
As new flu deaths are reported throughout the United States, a pair of studies highlights some of the strengths and weaknesses of the flu shot.

As new flu deaths are reported throughout the United States, a pair of studies highlights some of the strengths and weaknesses of the flu shot.
Could forcing pathogens to compete for resources be the key to fighting drug-resistance and extending the lives of existing drugs?

The US Department of Health and Human Services Tick-Borne Disease Working Group held its first public meetings in Washington, DC, this week and it has already generated plenty of eye-grabbing headlines.
Five outbreaks of hepatitis A continue to beat down on several states; can addressing the homelessness crisis prevent future outbreaks from happening?

A new study compares the long-term effects of combination ART (cART) initiation during primary HIV infection with therapy initiation during chronic HIV infection.
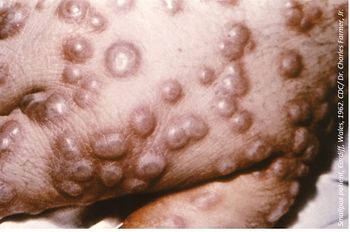
Although deemed eradicated throughout the world in 1980 thanks to a protective vaccine, research on smallpox continues to this day given the potential for the highly contagious virus to be used in biological warfare.

Despite the increase in the number of human infections with avian influenza A (H7N9) virus during the fifth epidemic in China, a new study suggests no change in the risk of transmission of the virus among humans over time.

Predicting the next infectious disease outbreak may be possible by analyzing trends on Twitter and Google.

Does following the NSQIP reduce post-operative UTIs?
However, findings from the study may provide a roadmap for future analyses of immune-based interventions seeking to relieve HIV patients of the lifelong burden of daily medication intake and enhance viral suppression.

Researchers have developed a new material for use in dental procedures that uses an antimicrobial agent to fight off bacteria and prevent plaque buildup.
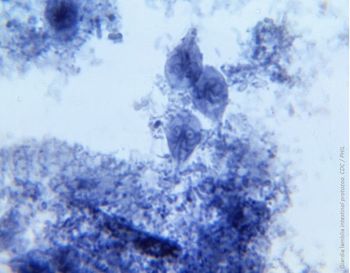
Single-dose tinidazole is the best available treatment for giardiasis in children and adults, a new study shows.

Stay up-to-date on the latest infectious disease news by checking out our top 5 articles of the week.

As the population of people living with HIV infection is living longer, age-related health issues are affecting these individuals in an accelerated or emphasized fashion.
A pair of studies recently conducted as part of the Human Vaccines Project are giving new insight into the human immune system and how researchers can develop better vaccines.
Investigators are hopeful that the global vaccine candidate will prevent a wide range of strains of the virus.
More than 110 suspected cases have already been reported, including 6 deaths.

Investigators are finding that a 4-days-a-week regimen of antiretroviral therapy (ART) may be as safe and effective as daily therapy in treating HIV, while keeping costs down and lowering risks of side effects.

Here are a few things your friendly infection control team would appreciate for the holidays.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a rapid diagnostic test for Valley Fever.
Experts from academia, industry, and public health agencies—including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the US Food and Drug Administration—discuss the new generation of antibody tests.
After 2 years, the risk for these men dropped only slightly, making them 14 times more likely to be reinfected.

Following a severe flu season in the Southern Hemisphere and mounting research that egg-based flu vaccines don’t offer enough protection, experts are warning that the Northern Hemisphere may be in for a tough flu season.

Questions regarding a finance executive’s expertise in infectious diseases aside, the move seems straightforward enough—at least on the surface.
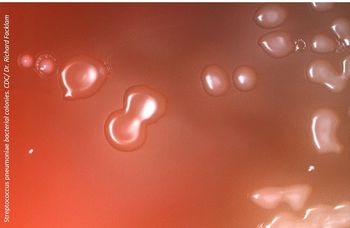
Researchers from Harvard Medical School conducted one of the largest studies to date to examine the impact of pneumococcal vaccines and antibiotic usage on trends in colonization in young, healthy children.

We break down the Top 5 infectious disease news reported by Contagion® for the month of November 2017.
A new study examines HCV treatment uptake in HCV patients coinfected with HIV.

A team of investigators explores if fecal microbiota transplant (FMT) capsules are just as effective as treatment via colonoscopy.

The results of 3 phase 1 clinical trials have shown that an investigational Zika purified inactivated virus vaccine was well-tolerated and induced an immune response in adult participants.

On National Cookie Day, it’s important to remember to avoid consuming any raw baking materials or you'll run the risk of infection.