Healthcare Associated Infections (HAI)
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

As antimicrobial therapies become less effective, more people are at risk for infections that can progress to sepsis.

A new study reveals that the type of surgery performed to treat these infections plays a more significant role in outcomes than other factors.

Glenn Tillotson, PhD discusses the development of new antibiotics and therapies for C diff during an era when antibiotic resistance is a serious global health threat.
Clostridium difficile infection leads to higher rates of overall mortality among patients with cirrhosis compared to those who do not, according to a new study.
Is the use of piperacillin/tazobactam for bacteremia caused by ceftriaxone-nonsusceptible Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae an obsolete practice?
As clinicians and health care executives work to strike a balance between reducing costs and improving clinical outcomes, the importance of sepsis identification and treatment cannot be underscored enough, and starts with evaluating current practices for infection management.

Edmund A. Hooker, MD, DrPH, discussed the gaps in disinfection in the hospital and how hospital beds can be properly sanitized to prevent the spread healthcare-associatedted infections.
Vascular graft infections are serious complications of reconstructive vascular surgery that may increase patients’ morbidity and mortality.

C diff and pneumonia still pose significant threats, according to the hospital survey.

A new study on a novel experimental nanotechnology-based organ transplant acceptance therapy offers hope for reduced organ rejection without immune suppression.
Despite concerning findings and warnings, fluoroquinolones have remained one of the world’s most commonly prescribed antibiotic classes, with the United States accounting for more than 32 million prescriptions in 2015 alone.

Editor-in-chief, Jason C. Gallagher, PharmD, FCCP, FIDSA, BCPS, shares how it is up to all of us in health care to evaluate the level of evidence in our practices and continue to evolve, just like the organisms we work to treat.
Because of the recent concern in the United States around the rise of resistant pathogens, intravenous fosfomycin has gained renewed interest because of its activity and demonstrated synergy with other classes of antibiotics.
The system allows for the rapid identification of bacteria directly from positive blood cultures, and can determine the antimicrobial susceptibility of the blood-borne pathogens.
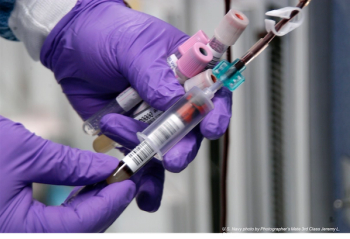
Use of the FDA–cleared Accelerate Pheno blood culture detection system can shorten the time required to analyze patients’ blood samples leading to improved clinical outcomes, according to the results of a recent study.

Key considerations when choosing a treatment for gram-negative nosocomial infections include the patient’s referring facility.

A new report from the CDC shows substantial progress on the incidence of health care-associated infections in the United States, but there is still more work to be done.

Stay up-to-date on the latest infectious disease news by checking out our top 5 articles of the week.
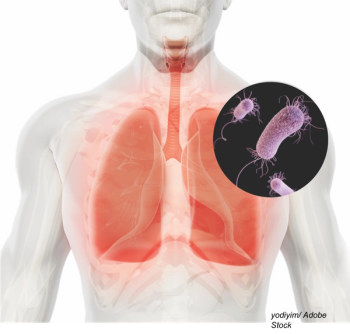
Hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia account for 22% of all hospital-acquired infections.

A new report highlights technologies with potential to prevent and reduce global catastrophic biological risks.
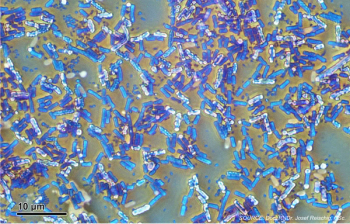
Probiotic Bacillus found to eliminate colonies of S aureus in mouse models and was associated with a lack of S aureus in human samples.
The drug presents a new option for patients at high risk of infections caused by organisms, such as carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae.
Jason Pogue, PharmD, BCPS-AQID, discusses the need for real-world data to support Ceftolozane/tazobactam and shares the findings of his comparative study on using the regimen to treat MDR/XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
George Thompson, MD, principal investigator of the STRIVE study discusses optimal dosing for rezafungin in treating candidemia and/or invasive candidiasis.

Dale N Gerding, MD, provides insight about prevention options for C diff that are expected in the future.