands to outpatients amid infusion complexity and stability limits, HHS and CDC add five ACIP members days before meeting, and more.
Bordetella bronchiseptica is a rare human respiratory pathogen that can be initially confused for Bordetella pertussis, leading to potentially inadequate treatment. This article reviews the organism and recent literature on the successful treatment of B bronchiseptica.

Ryan Shields, PharmD, MS, discusses the challenges of incorporating newer antibiotics for gram-negative infections, how he is using broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents for these infections, and the factors he looks for in considering new agents.

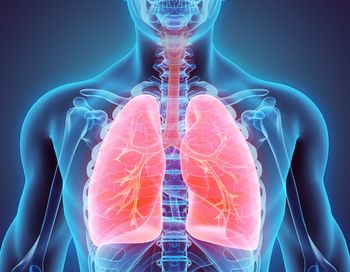
Monica V. Mahoney, PharmD, BCPS, BCIDP, FCCP, FIDSA, FIDP, FMSHP, provides insights on the outpatient side of therapy, including treating outpatients for gram-negative infections.

Rodney E. Rohde, PhD, SV/SM/MB(ASCP)CM, FACSc, offers some insights on the latest diagnostics, susceptibility testing for newer antimicrobials, and how infectious disease clinicians and laboratory professionals can collaborate on challenging cases.

In the second installment of an interview with Jacinda Abdul-Mutakabbir, PharmD, MPH, she continues the discussion around limited to no health care engagement due to these factors, and the importance of translating data from the bench to bedside when looking at disease and infection prevention.

Jacinda Abdul-Mutakabbir, PharmD, MPH, provides insights on her recently published study on this topic and how the 2 are connected.

In the midst of many changes surrounding aminoglycosides over the past several years, clinicians may be left wondering if these agents still have a role in modern clinical practice. This article summarizes changes impacting aminoglycosides, discusses where these agents may still have a role in the context of gram-negative infections, and explores future areas of study.
Compared to culture/sensitivity results (C/S) results, ICU-based PCR testing of hospital-acquired pneumonia was associated with lower treatment costs and better antibiotic stewardship, but not higher cure rates.

Iterum Therapeutics has launched its sulopenem etzadroxil and probenecid (Orlynvah), which is the first and only oral penem antibiotic in the US.
Ciprofloxacin monotherapy was non-inferior to aminoglycoside/ciprofloxacin combination for bubonic plague in multi-year trial in endemic region.

The NARROWS framework, developed within the IDSA Core Antimicrobial Stewardship Curriculum, provides a structured, behaviorally informed approach to communication that helps stewardship teams address the social, emotional, and cultural factors influencing prescribing decisions in order to optimize antimicrobial use and combat resistance.

Allegheny Health Network’s (AHN) Thomas Walsh, MD, talks about Allegheny General Hospital being recognized as an Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) Center of Excellence and some of the stewardship strategies they are employing to reduce antimicrobial usage.

Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is an opportunistic, multidrug-resistant pathogen that poses significant treatment challenges due to its complex resistance mechanisms, limited therapeutic options, and high mortality rates among vulnerable patients.

Deeksha Jandhyala, MD, discusses how her team works to prevent infections and provide clinical assistance for transplant candidates.
Clinical trial and real-world data, including the PROVE study, support its role as an effective and carbapenem-sparing therapy for serious infections, though outcomes vary depending on pathogen and infection type.

Doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis is associated with emerging tetracycline resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae and commensal organisms, highlighting the need for cautious, targeted use.

A recent literature review describes the current state of artificial intelligence tools for guiding antimicrobial therapy. Are you ready for change?

Jose Alexander, MD, offers insights on these antimicrobial combinations when treating against this bacterium.

If this GSK antibiotic is approved, it will provide a new oral option to patients in the US who are currently relying on injectable treatments.
A multi-prong approach reduces inappropriate antibiotic prescribing to outpatients with upper respiratory tract infection.

Emily Olsen, PhD, offers some insights on this underdiagnosed infection, including describing antimicrobial studies, particularly in biofilm and intracellular environments. Her findings look to create a standardized approach for treating all forms of the different presentations of bartonellosis.

Athena Hobbs, PharmD, BCIDP, looked at this issue through the lens of treating urinary tract infections.

Clarametyx Biosciences said its investigational antibody therapy, CMTX-101, which is in a phase 1b/2a study, remains on track for full trial enrollment by the end of 2025.

Can duration of therapy requirements at the time of antibiotic order entry decrease antibiotic use?







































































































































