Recent studies have shown how a commensal intestinal bacterium produces an enzyme that can help protect against pathogenic bacteria.

Recent studies have shown how a commensal intestinal bacterium produces an enzyme that can help protect against pathogenic bacteria.
Researchers have predicted that less than 10% of Escherichia coli 0157:H7 strains are likely to have the potential to cause human disease.

A case of hepatitis A in a bakery employee at a Shop ‘N Kart located in Washington state has been confirmed by the Lewis County Public Health & Social Services Department.
For the last six years Haiti has been fighting a severe cholera epidemic and it is unlikely that the fight will end soon.

As individual nations attempt to make meaningful progress on stemming antibiotic use, a troubling new study shows that hospitals in the United States have continued to dispense antibiotics at a steady rate in recent years.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is investigating a multi-state outbreak of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention warn infections from the consumption of raw milk and products made from raw milk will increase, especially in states where raw milk is legal.

The number of illnesses, hospitalizations, and deaths caused by Salmonella have been steadily rising each year, and now findings from new report on nontyphoidal Salmonella enterica show that some 20% of blood isolates of the bacteria have antibiotic resistance.

As health experts around the world take on the problem of antimicrobial resistance and overuse of antibiotics in humans as a prime cause, world leaders are reminding us of another contributor to this global health issue: our farming system.

The United Kingdom Food Standards Agency has published a guidance for health care and social service organizations who care for vulnerable populations at greater risk for contracting listeriosis and other food-borne diseases.

In Quebec, Atlantic Shellfish Products Inc. is recalling oysters from the marketplace after possible Salmonella contamination.

By targeting CabA, an extracellular matrix protein essential for biofilm formation, it may be possible to reduce the incidence of food-borne illnesses caused by the potentially lethal Vibrio vulnificus marine bacterium found in biofilms on oyster shells and meat.

Barry Kreiswirth, PhD, founding director, Public Health Research Institute Tuberculosis Center, professor of medicine at Rutgers University, discusses the implications of the findings of his study.

For consumers ordering pre-packaged foods, the United States Department of Agriculture recommends following several food safety tips.

Dubbed 'the perfect pathogen' by researchers, norovirus possesses all the markers of an ideal infectious agent.

As more people are choosing to keep live poultry as pets, educating the public on appropriate health and safety guidelines has become a priority. In response, the CDC is offering recommendations to backyard flock owners.

According to new research, applying antimicrobial coatings to whole cantaloupes during storage significantly reduces contamination and has the potential to improve their microbiological safety and extend their shelf life.

For the first time, the National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System includes whole genome sequencing data of bacteria from individuals with antibiotic-resistant Salmonella infections.

A voluntarily recall of 2.25 oz and 4 oz packages of Diamond of California Macadamia Nuts has been initiated after a sample tested positive for Salmonella contamination.

In a new ruling, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has declared that companies selling over-the-counter antiseptic washes will no longer be allowed to market their products as such due to doubts over these products’ safety and effectiveness.

A collaborative study at Michigan State University could lead to Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria prevention practices in the cattle farming industry.

Investigations into a multi-state, multi-year listeriosis outbreak continue, as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) change investigative tools, adding “leafy greens” to their Listeria Initiative questionnaire.
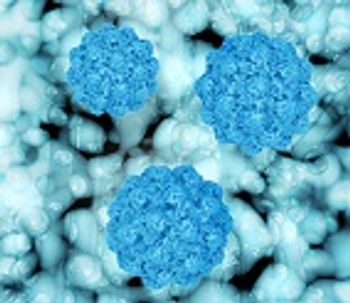
Researchers still know very little about just how norovirus works, but a new study has shed light on how norovirus gets into cells and causes disease.
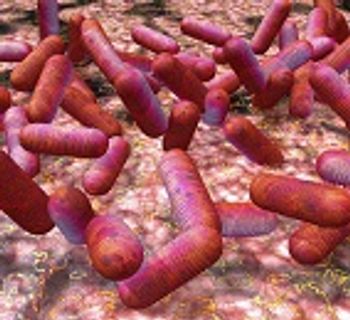
Studies demonstrate the effect of antibiotics on patients with hemolytic uremic syndrome and unique therapeutic challenges.

Many Louisiana residents have been impacted by severe flooding. In response, the United States Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) Food Safety and Inspection Service is issuing food safety recommendations to guide those in Louisiana who have been affected.