
A recent study finds a potential link between cannabis use and possible beneficial reduction in systemic inflammation and immune activation in ART-treated HIV patients.

A recent study finds a potential link between cannabis use and possible beneficial reduction in systemic inflammation and immune activation in ART-treated HIV patients.
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices has included HEPLISAV-B on its list of recommended products for use to vaccinate adults against hepatitis B.
The Iowa Department of Health releases case counts associated with a Salmonella outbreak linked with chicken salad sold at Fareway stores.
While a new report has found that the flu vaccine has been just 36% effective this year, a recent study suggests that history of exposure to flu may, in part, be to blame.

One agency estimates that at least 50% of all antibiotic prescriptions written in the United States do not fall under currently accepted practice guidelines.

The CDC have launched an investigation into a multistate outbreak of Salmonella I 4,[5],12:b:- infections that has been linked with opioid substitute kratom.

Mylan NV's new drug application for its combo regimen of dolutegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide, received tentative approval from the US Food and Drug Administration under the President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR).
A new study announced by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases may help cut the number of antibiotics unnecessarily prescribed for viral lower respiratory tract infections.
A molecule capable of clearing HSV-1 infection in the cells of the cornea could be a promising potential option for those who have developed resistance to current drugs.

A recent CDC report finds those between 15 and 44 years of age are significantly more likely to have never been tested for HIV.
Massive vaccination campaigns launched in Brazil and Nigeria strive to quell ongoing outbreaks.

A recent report documents the first recorded case of a human infestation with the cattle eyeworm Thelazia gulosa.

Can culturing process changes reduce the impact of catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs)?

In case you missed them, we’ve compiled a list of the latest recalls posted this week.

Stay up-to-date on the latest infectious disease news by checking out our top 5 articles of the week.
Providing investments in 10 vaccines during a 15-year period in low- and middle-income nations could prevent 36 million deaths and 24 million cases of poverty related to medical reasons.
Although rare, children inoculated against chicken pox can present with herpes zoster at or near the vaccination site.

The latest data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have revealed that adults who are vaccinated are 36% less likely to get the flu. That number jumps to a whopping 59% for young children.
A panel of experts from the Philippines Department of Health finds that Sanofi Pasteur's dengue fever vaccine, Dengvaxia (CYD-TDV), may be connected with 3 deaths.
Fecal transplantation and molecular testing are among the new recommendations.

Influenza A (H3N2) has caused most of the illnesses in this severe flu season, but influenza B is becoming increasingly responsible for more infections as the flu season continues to hit the United States.
Infectious disease specialists and public health professionals in search of a to-do list for 2018 need look no further.
Recognition of chronic Lyme disease and the role of long-term antibiotic treatment for persistent symptoms continue to be controversial among researchers, providers, patients, and advocates.

ViiV Healthcare has launched a phase 3 study to assess if adults with HIV-1 who have achieved viral suppression on a 3-drug regimen can maintain suppression when switched to a 2-drug regimen.

Efforts to curb antimicrobial resistance have hit a brick wall in India, where new research finds unapproved drug combinations are rampant.

A new systematic review of published research suggests that methotrexate could potentially be the best co-treatment option for chronic arthritis associated with the chikungunya virus.

The FDA has granted pre-market approval for a new HPV test that can detect and identify HPV genotypes that put women at increased risk for cervical cancer.

An international research team finds that targeting the social and risk networks of patients recently diagnosed with HIV is leading them to more patients unknowingly infected with the virus.

Was the situation in Flint, Michigan an outlier or an ominous warning of what’s to come?
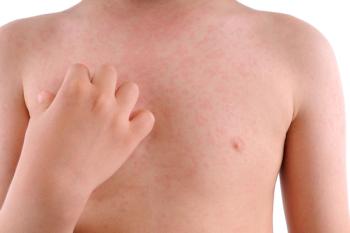
A Nebraska mother’s Facebook post has parents and health experts around the country wondering if an influenza B infection may have caused hives in a child who did not present with any other flu symptoms.