The Marburg virus, a rare, but serious filovirus virus, is a zoonotic virus in which outbreaks are frequently triggered by interaction with the African fruit bat, Rousettus aegyptiacus.

The Marburg virus, a rare, but serious filovirus virus, is a zoonotic virus in which outbreaks are frequently triggered by interaction with the African fruit bat, Rousettus aegyptiacus.

In case you missed them, we've compiled the top 5 articles from this past week.
A FDA committee decided against recommending approval for Linhaliq to treat NCFBE patients with chronic lung Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.

GlaxoSmithKline has announced that the FDA's Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research has approved expanding the indication for their influenza vaccine to include use in those 6 months of age and older.

We've compiled a list of the latest US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recalls posted this week that you should know about.

Health officials across the United States have their hands full as hepatitis A cases continue to spring up.

In a special supplement to the January 15th issue of Clinical Infectious Diseases, researchers from various institutions across the country shared the latest findings on the diagnosis and management of botulism and highlighted the need for greater clinical understanding of its symptoms and related complications.

Said to have killed more people in a single year than the infamous 14th century European Black Death, the pandemic infected a full third of the world’s population.

A common birth control shot has been linked with increased risk of HIV infection while NIAID investigators have found that putting ART on pause during a clinical trial might not be as detrimental as first thought.
Rates of re-hospitalization and long-term health effects remain high among sepsis survivors, which is why researchers are outlining ways to help sepsis patients after hospital discharge.

A pharmacist cuts through the noise surrounding Oscillococcinum and its alleged role in flu management.

The CDC releases first comprehensive reports on state progress made in the fight against antibiotic resistance since Congress’ investment in CDC’s Antibiotic Resistance Solutions Initiative.
The FDA releases notice on how to keep hospital mattresses and mattress covers safe to prevent the spread of deadly bugs throughout health care facilities.

Consumer interest in water that hasn’t been “treated, filtered, or processed in any way” is on the rise, and there are concerns that its consumption could result in the next public health crisis.
Most of the United States is now seeing widespread flu activity, as health officials urge flu sufferers to receive antiviral treatment as soon as possible.

A recent study suggests that the new antibiotic combination ceftazidime-avibactam may be a useful alternative for treating hospital-acquired pneumonia.

Contagion® interviews Tetraphase’s CEO Guy Macdonald about eravacycline, an investigational drug candidate for the treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections.

Investigators from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Brigham and Women's Hospital, and Lyndra, have developed a drug capsule that could drastically pare down ART to an easier-to-adhere-to weekly regimen.
A viral therapy developed to target cancer cells, also appears capable of destroying HIV-infected cells.
Investigators from the University of California San Diego Medical School report on the first case of Gardnerella bacteremia in an HIV-positive male following the placement of a urinary catheter.

Patients in intensive care units are at greater risk of acquiring antimicrobial-resistant infections, and now, a group of international infectious disease experts ar calling for better protection for these high-risk patients.

A Salmonella infection in a Kansas resident has been linked with the consumption of rattlesnake pills.
The development of mold-active azoles has led to enormous advancements in both prevention and treatment of invasive fungal infections.

Stay up-to-date on the latest infectious disease news by checking out our top 5 articles of the week.

We've compiled a list of the latest US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recalls posted this week you should know about.

How many of those who recovered from WWI-associated infections had residual neurological impairments that increased their risk for violence?
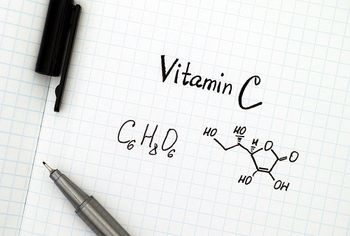
Investigators from the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, New York have found that when used in conjunction with anti-tuberculosis drugs, vitamin C helped eradicate Mycobacterium tuberculosis.

Preparing for biothreats, regardless of origin, requires that we strengthen the most basic surveillance and response systems within public health and health care.
With the discovery that stem cells enable a sustained immune response to HIV, scientists are hoping to eventually reduce patients’ long-term reliance on ART.

The estimated global burden of the disease ranges from 11 to 20 million cases and contributes to about 128,000 to 161,000 deaths each year.