Respiratory Infections
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
“Together these 2 diseases create a perfect storm�”: Black people with cancer were more likely to have severe or fatal COVID-19 disease.

The World Health Organization updated its guidelines for the treatment of nonsevere tuberculosis in children after a study showed a four-month duration was noninferior to six months.
The coronavirus pandemic caused the first global recorded decline in human life expectancy.

The Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response (ASPR) announced a pause in sotrovimab distribution in regions where BA.2 is the dominant COVID-19 variant, citing evidence that the monoclonal antibody therapy would not effectively neutralize the BA.2 Omicron variant.

A matched cohort study found COVID-19 infection increased the risk of new type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Compared to patients with acute upper respiratory tract infections, COVID-19 patients were 28% more likely to develop diabetes.

There are many unknowns about the BA.2 COVID-19 variant. It appears 50-60% more transmissible than the original Omicron variant, but health experts are mixed on whether cases will spike dramatically.

A Texas study found children and adolescents who previously contracted COVID-19 retained protective antibodies for 6 or more months after infection. However, natural infection plus vaccination remains the best defense against COVID-19.

In children and adolescents, the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine was only mildly effective against symptomatic and asymptomatic COVID-19 infections. Broken down by variant, Omicron infections were more likely to occur and more likely to be asymptomatic.
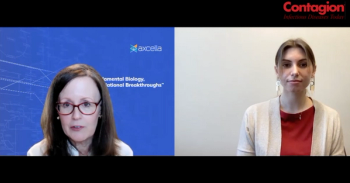
Axcella Therapeutics chief medical officer Dr. Margaret Koziel discusses the stage 2a clinical trial for their novel long covid treatment.
The new COVID-19 sub-variant, called “Deltacron” or “Stealth Omicron,” appears to be the most contagious strain yet. However, this does not necessarily mean there will be a dramatic spike in cases.

Findings of JAMA Network Open analysis reveal effects of interventions designed to prevent spread.

“Deltacron,” a COVID-19 strain with genes from both the Delta and Omicron variants, appears to have been circulating since the beginning of the year.

The war on Ukraine is expected to drive COVID-19 and other infectious diseases, meaning health organizations and neighboring countries should prepare to assist in the impending health crises.
Even a mild COVID-19 infection can change the brain. People infected had a greater reduction in brain volume and performed worse on cognitive tests than those who did not contract COVID-19.

Associations between social determinants of health (SDOH) and COVID-19 mortality varied across racial and ethnic groups and community types.
One study found people were more likely to take the COVID-19 pandemic seriously when they saw the overall number of infections, as opposed to being presented with only new daily cases.
Minnesota hospitals established to care exclusively for COVID-19 patients saw lower rates of mortality than general hospitals.

A single-dose injection of nirsevimab before RSV season was proven to reduce infants’ risk of lower respiratory tract infection by 74.5%.

“COVID-19 need no longer control our lives,” President Biden said, detailing a plan to immediately provide free antiviral pills to anyone who tests positive.

Due to decreased efficacy against the Omicron variant, the FDA is now recommending approved populations receive a higher dose of Evusheld (tixagevimab and cilgavimab) for COVID-19 prevention.

This flu season, the CDC reported at least 2.4 million flu illnesses, 23,000 hospitalizations, and 1,400 deaths from flu so far.

A pair of studies released last weekend found the COVID-19 pandemic was caused by at least 2 zoonotic transmission events at the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan, China.
Among fully vaccinated people, being older than 60 years and having kidney failure were the only consistent predictors of severe COVID-19 disease and death.

The IDSA, HIVMA, and SHEA released a statement opposing legal intervention on behalf of ivermectin as a COVID-19 treatment.

Moderna was endorsed to begin phase 3 clinical trials for mRNA-1345, what could be the first respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine.