Healthcare Associated Infections (HAI)
Latest News
Video Series

Latest Videos
Podcasts
CME Content
More News

Hospitals grapple with the costly burden of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), and artificial intelligence (AI) is emerging as a game-changer in revolutionizing infection prevention strategies.

Incidence of hospital-onset Clostridioides difficile infection differed between hospitals that implemented the CDC prevention strategies and those that did not, but not necessarily because of the strategies.

The federal agency did not request further trials for the investigational therapy, cefepime-taniborbactam, but wanted more information about its chemistry, manufacturing, and controls.

The Leapfrog Group finds there were improved health care-associated infection (HAIs) rates following an earlier spike during the acute phase of the COVID-19 pandemic.

Patients treated with oral metronidazole experienced significantly more first-line drug changes compared to those on fidaxomicin; although there were no significant differences observed in the global or clinical cure rate between the 2 treatments.

These study findings highlight higher in-hospital mortality rates for patients with preventable conditions during COVID-19.
Five organizations have updated the 2014 compendium, "Strategies to Prevent Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Transmission and Infection in Acute Care Hospitals." In doing so, they have elevated antimicrobial stewardship from an “additional practice” to an “essential practice.”
The CDC reports that during 2020-2021, the mortality rates for COVID-19—associated fungal Infections were significantly higher than non-COVID-19–associated fungal infections.
While COVID-19 patients had a higher risk of venous thromboembolic disease compared to influenza and sepsis patients, the risk of other adverse outcomes was comparable.
So far, the Virginia Mason Medical Center in Seattle has confirmed 33 patients have been infected with Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria, 9 of whom have died.

This study compares the mortality rates between Canada's public health care and the US private system, highlighting the complexities of pandemic response.
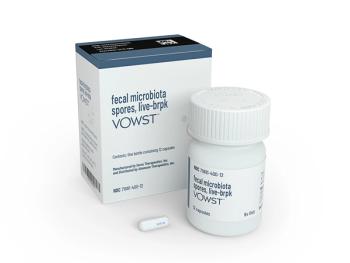
By repopulating the gut with healthy and diverse microbiota, Vowst aims to prevent further C diff recurrences and restore patients' quality of life.

Investigators revisit an 80-year-old antimicrobial to reduce its toxicity while preserving its activity against drug resistant gram-negative bacteria.
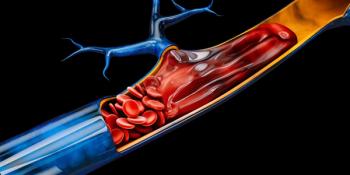
Anticoagulant treatment for 3 to 6 months was sufficient for the majority of COVID-19 patients with venous thromboembolism, the study authors found.

Sulbactam-durlobactam is efficacious against carbapenem-resistant infections, and Innoviva is preparing for the antibiotic's PDUFA at the end of this month.

The latest issue of the Morbidity and Mortality Report discusses the cases.

On the same day WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus declared the end of the COVID-19 public health emergency, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky announced she will be stepping down at the end of June.

Epidemiologists report cluster of pediatric intracranial abscess in Clark County, Nevada with Streptococcus intermedius the most common isolate.

COVID-19 symptom or viral rebound in the absence of antiviral treatment is common, but the combination of symptom and viral relapse is rare.

Decreased racial and ethnic disparities in COVID-19 mortalities between the first and Omicron waves of the pandemic could be explained by increased deaths in non-Hispanic White adults and changes in the geographic spread of the pandemic.

The WHO issued its first ever list of priority antibiotics for pediatrics to encourage research and development targeting needs of that population.

Members of both branches brought it back to gain support and passage of a bill aimed at greater development of antibiotics.

Rates of central line–associated bloodstream infection (CLABSI), catheter-associated urinary tract infection (CAUTI), and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteremia all increased in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.

The Veterans Administration reported a reduction in the bacterial infection in healthcare settings where infection prevention practices were continued.
This study of health care access and affordability found adults with long COVID reported more unmet health care needs in the past 12 months.