International research efforts developed recommendations to optimize, control, and validate quantitative viral DNA measurements of chronic hepatitis B in the liver.

International research efforts developed recommendations to optimize, control, and validate quantitative viral DNA measurements of chronic hepatitis B in the liver.

February 7 is National Black HIV/AIDS Awareness Day (#NBHAAD). In observance, we're recapping stories to raise awareness and work toward ending HIV/AIDS disparities in Black communities.
Point-of-care RNA viral load testing is associated with shorter times between testing and treatment initiation and higher treatment uptake, a recent study found.

In doing so, the country met the new target of the World Health Organization.
The mRNA vaccines reduced risk of COVID-19 and related complications in children, with less risk of myocarditis than is associated with the infection.
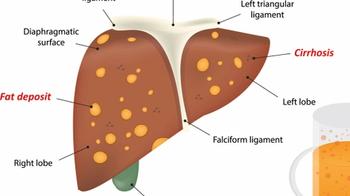
Investigators identify a mechanism that’s vital to the progression of alcohol-related hepatitis, paving the way for new treatments.

Tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV and hepatitis B, may be simultaneously depleting the energy of immune cells.
What is the hepatitis C treatment uptake among people who inject drugs?

Therapies to reach a functional cure for hepatitis B virus may differ among the phases of hepatitis B, including new antiviral agents and immunomodulatory strategies, the study authors predicted.
In this guest editorial, the author talks about the challenges associated with dealing with both health issues.

It's Friday the 13th, but you can counteract bad luck by catching up on this week's top infectious disease news.

It's your day, pharmacists! Here's a roundup of our top 5 stories by infectious disease pharmacists, for infectious disease pharmacists.

They developed clinical guidance and other resources looking to address potential drug interactions with these patient populations who have COVID-19 and may be treated with Paxlovid.

So far, these are Contagion's 5 most-read stories of 2023.
Health programs and efforts to inform the public about the importance of sharing liver education can play a major role in prevention as well as patient care.
Phase 2 trial with bepirovirsen demonstrates possibility of a functional cure of chronic hepatitis B infection that is sustained after treatment is discontinued.

Children as young as 12 can now receive tenofovir alafenamide for treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection with compensated liver disease, after the US Food and Drug Administration expanded the indication for the drug.
A germline-targeting HIV vaccine candidate elicited broadly neutralizing antibodies in 97% of recipients.
Resistance to hepatitis C infection may be much greater than previously thought, according to new research by investigators at Trinity College Dublin that revealed associated biological factors.
Alternative strategies to increase immunogenicity of COVID-19 vaccines in immunosuppressed kidney transplant recipients are evaluated in clinical trial.

As viral hepatitis is the most common blood-transmitted infection globally, assessing the toll of hepatitis and hepatitis-related conditions is critical.

Three posters on the subject were presented at The Liver Meeting and were among the meeting’s key presentation highlights called “Best of the Liver Meeting.”

What are the characteristics and demographics of the chronic hepatitis B patients who develop severe outcomes?

Looking for the latest developments in infectious disease? Here are the top stories Contagion covered this week.

Initially, 28-29% of patients with chronic hepatitis B achieved undetectable virus levels after 24 weeks of treatment with GSK’s bepirovirsen, but this dropped to 9-10% of patients during a phase 2b trial.