
The rise of the mcr-1 gene highlights the hurdles against the bigger fight that is antimicrobial resistance

The rise of the mcr-1 gene highlights the hurdles against the bigger fight that is antimicrobial resistance
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS and medical technology industry partners have announced new efforts to better diagnose bacterial infections at the recent World Economic Forum Annual Meeting in Davos, Switzerland.

Cancer specialists at the UT Southwestern Medical Center are reminding women to continue going for Pap smears even if they have received the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine.

Through environmental cleaning and student-oriented education, Humber College in Toronto, Canada, has managed to quell a nasty outbreak of norovirus.
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) plans to fund research projects designed to discover and develop new antibiotics to treat these troublesome bacteria.

While we look to emerging infectious disease outbreaks and the threat of biological weapons, it's easy to forget the responsibilities of our domestic research.

A new agent in the antibiotic pipeline, cefiderocol, has proved to be effective against complicated urinary tract infections (UTIs).

With flu season underway, a pair of recent studies highlight the impact of winter weather on influenza activity and raise questions about the right time to receive a flu shot.

New research from Pew Charitable Trusts has found that quality issues are not the only factor that contribute to drug shortages.

Researchers from the Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care at the University Medical Center in Utrecht, The Netherlands, examine the cost-effectiveness of the most commonly used treatments for community-acquired pneumonia.

This article is the second part of two-part coverage on a study conducted by Rutgers University researchers that analyzes the effects of misdiagnosing fungal infections on the increasing rates of antimicrobial resistance.

A recent study conducted by Rutgers University researchers analyzes the effects of misdiagnosing fungal infections on the increasing rates of antimicrobial resistance.

Stanford University researchers investigating potential use of wearable fitness trackers in healthcare find that the devices can be an important tool in the early detection of illness.
UCLA researchers have developed an online risk assessment calculator that will allow individuals to check their “PrEP score.”

Their commentary effectively represents a position statement for the ASTMH, with the leaders/authors pledging to continue working with political leaders and “global health stakeholders in support of evidence-based policies and programs” designed to ensure public health in the United States and abroad.
The researchers discovered that the protein is responsible for immune response and destruction of the bacteria.

An additional nine states are reporting widespread influenza activity, in what is already a busy flu season that has been marked by severe illness caused by the influenza A (H3N2) strain.

Insurance companies are denying members coverage to expensive drugs, like Harvoni, and those infected with HCV are filing lawsuits.
The CDC shares how a patient in Nevada died from a CRE that was resistant to a total of 26 different antimicrobial drugs.

Drug “buyers clubs” that include websites such as PrEPster and I Want PrEP Now are providing a number of at-risk individuals living in the United Kingdom with HIV drugs that can potentially save their lives.
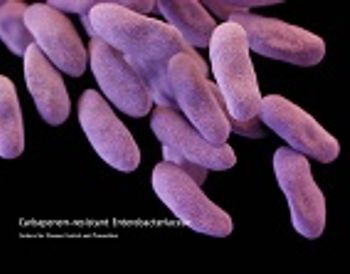
Researchers from Massachusetts have found that carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae have more genetic traits that enable antibiotic-resistance than previously thought and these traits are easily transferred among species.
Researchers have found that peripheral catheters used to administer saline could be more beneficial than central catheters.

According to their research, the model can be manipulated to recreate the process of immune-cell response and reproduce the function of the lymph nodes in immune cell activation.
Respiratory Syncytial Virus is an incredibly common virus that hits both the very young and the very old disproportionately.

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has released a consumer update encouraging participation as well as diversity within clinical trials.