
Researchers from the Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care at the University Medical Center in Utrecht, The Netherlands, examine the cost-effectiveness of the most commonly used treatments for community-acquired pneumonia.

Researchers from the Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care at the University Medical Center in Utrecht, The Netherlands, examine the cost-effectiveness of the most commonly used treatments for community-acquired pneumonia.

Researchers conducted a post hoc analysis to learn whether or not the length of time it took to attain initial viral suppression is related to sustained virologic response (SVR) rates for patients receiving the so-call 3D treatment, with or without ribavirin.
Researchers from Penn State College of Medicine have developed a Retro94-based compound that may be able to prevent cytomegalovirus (CMV) from copying itself.

As concerns over the spread of tropical infectious diseases increase, in the age of Zika virus and Dengue fever in particular, PRVs may have significant implications for the development of novel vaccines and antivirals, assuming the program is used effectively.

This article is the second part of two-part coverage on a study conducted by Rutgers University researchers that analyzes the effects of misdiagnosing fungal infections on the increasing rates of antimicrobial resistance.

A recent study conducted by Rutgers University researchers analyzes the effects of misdiagnosing fungal infections on the increasing rates of antimicrobial resistance.

A new study has revealed an alarmingly high rate of HPV infections in men in the United States.

Stanford University researchers investigating potential use of wearable fitness trackers in healthcare find that the devices can be an important tool in the early detection of illness.
The study is the first “head-to-head” comparison of fecal transplants and antibiotic treatments, which are presently the “standard” of care.
UCLA researchers have developed an online risk assessment calculator that will allow individuals to check their “PrEP score.”

The researchers evaluated populations of Aedes aegypti, Aedes albopictus, and Culex quinquefasciatus collected both in the field and raised in a lab setting to determine whether or not the mosquitoes required bacterial populations in their guts to develop, and which bacteria were necessary to the process.

Their commentary effectively represents a position statement for the ASTMH, with the leaders/authors pledging to continue working with political leaders and “global health stakeholders in support of evidence-based policies and programs” designed to ensure public health in the United States and abroad.
The researchers discovered that the protein is responsible for immune response and destruction of the bacteria.
Researchers have found that those with type 2 diabetes have a higher prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection than those with adult onset-autoimmune diabetes and those who do not have diabetes at all.

The World Health Organization issues a yellow fever outbreak warning in Brazil, a country that is already dealing with outbreaks of Zika virus, chikyngunya, and dengue.
New research has revealed just how creative some bacteria can get in order to survive and move between hosts.
Quest Diagnostics has just launched a new hepatitis B virus quantitative test that will allow physicians to more effectively monitor patient response to antiviral drugs and tailor treatment regimens.

An additional nine states are reporting widespread influenza activity, in what is already a busy flu season that has been marked by severe illness caused by the influenza A (H3N2) strain.

Insurance companies are denying members coverage to expensive drugs, like Harvoni, and those infected with HCV are filing lawsuits.

The research team noted that the study, which is the first of its kind, can be used by doctors to assess risk and counsel families regarding the risks and benefits of surgeries for overweight and obese patients.
Researchers from Germany recently published a new study that can change how future scientists study the replication of the Dengue and Zika viruses within the human body.

Researchers have found that it is possible to bolster the immunity of the Aedes aegypti mosquito, the species that transmits Dengue, Zika, and Chikungunya, against these viruses and effectively suppress its ability to transmit the disease.
The CDC shares how a patient in Nevada died from a CRE that was resistant to a total of 26 different antimicrobial drugs.

Drug “buyers clubs” that include websites such as PrEPster and I Want PrEP Now are providing a number of at-risk individuals living in the United Kingdom with HIV drugs that can potentially save their lives.
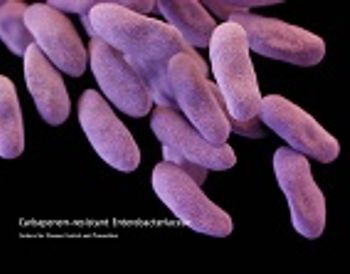
Researchers from Massachusetts have found that carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae have more genetic traits that enable antibiotic-resistance than previously thought and these traits are easily transferred among species.

A new project aims to develop and assess new hepatitis C vaccination strategies in an effort to improve treatment.

A team of dermatologists and gynecologists recently described their work with a 23-year-old pregnant woman in Florida who was eventually confirmed as the first documented case of Zika virus infection acquired via a mosquito bite sustained in the local area.

Researchers offer more insight on the role of IFN-I and find a potential therapeutic target that may be able to protect against chronic viral infections.
Researchers have found that peripheral catheters used to administer saline could be more beneficial than central catheters.
Diverse vaginal bacteria that’s deficient in lactobacilli appears to raise the risk of contracting HIV.