
At AIDS 2022, Gilead presented data suggesting Biktarvy was a safe and effective complete HIV treatment regimen, including for those coinfected with hepatitis B.

At AIDS 2022, Gilead presented data suggesting Biktarvy was a safe and effective complete HIV treatment regimen, including for those coinfected with hepatitis B.

After 5 years of treatment, fostemsavir improved immunologic response and virologic outcome in patients with highly resistant HIV infection.

A clinician discusses the disease burden of reoccurring CDI, but sees a silver lining in the new investigational therapies potentially changing the treatment paradigm for the better.

A clinician is advocating for incorporating diagnostic stewardship practices within antimicrobial stewardship programs, which could someday lead to best practice guidelines on a larger scale.

Utilizing a newer technology, investigators wanted to see if a reduction in time led to clinically significant antimicrobial adjustments.

A multicenter study looked at treating these infections with omadacycline.
The investigational, fully human IgG1 monoclonal antibody ADG20 prevented and treated infection with COVID-19 variants of concern.

A medical center wanted to review prescribing and documentation practices for their pharmacists.
RBX2660, an investigational microbiota-based live biotherapeutic for the treatment of C difficile, safely and effectively reduced recurrent C diff for 6 months.

With limitations on fidaxomicin at their facility, a hospital looked at vancomycin usage to determine if they needed to align with the new IDSA/SHEA CDI treatment guideline.

A team of investigators studied Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) isolates to gauge resistance in the 2 antibiotics.

A health system piloted a program that explored having an infectious disease pharmacist aid in guiding treatment.
Designing a transitions of care stewardship program and engaging all stakeholders can help cut down on unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions.

Can clinicians rely on dosing strategy to avoid acute kidney injury for patients receiving vancomycin with a β-lactam like piperacillin-tazobactam?

Investigators sought information on how the infection is treated in outpatient clinics

Jason Pogue, PharmD, BCPS, BCIDP, shares key takeaways from his 2 presentations at MAD-ID 2022, including a new alternative to the SPACE acronym, as well as how to navigate any anxieties around oral carbapenems.

A MAD-ID 2022 poster sought to better understand the current antibiotic prescribing patterns at adult primary care clinics affiliated with Maimonides Medical Center in New York.
In a poster presented at MAD-ID 2022, Margaret Pertzborn, PharmD, evaluated the efficacy of a PrEP Provider Toolkit on non-infectious disease provider comfort prescribing PrEP with their patients.

A study looked at the utilization of the technology with this antibiotic class in hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) and ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP).

In a poster presented at MAD-ID 2022, Glenn S. Tillotson, PhD, FIDSA, FCCP, shares data from the Premier Healthcare Database on more than 100,000 patients with C diff.

AdventHealth Orlando studied a small number of these fungal isolates to examine treatment resistance patterns.

At MAD-ID 2022, Payal K. Patel, MD, MPH, FIDSA, discussed how COVID-19 misinformation and lags in diagnostics contributed to inappropriate antibiotic use and offers some way to combat this trend.

In hospitalized COVID-19 patients, remdesivir stewardship reduced hospital length of stay and therapy duration.

Colleen R. Kelly, MD, FACG, speaks at MAD-ID 2022 on alternatives to antibiotics for C diff infection, including the use of probiotics and fecal microbiota transplantation.

“Clearly, stewardship is a team operation. It starts [with] the leadership, the clinical pharmacy, and coordination with infectious disease physicians truly has to be synergistic,” Goetz said in the keynote address at MAD-ID 2022.

Among community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) outpatients, 49% were prescribed unnecessary antibiotics.
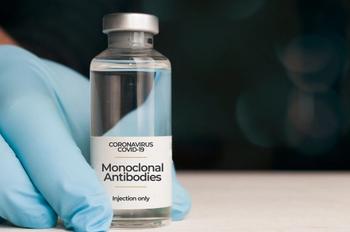
Leveraging antimicrobial stewardship programs was crucial to ensure COVID-19 hospital inpatients received monoclonal antibody therapy quickly and safely.

To reduce the risk of antimicrobial resistance, rapid laboratory diagnostics are needed to identify the pathogens in hospital patients with COVID-19 and sepsis.

A study of pregnant women positive for COVID-19 at delivery found no evidence of vertical transmission, but increased gastrointestinal problems in their newborn infants.

A comparison of COVID-19 PCR tests and rapid self-tests found self-tests to be highly accurate and user-friendly for children.