
Work group from infectious disease associations proposes prioritizing 6 areas of research to improve efficacy and precision of antibiotic therapy

Work group from infectious disease associations proposes prioritizing 6 areas of research to improve efficacy and precision of antibiotic therapy
Omicron significantly diminishes the protective abilities of both natural immunity and vaccine-granted immunity.
The report showed the protective benefits varied somewhat by cardiovascular disease subtype.

A positive recommendation now heads to the European Commission, which can grant marketing authorization for 27 European Union member states.

Research shows specific climate elements affect mosquito proliferation and can play a role in predictors of vector activity and insect control interventions.
From December 2020-September 2021, approximately 27 million COVID-19 infections, 1.6 million hospitalizations, and 235000 deaths were prevented by vaccination.

Treatment with the novel antiviral sabizabulin reduced COVID-19 death by 55.2% in hospitalized patients with moderate to severe disease.
In an age of COVID-19, it is difficult for clinicians and public health officials to pivot and think about obscure infections like Pneumonic plague. However, a case of this plague occurred in Wyoming, and the local public health officials offer some insights into the clinical care of the patient as well as communicating with close contacts.

The revised Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir and ritonavir) allows these providers to offer this COVID-19 therapy.

Dr. Arlene Sena and her team are working to develop a syphilis vaccine, “But we need to know what’s circulating worldwide first.”

We want YOU to take our survey and tell us which infectious disease topics you want covered.

Access to antifungal susceptibility testing (AFST) remains limited in the United States. Therefore, providers must recognize clinical situations where AFST will provide its greatest value. In the latest article from SIDP, infectious disease pharmacists offers some insights on this subject.
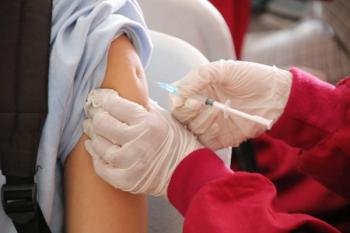
Investigational vaccine demonstrates efficacy against respiratory syncytial virus in trial with adults inoculated with active RSV.
The commitment to ending the HIV epidemic endures, despite drops in testing and new diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic.
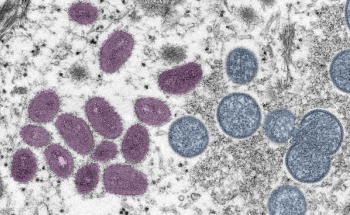
This first study of the UK’s ongoing monkeypox outbreak reported the clinical and demographic features of 54 confirmed cases.

Here is a rundown of the most popular and significant stories we covered this past week.
All studies included in this research found a correlation between area-level racial prejudice and adverse health outcomes among racial and ethnic minority populations.

The federal agency has reported 1 death and 22 hospitalizations stemming back to January of 2021.

Maternal mortalities increased 33.3% during the COVID-19 pandemic, while overall deaths increased 22%. Excess deaths were most prevalent in Hispanic and Black mothers.

The submission is based off both non-clinical and clinical data, including results from the phase 2/3 EPIC-HR study.
A computational framework for estimating vaccine effectiveness based on genetic differences of SARS-CoV-2 variants showed promising results in a new study that verified the model with clinical trial data.
Emergency medicine physicians are leaving behind their emergency rooms and opening primary care practices, which does not necessarily translate to a smooth transition with some inherent challenges associated with training and expectations.

Many people who self-report as symptomatic for COVID-19 neglect to get tested, largely citing not knowing where to go for a test as the reason.

After an all-day meeting, the FDA’s Vaccine and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) voted 90% YES to recommend this fall’s COVID-19 booster doses target Omicron.
With the impending start to the 2022-2023 influenza season just a few months away, here is some information on what is being studied for vaccines as well as recommendations and new testing.

Algorithm offers guidance on clinically managing pregnant individuals exposed to monkeypox and on treating the virus during pregnancy.

Sanofi and GSK, Pfizer-BioNTech, and Moderna are all working on booster candidates specifically designed to neutralize Omicron and its subvariants.

The World Health Organization did not declare monkeypox a global health emergency, instead calling it an “evolving health threat” that requires continued monitoring.

The investigational therapy’s data points to a path towards a potential functional cure.

In a phase 3 trial, if HIV patients received treatment for precancerous HSILs, their risk for developing anal cancer was reduced by half.