
Ebola virus tracking and mechanisms to detect threats to our national food supply are highlighted.

Ebola virus tracking and mechanisms to detect threats to our national food supply are highlighted.
A team of investigators are dedicating their efforts to pinpointing a source of the E. coli outbreak that has sprung up on the Utah-Arizona border.
The CDC recently released a national botulism surveillance summary for 2015.
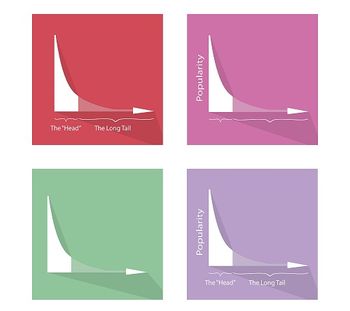
Could a power law be used to predict food-borne outbreaks and thus help public health agencies better prepare?

David A. Schwartz, MD, MS Hyg, FCAP, clinical professor of pathology at Medical College of Georgia, Augusta University, explains how congenital infection with Zika virus differs from congenital infection with other viruses.

Be careful when handling chicks or bunnies this Easter, as they may transmit Salmonella to you or your loved one.

This week’s Public Health News Watch highlights initiatives taking place this week in celebration of National Public Health Week, as well as two new pieces of legislation being considered in Congress that could impact food safety in the country and healthcare, in general.
Researchers in China have discovered a troubling case of the presence of a variant of the multidrug-resistant gene MCR-1 in a common strain of Salmonella in a healthy patient.

CDC researchers found that not only is the proportion of US food that is imported is increasing, but the number of food-borne disease outbreaks associated with imported foods is also increasing.

The Centers for Disease Control and Pevention and the US Food and Drug Administration are currently investigating an E. coli outbreak that has managed to spread over five states and has infected twelve individuals thus far.

This Valentine’s Day, be sure to remember these food safety tips to protect you and your loved one from any pesky food-borne illnesses.
Researchers from Salk Institute make a surprising discovery regarding the link between sickness-induced behaviors, such as loss of appetite, and their role in how the body fights off infection.

Throwing a Super Bowl party? There are a few food poisoning hazards that you should be mindful of this weekend.

A team of researchers has found that urbanized white ibises may be shedding Salmonella enterica and transmitting it to humans visiting parks.

Elizabeth Nolan, PhD, and her team at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, recently explored the fight between microbes and hosts over essential metals and how understanding this battle may open the door for alternate treatments for bacterial infections.
A new study explores why some animals and humans might be more susceptible than others to develop prion diseases.

As Hawaii struggles to recover from two food-borne outbreaks, DOH officials seek to make revisions to their food safety regulations to enhance food-borne illness prevention.

University of New Hampshire (UNH) scientists are developing an algorithm to predict when NH’s Great Bay Estuary’s oysters may be at risk of contamination.
Australian students manufactured the $750 pill in their school lab.

Researchers have found evidence that pre-cut bagged salads may encourage Salmonella colonization.

Public Health England and the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs researchers in the United Kingdom found drug-resistant E. coli in a large number of chicken samples, while much lower rates of contamination were observed in beef and pork samples.

A recent presentation by US Food and Drug Administration representatives explained why contaminated sprouts continue to be the cause of many food-borne illnesses.

IBM, Walmart, and Tsinghua University have partnered up to improve food safety practices in China.

The US Food and Drug Administration has announced that Sabra Dipping Co., LLC has recalled certain hummus products due to concerns about Listeria monocytogenes.
York’s Lassonde School’s Micro and Nano-scale Transport (MNT) Lab researchers have discovered “DipTreat,” a water treatment device capable of detecting and removing E. coli from drinking water.