
With as many as 30 million new cases annually, resulting in more than 6 million deaths worldwide, new initiatives are focusing on an age-old problem—sepsis, and its related complications.

With as many as 30 million new cases annually, resulting in more than 6 million deaths worldwide, new initiatives are focusing on an age-old problem—sepsis, and its related complications.

For the most challenging of microbial threats, one microbiologist is trying an old tactic in a new era.

Researchers from EcoHealth Alliance have developed a predictive “map” that identifies the zoonotic host species that are “likely to harbor the next human virus” and documents the regions of the world where they can be found.
Cases of antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea are on the rise, and the bacteria may soon become untreatable if new antibiotics and diagnostic tools are not developed.
Researchers from the University of Pittsburgh find a way to successfully treat a patient with ceftazidime-avibactam-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae.
A group of researchers examine the feasibility of a low-resource behavioral intervention created to promote retention in HIV care.
In a new study from Amsterdam, researchers have found that patients who were recently treated with azithromycin showed increased resistance to treatment for Neisseria gonorrhoeae.

A Canadian researcher recently built horsepox from mail-ordered DNA and with it comes an extra delivery of dual-use scrutiny.
Penn researchers find that cases of recurrent C. difficile infections are rapidly increasing, underscoring the need for new treatment options, such as fecal microbiota transplants.

A look into how health information exchange interventions are beneficial in HIV care; the discovery of 3 mutations that could help the bird flu spread among humans; news about a new patch formulation for the flu vaccine; progress towards an HIV vaccine; and information on an interactive map that visualizes the US HIV epidemic, make up the Top 5 articles for this week.

Brenda Fitzgerald, MD has been named the 17th Director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and Administrator of the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR).

In a new study conducted in a healthcare system in the Bronx, a team of healthcare providers has created a new program to cut hospital readmission rates in patients receiving outpatient IV antibiotic treatment.
The Hawaii Department of Health continues to investigate the growing number of mumps infections in the state.

What's the best recipe for MRSA screening and isolation practices?
The World Health Organization has officially declared that the recent Ebola outbreak in the Democratic Republic of Congo is over.

Following a request from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Endo Pharmaceuticals has pulled its opioid agonist Opana ER (oxymorphone hydrochloride extended release).

The number of RSV-infected adults in an African study who also had HIV was quite high, with the burden of HIV disproportionately in the young.

New HPV vaccine recommendations from the World Health Organization, information on a new once-daily treatment for HIV, the potential underestimation of tick-borne diseases in the Western United States, norovirus outbreaks in California schools, and how reservoirs of latent HIV hinder the quest for a cure, make up the Top 5 articles for the month of June 2017.

A recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention takes a closer look at a case of late-onset neonatal Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS) infection and its association with maternal consumption of placenta capsules.
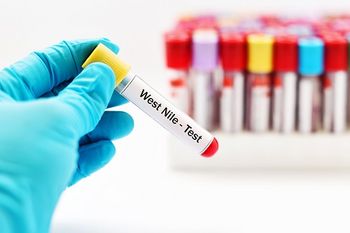
As Colorado reports its first human West Nile virus case of the season and California reports its third, health officials around the country are emphasizing the importance of mosquito control and prevention.

The World Bank recently announced plans to issue “pandemic bonds and derivatives” to help fund its Pandemic Emergency Finance Facility, which will “channel surge funding” to at-risk countries in the developing world.

Scientists have identified 3 mutations that could allow the avian influenza strain H7N9 to spread among humans.

A recent study suggests that in vivo corneal confocal microscopy can be used to assess HIV-associated sensory neuropathy, a disorder that is increasing worldwide.

HIV surveillance data is being used to populate an interactive map, capable of depicting the impact of HIV and mortality in the United States on national, state, and local levels.

Researchers have developed an adhesive patch delivery method for the influenza vaccine and new study shows it is as effective as the flu shot.
A study has found that health information exchange interventions are beneficial in several ways when it comes to HIV care.
Scientists from The Scripps Research Institute and the La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology may have found the best delivery mode for a vaccine against HIV.

More than 200 scientists, medical professionals, and environmental researchers have released a statement calling on the international community to take further steps to limit the use of triclosan, triclocarban, and other antimicrobial compounds.

Measles in Ontario, more endoscope-related infections, a study of postnatal Zika infections, research and development on a river blindness vaccine, and using CRISPR to tackle Zika are the articles that make up this week’s Top 5.

The World Health Organization (WHO) is expanding its essential guidance to include diagnostic equipment and other vital technologies, following years of lobbying from clinicians, researchers, and industry groups alike.