
Johns Hopkins Hospital evacuates over tuberculosis concerns.

We’ve rounded up a list of important US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recalls from this past week:

Stay up-to-date on the latest infectious disease news by reading the top 5 articles of the week.
CDC researchers say that some influenza respiratory infections may be originating in the eye, and thus, more research is needed pertaining to ocular transmission.
Development of the drug has been deemed necessary because of the potential for the use of the virus in a bioterrorism attack and waning herd immunity against the virus among the general population.

Text messaging is an easy way to improve medication adherence rates, but success depends on a number of factors including youth and race.
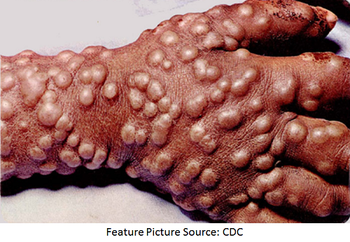
Hepatitis A outbreaks that have been crippling states across the nation since March of 2017 continue to wreak havoc in several cities.
A new study conducted by Tufts University School of Medicine identifies gender-specific signatures in gonorrhea infection as well as resistant genes.

Patients receiving home-based outpatient parenteral antimicrobial therapy who are female and have comorbidities are more likely to have worse outcomes, new research finds.
New CDC recommendations include the use of 3HP in children and individuals with LTBI who have HIV infection, including AIDS.
A recent study finds that shortening the rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen is both effective and safe.

Increased testing and education, as well as assistance in financing the cost of care, are clearly needed.
There have been no confirmed cases of Ebola in the Democratic Republic of the Congo since June 6.

New research finds patients with HIV living in 5 southern states had lower rates of viral suppression and linkage to care compared to people in northern states.
Clinical pharmacy formulations are an affordable and viable approach.

Doctors are prescribing antibiotics too often for viral acute respiratory infections.
Current research trends indicate a need for updated guidelines and new technology to differentiate between Zika and other mosquito-borne infections.

Suicide is a major problem for many patients with infectious diseases but pinpointing the exact cause has proven difficult.

A collection of survey data from 2006 through 2016 found that on average, higher-risk individuals get tested for HIV every 1.4 years.

In case you missed them, we’ve compiled a list of the latest recalls posted this week.

In case you missed them, we've compiled the top 5 articles from this past week.
Individuals with a dense sexual network and a history of antimicrobial drug use, such as men who have sex with men, are at a greater risk for antimicrobial resistance and gonorrhea.
State health departments around the United States are reporting their first human and mosquito cases of West Nile virus for the 2018 season, prompting reminders to practice mosquito bite prevention.
Research presented at the 2018 ASM Microbe Meeting has reinforced the value of the just-approved next-generation aminoglycoside antibiotic, plazomicin, in treating multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae.

New study reports that many individuals with a higher risk for HIV are not being offered an HIV test by their health care provider.

The new edition is fully electronic and makes key changes related to antimicrobial resistance and HIV.
Researchers have uncovered key pathways that increase resiliency to sepsis in children.
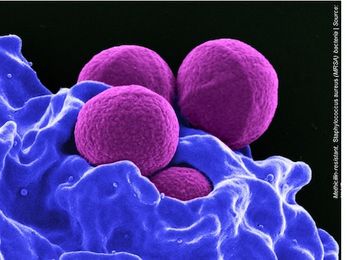
Skin and soft tissue infections appear to be on the decline in the general population, but individuals with HIV have a higher risk.

The FDA has accepted an NDA and granted Priority Review for Genentech’s baloxavir marboxil for the treatment of acute, uncomplicated influenza in individuals aged 12 and older.
Catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) account for about 40% of all nosocomial infections in hospitals and nursing homes.