Resistance to hepatitis C infection may be much greater than previously thought, according to new research by investigators at Trinity College Dublin that revealed associated biological factors.
Jonna Lorenz is a freelance journalist with more than 20 years of experience. Her background is in business and health care news, including reporting, editing and research for newspapers and websites.

Resistance to hepatitis C infection may be much greater than previously thought, according to new research by investigators at Trinity College Dublin that revealed associated biological factors.

A recent study by investigators at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine found few mild adverse events from monoclonal antibody treatment among pregnant people with COVID-19, but no difference in COVID-19 outcomes.
Sanofi and GlaxoSmithKline are the latest companies to bring their COVID-19 booster vaccine to the marketplace with the European Commission’s approval of VidPrevtyn Beta.

The benefits to children of wearing face masks to prevent COVID-19 outweigh potential infectious risks from face touching, according to a study analyzing hand-to-face contact in a simulated school environment.
Vaxxinity is moving forward with research to bring its UB-612 COVID-19 vaccine to market as a mix-and-match booster to authorized vaccines.
Nearly 150 million people were affected by common symptoms of long COVID in 2020 and 2021, according to an analysis of global data on more than 1.2 million people.

Venatorx Pharmaceuticals is advancing the fight against difficult-to-treat, drug-resistant, gram-negative bacteria with a successful phase 3 clinical trial of its investigational antibiotic cefepime-taniborbactam.

Moderna’s new bivalent COVID-19 booster, which includes 25 micrograms each of messenger RNAs from the Wuhan-Hu-1 and Omicron B.1.1.529 variants of SARS-CoV-2, elicited antibody responses that were superior to those elicited by the original vaccine.

A comprehensive cohort study of COVID-19 data has reinforced the effectiveness of the various vaccines, boosters, and prior infection in protecting against infection, hospitalization and death.
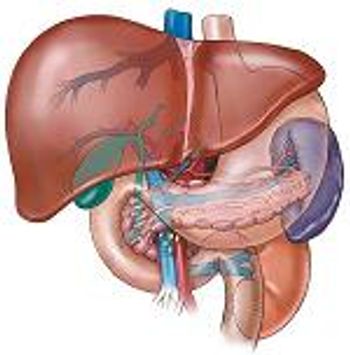
Bulevirtide, a first-in-class entry inhibitor, showed promise for the treatment of hepatitis B and hepatitis D coinfection, a phase 2 trial found.

Bifidobacterium and Bacteroides in the gut microbiome are important to vaccine responsiveness and could be used in vaccine adjuvants in the future, a recent review shows.

Injected COVID-19 mRNA vaccines alone were ineffective at producing mucosal antibody responses, according to a recent study that suggested seeking new strategies such as intranasal vaccines.
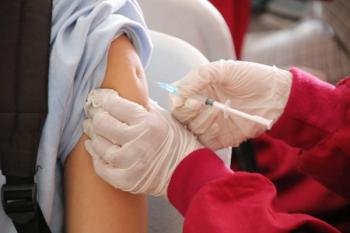
COVID-19 disease severity was mild in individuals in Qatar infected with the Omicron BA.1 and BA.2 sublineages with vaccination and booster doses reducing risks even further, a new study showed.
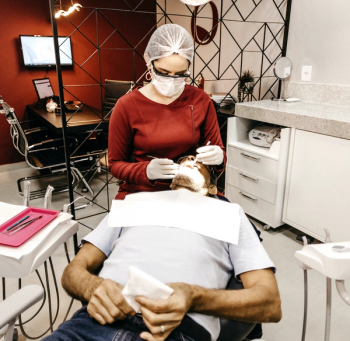
Dentists write about 25.7 million prescriptions annually, amounting to about 10% of all outpatient antibiotic prescriptions in the United States. A recent study showed that educating dentists about the risks of antibiotics—including antimicrobial resistance and Clostridioides difficile infections—led to sharp decreases in prescriptions.

Rates of hepatitis C reinfection were low among people receiving opioid agonist therapy, according to a new study, which highlights the importance of risk reduction interventions and HCV treatment for people who inject drugs and people receiving opioid agonist therapy.

A third dose of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines may allow most immune compromised patients with hematologic cancers to achieve antibody response levels similar to those of healthy adults after a two-dose series.

After widespread implementation of HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) among gay and bisexual men in Australia, population-level incidence of chlamydia and gonorrhea stabilized, allaying fears that PrEP would lead to a rise in STIs, a recent study found.
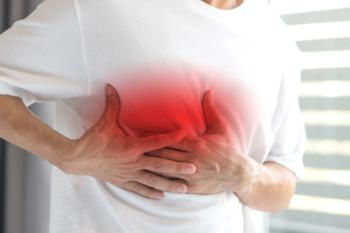
The highest rate of myocarditis or pericarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination occurred among young men ages 18 to 24 after receiving a second dose of the Moderna vaccine.
HIV epidemics are emerging among key populations in the Middle East and North Africa, and the region ranks lowest globally in response indicators.
Frequent recurrence of Clostridioides difficile infection drives up financial burdens of the disease and underscores the need to improve access to treatment, infection prevention, and new therapies.
Most children with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) associated with COVID-19 receive improper antimicrobial treatment, according to a recent study that highlights an urgent need to improve diagnosis and treatment of the condition.
Health care workers in Italy infected with SARS-CoV-2 were less likely to develop long COVID symptoms if they were fully vaccinated and boosted with an mRNA vaccine, a recent study found.
A computational framework for estimating vaccine effectiveness based on genetic differences of SARS-CoV-2 variants showed promising results in a new study that verified the model with clinical trial data.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is seeking more data on a possible cause of acute hepatitis in children, calling on clinicians to screen for adenovirus infections along with a broad range of possible exposures.

Patients with recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection saw improvements in fecal microbiome and bile acid after treatment with the investigational microbiota-based live biotherapeutic RBX2660.
High vaccination rates at Cornell University prevented severe disease during the Omicron surge of the COVID-19 pandemic but didn’t stop the rapid spread of the virus, even with comprehensive public health measures.

Merck’s antiviral drug molnupiravir may benefit nonhospitalized patients with mild or moderate COVID-19, according to a secondary analysis of phase 3 clinical trial data.
A recent study in the United Kingdom suggests that more research into the possible benefits of antiviral drug tecovirimat for treating monkeypox may be warranted after showing positive results in one patient.

New research in Israel offers hope that multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children—a serious complication of COVID-19—declined during the Omicron surge of the pandemic.

A new study from the CDC underscores the importance of staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines and boosters, showing a rapid drop in vaccine effectiveness among children during the Omicron wave that increased with booster doses.