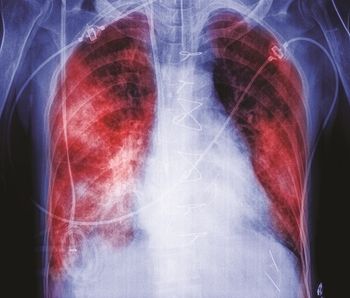
Tuberculosis (TB) remains the #1 infectious killer, worldwide, surpassing HIV / AIDS, according to the latest global TB report from the World Health Organization.

Tuberculosis (TB) remains the #1 infectious killer, worldwide, surpassing HIV / AIDS, according to the latest global TB report from the World Health Organization.
Another prong in the battle against resistant Gram-negative infections is the addition of beta-lactamase inhibitors to restore or improve the activity of older carbapenems.
The plague outbreak in Madagascar appears to be winding down, but will a centuries-old ritual reverse the progress?

Investigators in China have found that the presence of the MCR-1 gene has increased in humans over a period of 5 years.
Antimicrobial-resistant organisms, particularly Gram-negative bacteria, present a critical threat and a substantial burden.

C. difficile prevention is usually thought of in terms of environmental disinfection and health care worker hand hygiene; what about the patient's role?

In case you missed them, we've compiled the top 5 articles from this past week.

After 1 week of treatment, heavily treatment-experienced (HTE) patients who received fotemsavir, added to a failing regimen, had a greater reduction in viral load than patients on placebo.
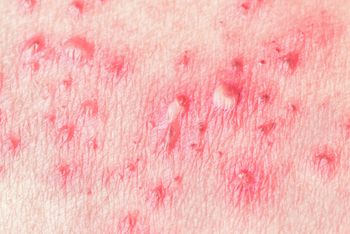
The CDC’s ACIP recommends newly FDA-approved Shingrix as the preferred vaccine for the prevention of shingles in individuals 50 years of age or older.
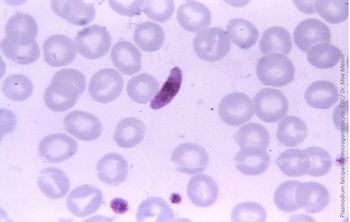
Almost 430,000 individuals succumbed to malaria infection in 2015.
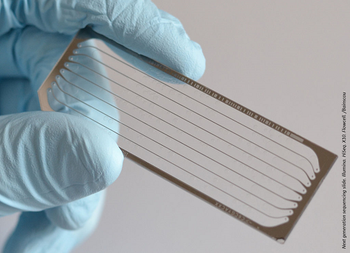
In a new study, investigators examine the advantages and drawbacks of using metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) for the identification of pathogens.
A proven marker of host response to bacterial infection may help providers avoid contributing to the rise of antibiotic resistance.
One doctor in Bangladesh has created a low-cost continuous positive airway pressure device out of an empty shampoo bottle; a study finds that the device cut pneumonia mortality rates by 75%.
Biopharmaceutical company Achaogen submitted a New Drug Application for plazomicin for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections and bloodstream infections.

New research is drawing attention to the underlying risk of spreading infectious diseases when participating in organized athletic activities.
The pivotal phase 3 AMBER study regarding the safety and efficacy of the investigational darunavir-based single tablet HIV regimen has achieved its primary endpoint.
As health officials continue to recommend the injectable influenza vaccine to prevent illness this season, a new study examines whether vaccination rates changed after the CDC stopped recommending the nasal spray vaccine

Research on emerging infectious diseases continues to grow; however, some practitioners feel that a focus on knowledge acquisition has overshadowed the distribution of that knowledge to the frontline providers who need it most.
According to recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, millions of Americans aged 13-17 are under-vaccinated against serious infectious diseases.

More information continues to be revealed about the Zika virus as research on a vaccine continues to advance as well.

Alnylam Pharmaceuticals announces exclusive licensing agreement with Vir Biotechnology for the development and commercialization of RNA Interference therapeutics for infectious diseases.

A new CDC report finds that although vaccination coverage is high for kindergarteners in the United States, pockets of undervaccination are a cause for concern among health officials.

The FDA has approved Shingrix, GlaxoSmithKline’s recombinant zoster vaccine against shingles, for patients 50 and older.
At ID Week 2017, Dr. Laura Cooley, CDC, discussed the increasing number of Legionnaires’ cases in the United States, underscoring the need for stronger water management practices.

Researchers turn to the literature to assess if the antibiotic cefepime causes neurotoxicity.
Although there have been important improvements to existing vaccines, the list of vaccine-preventable diseases has barely changed at all in over two decades.

It's time to talk about the horsepox synthesis and what it means for the biosecurity world and public health overall.

Stay up-to-date on the latest infectious disease news by checking out our top 5 articles of the week.

Both test vaccines produced immune responses by 1 month after vaccination and the immune response lasted for at least 1 year.

A pair of papers published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases highlight the effort to fight and monitor drug-resistant HIV, which poses a threat to achieving the global targets designed to end the AIDS epidemic.